- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Purification of Recombinant Human Amphiphysin 1 and its N-BAR Domain
重组人 Amphiphysin 1 及其 N-BAR 结构域的纯化
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2023年06月20日第13卷第12期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4699 浏览次数: 1982
评审: David PaulAnindita SarkarAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
基于蛋白筛选策略从合成文库中分离抗原特异性纳米抗体:结合 MACS 的酵母展示筛选与 FLI-TRAP 方法
Apisitt Thaiprayoon [...] Dujduan Waraho-Zhmayev
2026年01月20日 406 阅读
Abstract
Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) proteins are known as classical membrane curvature generators during endocytosis. Amphiphysin, a member of the N-BAR sub-family of proteins that contain a characteristic amphipathic sequence at the N-terminus of the BAR domain, is involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Full-length amphiphysin contains a ~ 400 amino acid long disordered linker connecting the N-BAR domain and a C-terminal Src homology 3 (SH3) domain. We express and purify recombinant amphiphysin and its N-BAR domain along with an N-terminal glutathione-S-transferase (GST) tag. The GST tag allows extraction of the protein of interest using affinity chromatography and is removed in the subsequent protease treatment and ion-exchange chromatography steps. In the case of the N-BAR domain, cleavage of the GST tag was found to cause precipitation. This issue can be minimized by adding glycerol to the protein purification buffers. In the final step, size exclusion chromatography removes any potential oligomeric species. This protocol has also been successfully used to purify other N-BAR proteins, such as endophilin, Bin1, and their corresponding BAR domains.
Graphical overview
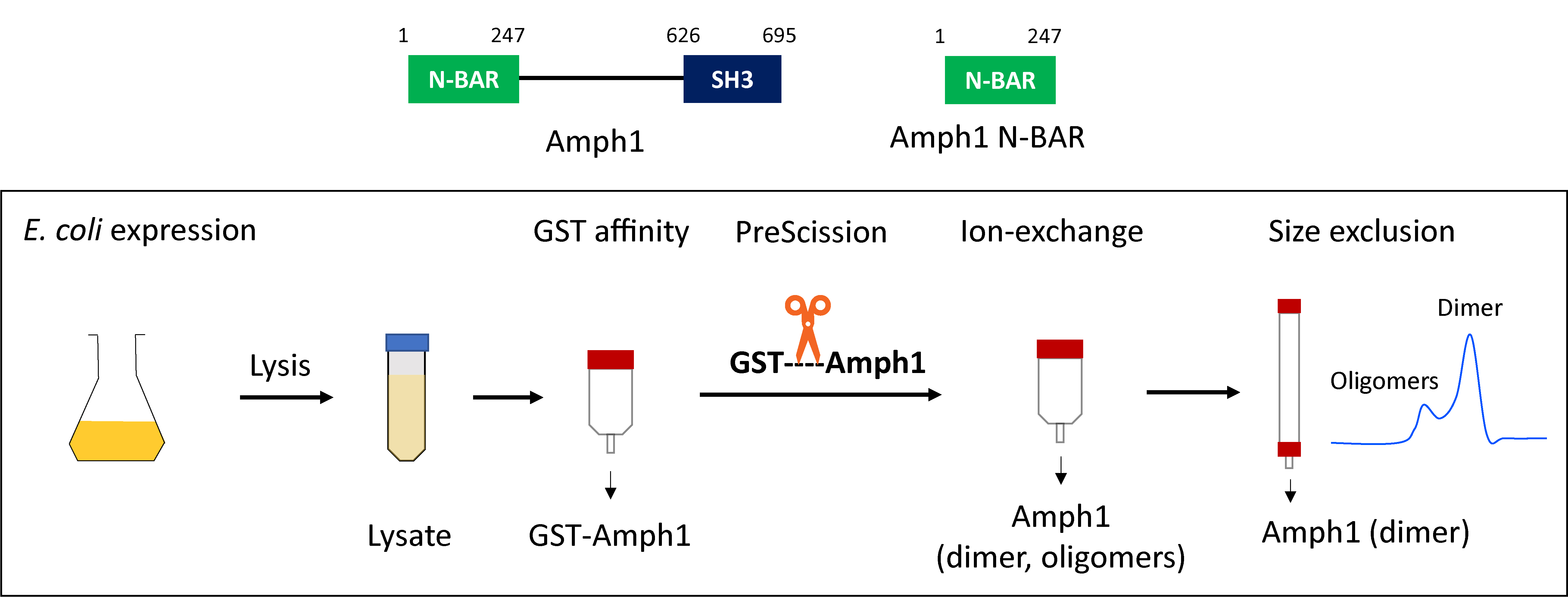
Background
Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) family proteins have drawn wide interest due to their roles in several membrane trafficking pathways (Frost et al., 2009). During clathrin-mediated endocytosis, the N-BAR proteins endophilin and amphiphysin are recruited to the neck of endocytic buds and facilitate membrane scission (Takei et al., 1999; Milosevic et al., 2011). The N-BAR domain forms a homodimer in solution and adopts a crescent-like shape known for generating, sensing, and stabilizing highly curved endocytic membrane nanostructures (Gallop et al., 2006). Our group's recent in vitro reconstitution study has shown that endophilin can undergo phase separation via self-association and, alternatively, via multivalent interactions with its binding partners (Mondal et al., 2022). Unlike endophilin, amphiphysin (full length protein) did not show phase separation behavior, although its N-BAR domain did phase separate. These recent observations suggest that spatiotemporal organization on the membrane and curvature generation properties of BAR proteins could be regulated by a phase separation–dependent mechanism.
