- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Determination of Antibody Activity by Platelet Aggregation
血小板聚集法测定抗体活性
发布: 2023年09月05日第13卷第17期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4804 浏览次数: 2188
评审: Meenal SinhaLuis Alberto Sánchez Vargas
Abstract
Platelets play an important role in hemostasis by forming clots and stopping bleeding. In immune thrombotic conditions, platelets and leukocytes are aberrantly activated by pathogenic antibodies resulting in platelet aggregates and NETosis, leading to thrombosis and thrombocytopenia. A simple assay that assesses platelet function and antibody activity is light transmission aggregometry. This assay can be used to determine antibody activity in patients with disorders such as heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT). Briefly, for detection of pathogenic antibody, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is treated with a specific agent (e.g., patient sera or purified patient antibodies) with constant stirring. Upon activation, platelets undergo a shape change and adhere to each other forming aggregates. This causes a reduction in opacity allowing more light to pass through PRP. Light transmission through the cuvette is proportional to the degree of platelet aggregation and is measured by the photocell over time. The advantage of this protocol is that it is a simple, reliable assay that can be applied to assess antibody activity in thrombotic conditions. Light transmission aggregometry does not require the use of radioactive reagents and is technically less demanding compared with 14C-serotonin release assay, another common assay for detecting antibody activity.
Key features
• This protocol can be used to assess platelet function and to detect platelet activating antibodies in diseases such as HIT and VITT.
• Does not require radioactive reagents, requires an aggregometer; based on the light transmission aggregometry protocol, adapted for detection of VITT and other platelet-activating antibodies.
• Two positive controls are required for reliable detection of antibodies in diseases such as HIT/VITT, namely a weak HIT/VITT antibody and a physiological agonist.
• For detection of HIT/VITT antibodies, it is essential to use donors known to have platelets reactive to these antibodies to avoid false negative results.
Keywords: Platelet activation (血小板活化)Background
Platelets play an essential role in hemostasis, bleeding, and thrombosis. Upon activation, platelets undergo shape changes and aggregate, leading to platelet clumping. The rate and extent of aggregation can be measured by light transmission via a platelet aggregometer. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which is turbid, is stirred in a test cuvette. When the agonist is added, the platelets will form increasingly larger aggregates and the PRP will begin to clear, allowing more light to pass through. This increase in light transmittance is directly proportional to the amount of aggregation.
First described by Born in the 1960s (Born, 1962), light transmission aggregometry is considered a gold standard assay for platelet function, often assigned as the first step for analyzing platelet dysfunction in hemorrhagic patients (Kottke-Marchant and Corcoran, 2002; Hayward, 2008; Gadisseur et al., 2009; Hayward et al., 2009; Podda et al., 2012). To detect the presence and activity of pathogenic antibodies, patient sera or purified patient IgG can be used. Purified IgG confirms that the IgG is the component that induces platelet activation, thus excluding other potential platelet activating agents in patient sera. Standardization of the use of light transmission aggregometry to assess platelet function has been published by the International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis (Cattaneo et al., 2013).
Another method of analyzing platelet activation is whole-blood aggregometry (Park et al., 2012; Mencarini et al., 2021). This method measures the change in electrical impedance between two electrodes to indicate platelet aggregation. Although this process accounts for the effect of all blood cells on platelet function, it cannot determine with accuracy the direct or indirect contributions of other blood cells to the platelet activation observed. To avoid confounding factors in whole blood, light transmission aggregometry using PRP is an ideal, relatively simple, and reliable method to specifically determine platelet activity.
