- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Rapid and Simple Procedure for the Isolation of Embryonic Cells from Fish Eggs
一种快速简便的从鱼卵中分离胚胎细胞的方法
发布: 2023年10月05日第13卷第19期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4836 浏览次数: 1399
评审: Anonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
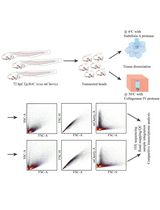
Fertilized teleost fish eggs are a complex formation, in which dividing cells arelocated in a small point in the entire volume of eggs. Isolating embryonic cellscan be considered a necessary step in the research of developmentalpeculiarities of fish cells at the earliest stages of embryogenesis beforeembryo formation. The main advantages of the offered protocol are rapidisolation, no enzymes, and overall low cost compared to other protocols. Theprotocol is suitable for the isolation of embryonic cells from medium-sized eggsat the stages of blastula or gastrula, for studies in a variety of applications(e.g., microscopy, flow cytometry, and other methods). Fertilized nelma eggs(Stenodus leucichthys nelma) are used in the protocol as a model.
Key features
• Fast and cheap isolation of cells from fish eggs at early stages (blastula orgastrula).
• Applicable for most of the methods for cell study (any staining, microscopy, flowcytometry, etc.).
• Can be applied to other teleost fish eggs with medium egg diameter of 3–4mm.
Graphical overview
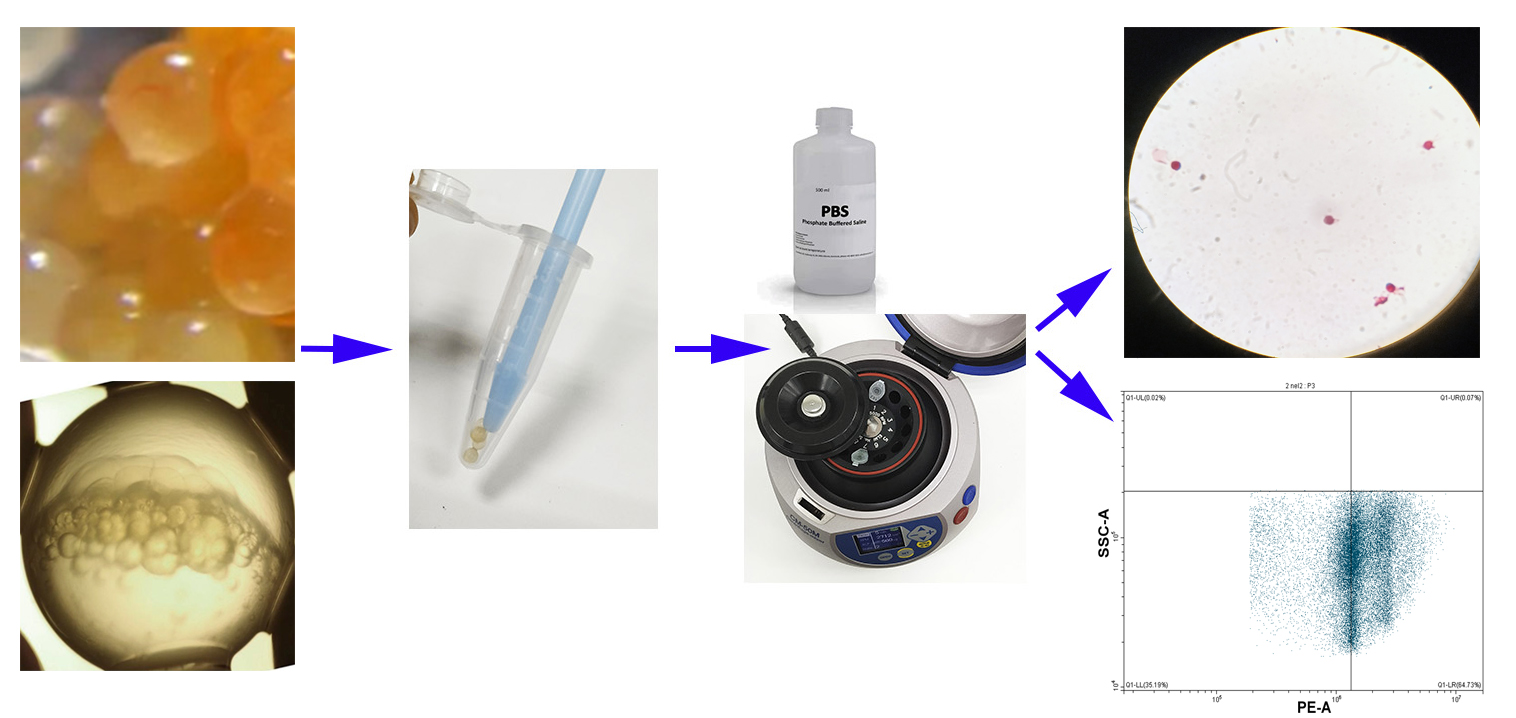

Background
To date, many methods for isolating living cells from various tissues are used fordifferent purposes. Mainly, living cells from tissues are disaggregated bytrypsinization. This method is very common and involves the extraction of an embryoor tissue with further trypsinization (Durkin et al.,2013). Some other protocols are based on mechanical crushing of tissues orformed embryos to obtain cells (Fetherman et al., 2015).
