- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Human Auto-IgG Purification from High Volume Serum Sample by Protein G Affinity Purification
用蛋白G亲和纯化法从大量血清样品中纯化人类自身 IgG
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2022年12月05日第12卷第23期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4562 浏览次数: 2817
评审: Anonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案

适用于 LC–MS/MS 蛋白质组学分析的大体积细胞培养上清分泌组样品制备方法优化
Basil Baby Mattamana [...] Peter Allen Faull
2025年12月20日 1211 阅读
Abstract
Immunoglobulins are proteins produced by the immune system, which bind specifically to the antigen that induced their formation and target it for destruction. Highly purified human immunoglobulins are commonly used in research laboratories for several applications, such as in vitro to obtain hybridomas and in vivo animal immunisation. Several affinity purification methods are used to purify immunoglobulins from human serum, such as protein A/G Sepharose beads, polyethylene glycol, and caprylic acid ammonium sulphate precipitation. Here, we provide a detailed protocol for purification of high-quality IgG from human serum, using affinity chromatography with protein G. The protocol is divided into four main steps (column preparation, serum running, wash, and elution) for IgG purification, and two extra steps (protein dialysis and sucrose concentration) that should be performed when buffer exchange and protein concentration are required. Several IgG affinity purification methods using protein A or G are available in the literature, but protein A has a higher affinity for rabbit, pig, dog, and cat IgG, while protein G has a higher affinity for mouse and human IgG. This affinity-based purification protocol uses protein G for a highly specific purification of human IgG for animal immunization, and it is particularly useful to purify large amounts of human IgG.
Graphical abstract
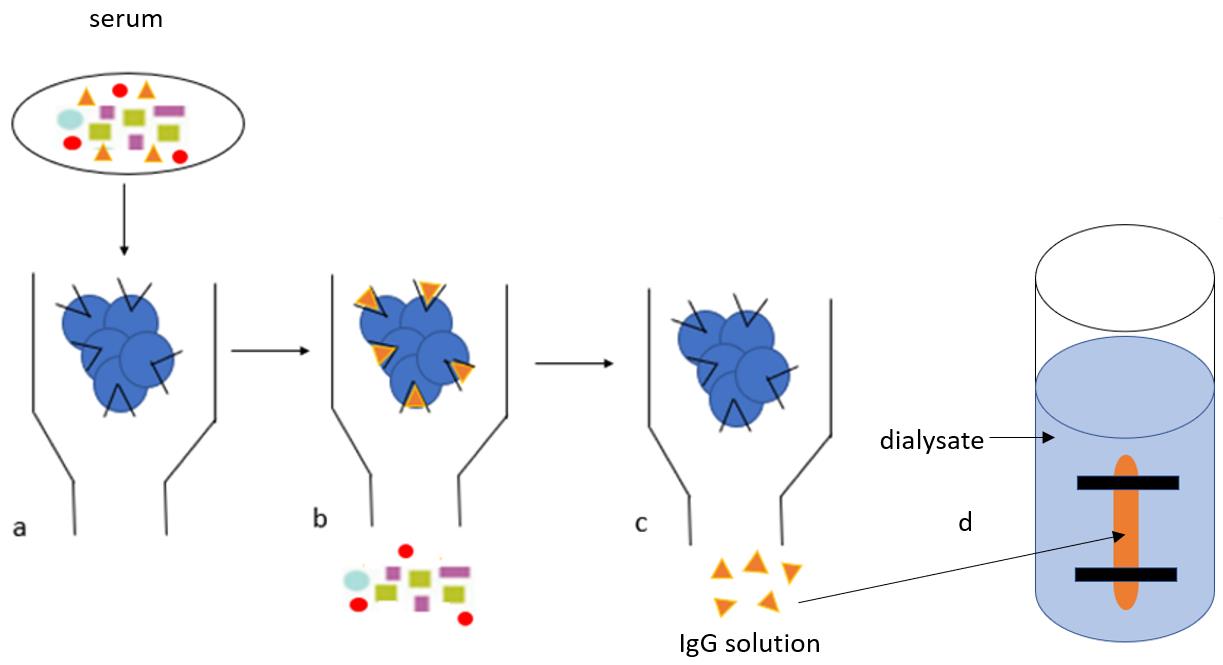
IgG purification protocol. The IgG purification protocol consists of four main steps (column preparation, serum running, wash, and elution) and two extra steps (protein dialysis and concentration). a. Diluted serum is added to the protein G beads and IgG binds to the Fc receptors on protein G beads. b. Beads are washed in Hartman’s solution to fully remove the complex protein mixture (multicolour shapes, as depicted in the graphical abstract). c. IgG (orange triangles, as depicted in the graphical abstract) are removed from protein G with glycine and collected in Tris buffer. d. The IgG is transferred into a semi-permeable membrane (‘snake skin’) and allowed to dialyse overnight for buffer exchange with a physiological solution (Hartmann’s).