Purification of recombinant amphiphysin and endophilin as GST fusion proteins was first reported by DeCamilli and coworkers (David et al., 1996; Ringstad et al., 1997). The GST tag facilitates the purification of the protein of interest from E. coli lysate by affinity chromatography. Moreover, it is recognized for its ability to improve protein solubility and enhance expression efficiency (Smith and Johnson, 1988). Additionally, Gallop et al. (2005) demonstrated that using a GST tag instead of a polyhistidine tag resulted in more efficient purification of the endophilin N-BAR domain. A general strategy to purify the GST-tagged BAR proteins involves extraction of the fusion protein from bacterial cell lysate by GST affinity chromatography, removal of the GST tag by PreScission protease cleavage followed by ion exchange chromatography, and finally, size exclusion chromatography. Later on, several other groups adopted this basic purification strategy to purify various N-BAR proteins (Gallop et al., 2006; Capraro et al., 2013; Ambroso et al., 2014). Our present protocol allows the purification of various full-length N-BAR proteins, their N-BAR domains, and their mutants, with minor or no further optimization. We found that additional optimization is needed when purifying the amphiphysin N-BAR domain, since the protein tends to precipitate upon removal of the GST tag and for that reason the N-BAR domain loses its membrane curvature generation activity. The protein stability in aqueous solutions can be enhanced by the addition of cosolvents such as glycerol. Vagenende et al. (2009) reported that glycerol prevents protein aggregation by inhibiting protein unfolding and by interaction with hydrophobic surface regions of the protein to form amphiphilic interfaces. The addition of glycerol to buffers for all the chromatography steps was found to minimize precipitation, and the protein retained its curvature generation abilities. Here, we provide a step-by-step guide to purifying full-length amphiphysin and the N-BAR domain. Steps that are common and different for full-length proteins and the N-BAR domain are indicated.
Materials and reagents
Pipette tips 10 μL (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 2139)
Pipette tips 200 μL (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 02-707-500)
Pipette tips 1 mL (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 02707508)
Disposable cuvettes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14955127)
Polypropylene round-bottom tube (Corning, catalog number: 352059)
Petri dishes (Corning, catalog number: 353003)
0.22 μm filter (Merck Millipore, catalog number: SLGVR33RS)
10 mL syringes (Becton, Dickinson and Company, catalog number: 301029)
Collection tubes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-961-26)
Syringe (Henke Sass Wolf, catalog number: 4850001000)
Gel-loading tips (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 05-408-150)
E. coli BL21 DE3 codon plus (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 230280)
Plasmids: full length human amphiphysin 1 (1-695) and its N-BAR domain (1-247) sequences contained in pGEX-6P vectors were generously provided by Pietro DeCamilli’s lab. Plasmids are available from the Baumgart lab upon request.