When rapid testing of samples is required as soon as possible after eggfertilization, it is necessary to isolate cells directly from the blastodisc at theearliest stages of teleost fish embryogenesis before formation of embryo, larva, orfry. Cell isolation from fertilized eggs by the methods described above does notlead to the desired result, since the eggs contain huge amounts of varioussubstances and a small number of cells relative to the weight of the egg. Inaddition, the cells in the blastodisc are not tightly connected with each other.That is why the use of trypsin (and other enzymes) is not ideal, with undesirablechemical effects on the cells that can lead to the destruction of cell membranes.
To date, we have only found one other protocol describing a similar procedure (Rieger, 2019). That protocol requires thepresence of pronase from Streptomyces griseus for thedechorionization of embryos. The pronase only softens the chondrion, requiringadditional washing to remove it from the embryo. Besides, the isolation procedure iscomplicated by particular features of enzymes, as most biological catalysts havenarrow operating limits as well as a short shelf life. We aimed to ensure maximumsimplicity and low cost of the isolation method with minimal requirements forlaboratory equipment.
Materials and reagents
Biological materials
Fertilized fish eggs in the stages from blastodisc to the late gastrula.
Solutions
PBS soluble tablets (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4417), for cell isolation
70% ethanol solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 65348-85), for cell preservation
o-safranin ready-to-use solution 0.1% (Scientific Laboratory Supplies, catalog number: TMS-009-C), for protocol verification
Propidium iodide ready-to-use solution 1 mg/mL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P3566), for protocol verification
RNAse A ready-to-use solution 10 mg/mL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EN0531)
Phosphate-saline buffer solution (see Recipes)
70% ethanol (see Recipes)
Recipes
Phosphate-saline buffer solution
Reagent Final concentration Quantity PBS 150 mM total of all salts:
137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8 mM Na2HPO4, 2 mM KH2PO4
1 tablet H2O n/a Up to 100 mL Total n/a 100 mL 70% ethanol
Reagent Final concentration Quantity Ethanol (95%) 70% 74 mL H2O n/a 26 mL Total n/a 100 mL
Laboratory supplies
Microcentrifuge tube pestles (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: BAF199230001-100EA)
Conical bottom microcentrifuge tubes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: HS4325-1000EA)
Centrifuge tubes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CLS430790)
Equipment
Microcentrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 75004081)
Microscope with 8–20× zoom lens for data validation (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 4479672)
Vortex mixer (VELP Scientifica, catalog number: F202A0173)
Dissecting needles (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 13-820-024)
Flow cytometer for data validation (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: CO9752)
Software and datasets
CytExpert software for flow cytometry (used for data validation)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Golotin, V., Lyutikov, A., Filatova, T., Sharoyko, V. and Apalikova, O. (2023). A Rapid and Simple Procedure for the Isolation of Embryonic Cells from Fish Eggs. Bio-protocol 13(19): e4836. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4836.
分类
发育生物学
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离
生物科学 > 生物技术
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link