The 14C-serotonin release assay (SRA) and the heparin-induced platelet activation (HIPA) test are also common assays used to test antibody activity (Arepally et al., 1995; Greinacher et al., 2012 and 2022). They are based on the principle that incubation of patient serum (containing the pathogenic antibody) will activate donor platelets resulting in release of intraplatelet serotonin (SRA) and platelet aggregation (HIPA). SRA is a sensitive method used to detect pathogenic antibody in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) (Warkentin et al., 2015) and more recently, vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) (Leung et al., 2022). For SRA, washed platelets are incubated with radiolabeled serotonin. Upon activation, platelets release radiolabeled serotonin, and this is measured by a beta counter. Despite the high sensitivity of SRA, this method is labor intensive and technically demanding, requiring the user to have radiation training and certification, access to radiation laboratory, and waste disposal streams for the radioactive waste. Due to this, platelet aggregometry is a simpler, more convenient method of assessing platelet activation.
The HIPA test, developed in 1991, is based on the visual assessment of platelet aggregates (Greinacher et al., 1991). It is performed in microtiter plates, allowing multiple samples and platelet donors to be tested simultaneously, uses washed platelets, and is generally considered more sensitive than platelet aggregation tests (Greinacher et al., 1994; Tardy et al., 2020). Experienced personnel are required to conduct this assay, as platelet washing can over-activate platelets, giving false positive results, and estimation of platelet aggregation by eye can be imprecise. In comparison, platelet aggregometry is technically less demanding, does not rely on personnel to be experienced in identifying visual changes in platelet morphology, and the real-time trace clearly shows when platelet activation has taken place. By using platelets from donors pre-determined to be reactive to HIT antibodies, the sensitivity of the assay should approach that of HIPA (Chong et al., 1993). Platelet aggregometry has certain limitations as it cannot be used if donors have low platelet counts and, unlike whole-blood aggregometry, some sample preparation is required.
Here, we provide details on an updated version of Born’s method for determining antibody activity by platelet aggregation (Figure 1). This protocol is improved by standardization, with added appropriate controls and use of reactive donor platelets to increase accuracy, and adapted to test IgG, along with serum and plasma. This protocol can be used for research purposes, as well as in clinical laboratories for testing of HIT/VITT antibodies.
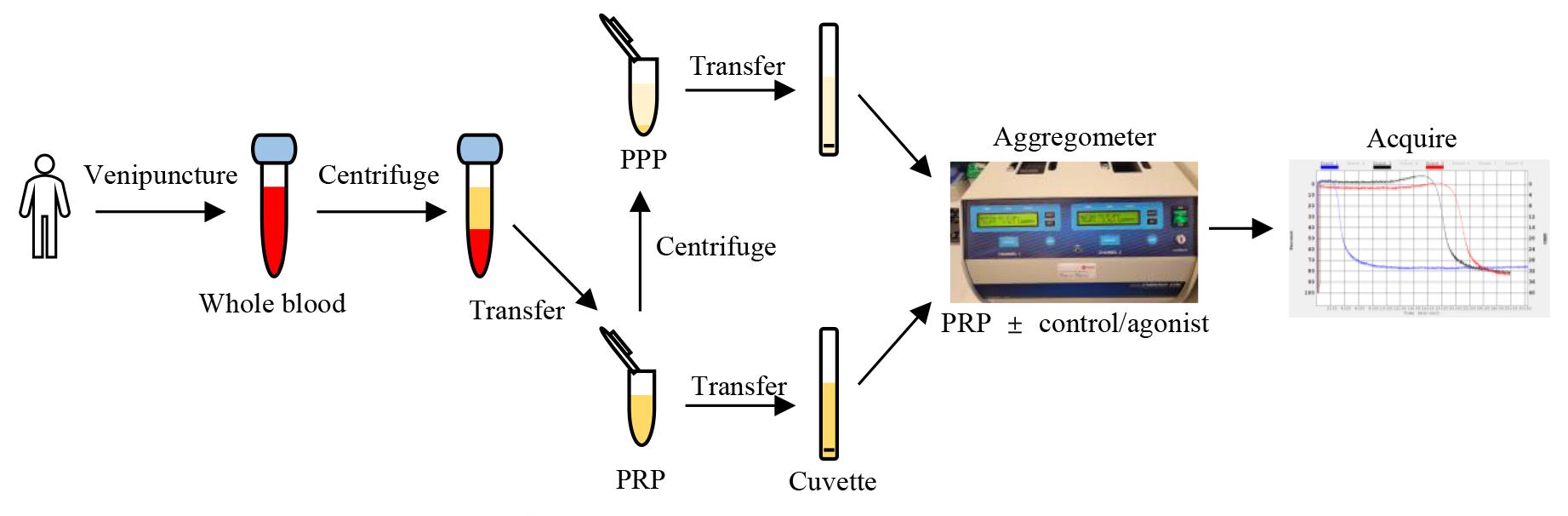
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the platelet aggregometry assay. Centrifuged tubes show the different layers of blood cells and plasma. PPP: platelet-poor plasma; PRP: platelet-rich plasma.