Background
Immunoglobulins (Ig) or antibodies (Ab) are glycoproteins found in serum and tissue fluids, which are produced in large amounts after contact with immunogenic foreign molecules. They are Y-shaped and consist of five classes or isotypes: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a type of antibody normally found in blood and extracellular fluid that is predominant in adaptive immune responses. The IgG isotype is 75% of normal serum immunoglobulins (14 mg/mL) and is divided into four sub-classes, called IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, in the following proportion: 70%, 20%, 8%, and 2%, respectively. All antibodies have the same basic structure divided into variable and constant regions; the variable region is antigen specific and contains two fragment antigen binding (Fab) sites, while the constant region, also known as fragment crystallizable (Fc), is isotype specific and stimulates antigen destruction. Human-derived IgGs are a subgroup of immunoglobulins that are commonly used for a variety of research methods or as effective therapeutics in inflammation, cancer, as well as autoimmune and infectious diseases. For in vitro methods, antibodies can be used directly in their crude form (serum) or in a pure form (IgG); however, purified antibodies are more advantageous than the whole serum because they reduce cross-reactivity, can be easily stored, and are stable for longer periods. Several autoimmune syndromes have been successfully "transferred" in animals immunized with highly purified human autoantibodies (Cuhadar et al., 2019; Goebel et al., 2021; Helyes et al., 2019; Pohoczky et al., 2022). Several protocols for antibody purification are available in the literature, and these are divided in two main groups: non chromatographic techniques, such as polyethylene glycol, and caprylic acid ammonium sulphate precipitation, and chromatographic techniques, such as affinity chromatography with protein A/G beads. Non-chromatographic techniques depend on the combination of several factors, and are therefore complex, laborious, and expensive, especially due to the usage of polyethylene glycol. Affinity chromatography with commercially available protein-A or protein-G beads is the standard methodology for purification of antibodies from serum, for the relative simplicity and reliability of results. While protein A has a higher affinity for rabbit, pig, dog, and cat IgG1, IgG2, and IgG4, protein G has a higher affinity for mouse and human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4. Furthermore, protein G beads have a wider binding range than protein A beads because they can bind to intact IgG as well as antibody fragments F(ab) 2 and Fc regions, while protein A binds strongly to the Fc part and weakly to the Fab region. Here, we provide a detailed and easy to follow protocol for purification of high-quality IgG from human serum, using affinity chromatography with protein G. Differently from previously published methods, this protocol is specifically designed for purification of large amounts of human serum (20 mL), whereby serum is diluted before purification, and Hartmann’s solution is used as a binding buffer instead of PBS, to keep neutral pH and physiological ionic strength(Cuhadar et al., 2019; Goebel et al., 2021; Helyes et al., 2019; Pohoczky et al., 2022). These steps significantly improved the human IgG purification. Furthermore, this protocol contains useful comments regarding factors affecting IgG binding and stability. This protocol could also be used for purification of antibodies from hybridoma culture supernatant or ascites.
Materials and Reagents
Nunc 96-Well U Bottom (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 268200)
Syringes PlastipakTM 20 mL Luer-LokTM (BD, catalog number: 302237)
0.2 µm filters (Sigma-Aldrich, Millipore, catalog number: SLGP033RS)
50 mL centrifuge tubes (Sigma-Aldrich, Greiner, catalog number: T2318-500EA)
1.5 mL Eppendorf Safe-Lock Tubes (Eppendorfs, catalog number: 0030120086)
SnakeSkinTM Dialysis Tubing, 10K MWCO, 22 mm (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 68100)
SnakeSkinTM Dialysis Clips (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 68011)
Protein G Sepharose 4 Fast Flow, 5 mL (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: GE17-0618-01) storage at 4 °C
Econo-pac chromatography columns, package of 50 (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 7321010)
Two-way Stopcocks (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 7328102)
Compound Sodium Lactate Solution for Infusion BP (Hartmann's Solution for infusion) in Viaflo, 1,000 mL (Baxter, catalog number: FKE2324)
Bradford Reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6916)
Ethanol, Absolute, Molecular Biology Grade, 500 mL (ThermoFisher, catalog number: 16606002)
Sucrose, Molecular Biology Grade (AlfaAesar by Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: J65148.A1)
Trizima Base (ThermoFisher, catalog number: BP152-500)
Glycine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 50046)
HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H1758)
Neutralisation Buffer: Trizma base 1 M (pH 8.0) (see Recipes)
Elution Buffer: Glycine 100 mM (pH 2.3) (see Recipes)
Storage buffer: 20% Ethanol (see Recipes)
Washing buffer: Hartmann's Solution for Infusion (Compound Sodium Lactate) in Viaflo, 1,000 mL (see Recipes)
Equipment
pH Meter Mettler ToledoTM FiveEasyTM F20 pH/mV Meter (Mettler Toledo, catalog number: 15543360)
Centrifuge 5810R (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5811000465)
PIPETMAN Classic Starter Kit, P20, P200, P1000 (Gilson, catalog number: F167300)
Laboratory stand Model SBS-LS-100 (Expondo, catalog number: EX10030473)
Borosilicate Glass Tall Form Beakers 2 L (ThermoFisher, catalog number: 15499083)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Sensi, S. and Goebel, A. (2022). Human Auto-IgG Purification from High Volume Serum Sample by Protein G Affinity Purification. Bio-protocol 12(23): e4562. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4562.
分类
免疫学 > 抗体分析 > 抗体检测
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 分离和纯化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link