PreScission protease (Genscript, catalog number: Z02799)
SOC medium (Corning, catalog number: 46-003-CR)
LB agar, Miller (Fisher BioReagents, catalog number: BP1425-500)
Ampicillin (Fisher BioReagents, catalog number: BP1760-25)
Chloramphenicol (Acros Organics, catalog number: 227920250)
200 proof ethanol (Decon Laboratories, catalog number: 2716)
Parafilm (Bemis, catalog number: PM-999)
LB broth, Miller (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L3152)
Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Lab Scientific, catalog number: I-555)
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 11359061001)
Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7893)
Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S271-3)
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) (Fisher BioReagents, catalog number: BP152-1)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP120-500)
Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Fisher BioReagents, catalog number: BP172-5)
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A144-500)
Glutathione (GSH) (Acros Organics, catalog number: 120001000)
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP310-500)
Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: PG82089)
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP329-500)
Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S374-500)
Sodium hydroxide (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S318-500)
Acrylamide, 30% (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1610158)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Acros Organics, catalog number: 327311000)
NovexTM sharp prestained protein ladder (Invitrogen, catalog number: 57318)
Loading buffer for SDS-PAGE (0.3 M Tris, 60% v/v glycerol, 12% w/v SDS, 0.3 M DTT, 0.6% bromophenol blue)
GelCodeTM Blue safe protein stain (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 24596)
Amicon® ultra centrifugal filters (Millipore Sigma, catalog numbers: UFC901024, and UFC903024)
LB agar plates (see Recipes)
Luria Bertani (LB) media (see Recipes)
PMSF stock solution (see Recipes)
Buffers (see Recipes)
GST lysis buffer
GST wash buffer
GST elution buffer
Cation exchange buffer A
Cation exchange buffer B
Size exclusion buffer
SDS-PAGE running buffer
Equipment
Incubator and shaker (Eppendorf, catalog number: M1335-0004)
UV Vis spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: G1103A)
Sonicator (QSonica, catalog number: Q700)
Centrifuge (Sorvall, catalog number: SO-RC5B)
PTI F10S-6 × 500 rotor (Piramoon Technologies, catalog number: I590496)
SS34 8 × 50 rotor (Sorvall, catalog number: SO-34)
Centrifuge bottles, 500 mL (Nalgene, Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 3120-9500)
High-speed centrifuge tubes, 50 mL (Nalgene, Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 3114-0050)
Tabletop centrifuge (Sorvall, catalog number: SO-RT7)
Swing buckets (Sorvall, catalog number: 00436)
pH sensor (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 13-620-631)
Akta Purifier (GE Healthcare) or Akta Pure (Cytiva)
GST column (Cytiva, catalog number: 17528202)
Cation exchange column (Cytiva, catalog number: 17115201)
Superdex 200 column (Cytiva, catalog number: 28989335)
Hot water bath (Precision Scientific, catalog number: 66643)
Autoclave (Steris, model: Amsco Lab 250)
Mini gel tank (Life Technologies, catalog number: A25977)
Electrophoresis power supply (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 55860-4)
NanoDrop (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: ND-ONE-W)
Gel imagers: ChemiDocTM MP Imaging System (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 12003154) and Typhoon FLA 7000 (GE Healthcare)
Software
Unicorn: version 5.20 for Akta purifier (GE Healthcare) and version 7.6 for Akta Pure (Cytiva)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2023 The Author(s); This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
如何引用
Mondal, S., James, H. P., Milano, F., Jin, R. and Baumgart, T. (2023). Purification of Recombinant Human Amphiphysin 1 and its N-BAR Domain. Bio-protocol 13(12): e4699. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4699.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 表达
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link