Materials and reagents
15 mL centrifuge tubes (Greiner, catalog number: 188271)
1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube (Greiner Bio-One, catalog number: 616201)
Pasteur pipette (Transfer) (Labtek, catalog number: 650.050.523)
Direct detect assay-free cards (Merck, catalog number: DDAC00010-GR)
Stir bar, disposable siliconized for P/N 312 cuvettes (DKSH, Part No 311)
Cuvettes, 450 μL (DKSH, Part No 312)
100 kDa Amicon Ultra-15 centrifugal filter unit (Merck, catalog number: UFC910024)
Econo-Column® chromatography column, 1.5 cm × 10 cm (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 7374151)
Fresh or frozen plasma (stored at -80 °C) collected in ACD (BD, catalog number: 366645), trisodium citrate (BD, catalog number: 363095), or EDTA (BD, catalog number: 367839), or sera collected in clot activator/gel vacutainer (BD, catalog number: 367954) from patient for IgG purification
Fresh or frozen plasma (stored at -80 °C) collected in trisodium citrate or sera collected in clot activator/gel vacutainer from patient for direct testing in platelet aggregation
Whole blood from healthy donor, collected in trisodium citrate vacutainer (BD, catalog number: 363095)
Protein G agarose beads (SeraCare, catalog number: 5720-0002)
Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8537)
Control agonists such as collagen (1 μg/mL), thrombin (1 U/mL), plasma sample from positive HIT patients
Sodium phosphate (Merck, catalog number: S8282)
Glycine (Astral Scientific, catalog number: BIOGB0235)
Tris (Amresco, catalog number: 0497)
HCl (Merck, catalog number: 320331)
NaOH (Sigma, catalog number: S-0899)
NaCl (Merck, catalog number: S9625)
EDTA (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15576028)
Starting buffer, pH 7.0 (see Recipes)
Elution buffer, pH 2.7 (see Recipes)
Neutralization buffer, pH 9.0 (see Recipes)
Washing buffer, pH 7.0 (see Recipes)
Equipment
Benchtop centrifuge (Spintron, model: GT-10 SV3)
Tabletop microfuge (Beckman Coulter, Microfuge 20 Centrifuge, model: B31603)
Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5810 R)
Aggregometer (Chrono-Log, model: 700)
Chromatography system (GE Healthcare, model: AKTA Pure. catalog number: 29-0182-24)
Direct detect infrared spectrometer (Millipore, model: DDHW00010)
Rotatory tube mixer (Ratek, model: RSM7DC)
Magnetic stirrer (Bacto Laboratories, model: MS7-H550-Pro)
Calibrated pipettes
-80 °C freezer
4 °C fridge
Software
Aggro/Link8 software (Chronolog, USA)
GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software, USA)
Microsoft Excel (Microsoft, USA)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Leung, H., Perdomo, J., Ahmadi, Z. and Chong, B. H. (2023). Determination of Antibody Activity by Platelet Aggregation. Bio-protocol 13(17): e4804. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4804.
分类
免疫学 > 免疫机理 > 体外模型
免疫学 > 抗体分析 > 抗体检测
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link