- EN - English
- CN - 中文
An Unbiased CRISPR-Cas9 Screening Method for the Identification of Positive and Negative Regulatory Proteins of Cell Adhesion
鉴定细胞粘附正负调节蛋白的无偏差CRISPR-Cas9的筛选方法
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2022年11月05日第12卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4545 浏览次数: 2790
评审: Giusy TornilloAlfano LuigiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Mature B-cell lymphomas are highly dependent upon the protective lymphoid organ microenvironment for their growth and survival. Targeting integrin-mediated homing and retention of the malignant B cells in the lymphoid organs, using the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib, is a highly efficacious FDA-approved therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM). Unfortunately, a significant subset of patients is intrinsically resistant to ibrutinib or will develop resistance upon prolonged treatment. Here, we describe an unbiased functional genomic CRISPR-Cas9 screening method to identify novel proteins involved in B-cell receptor–controlled integrin-mediated adhesion, which provides novel therapeutic targets to overcome ibrutinib resistance. This screening method is highly flexible and can be easily adapted to identify cell adhesion–regulatory proteins and signaling pathways for other stimuli, adhesion molecules, and cell types.
Graphical abstract:
Background
In mature B-cell lymphomas, the malignant B cells are highly dependent on their protective lymphoid organ microenvironment; the stromal cells, T cells, and macrophages in the lymph node and bone marrow secrete a variety of cytokines and chemokines and express several adhesion molecules, which stimulate survival and proliferation of the malignant B cells (Burger and Wiestner, 2018). The retention of the malignant cells in these protective niches is mediated by cell adhesion to extracellular matrix components (e.g., fibronectin) and cellular ligands (e.g., VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and cadherins).
In many mature B-cell malignancies, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM), the activation of integrins is controlled by the B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling (Figure 1), among others (de Rooij et al., 2012; Chang et al., 2013; de Rooij et al., 2016). Targeting the BCR signalosome [e.g., by the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib or the PI3Kδ inhibitor idelalisib] has demonstrated an unprecedented clinical efficacy in these malignancies, with objective response rates of 70%–90% (Burger and Wiestner, 2018). We and others have shown that these drugs do not act by directly killing the lymphoma cells, but rather by mobilizing the cells from their protective niches into the peripheral blood, where they are deprived from survival and growth signals, eventually dying (de Rooij et al., 2012, 2016; Byrd et al., 2013; Chang et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2013; Brown et al., 2014; Treon et al., 2015).
Notwithstanding the high clinical efficacy of these drugs, a subset of patients does not respond at all or develops resistance upon prolonged treatment (Stephens and Byrd, 2021). Considering the microenvironment dependence as the Achilles’ heel of many B-cell malignancies, we aimed to identify novel signaling molecules involved in the regulation of B-cell homing and retention.
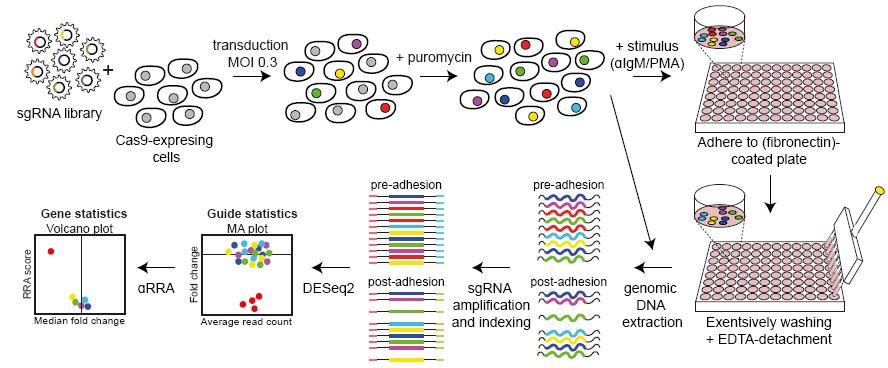
Over the last decade, pooled genetic screening platforms, either using shRNAs or CRISPR-Cas9 libraries, have been widely used not only in the context of (synthetic) lethality and drug resistance, but also in more functional assays, such as FACS-based reporter or signaling screens (Przybyla and Gilbert, 2022). Here, we describe the detailed method of a pooled genetic CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout screening method to identify genes involved in integrin-mediated adhesion: a loss-of-adhesion screen. This screen is suitable for studying a variety of different cell types, stimuli (chemokines or cytokines), cell adhesion molecules (integrins, cadherins, and selectins), and their ligands [(extra)cellular matrix components].
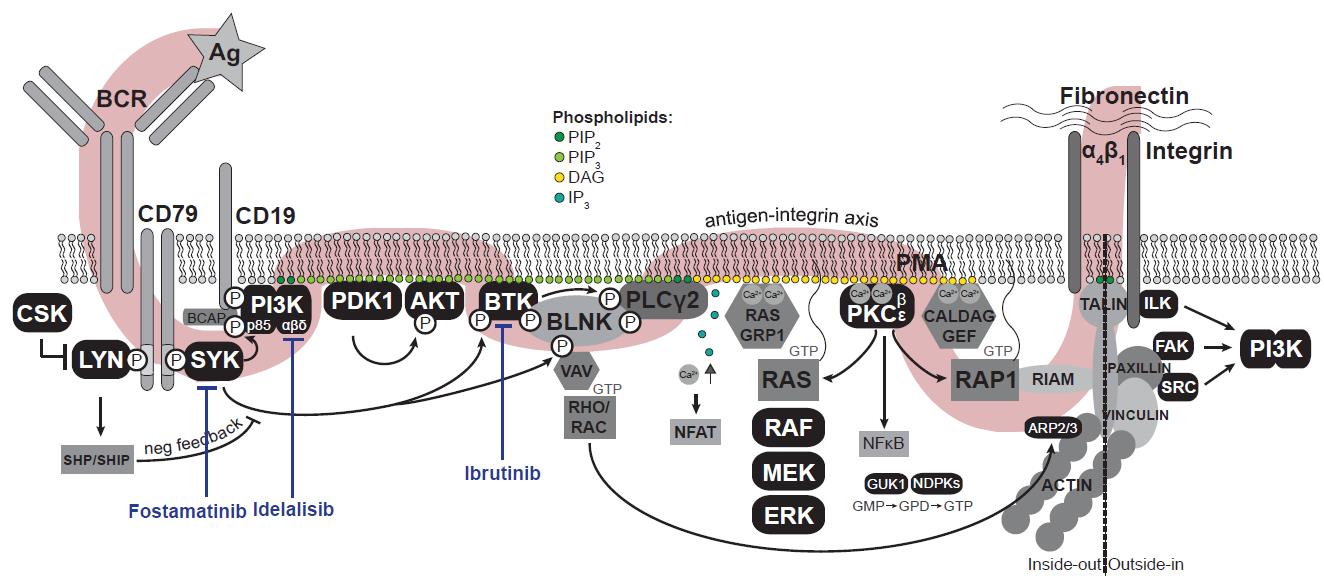
Figure 1. The B-cell receptor signaling pathway. Antigen (Ag) binding to the B-cell receptor (BCR) induces a signaling cascade resulting in the activation of integrins. In black, all kinase(-related) proteins are depicted. Adapted from De Rooij et al. (2022). Ag: antigen (αIgM); BCR: B-cell receptor; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol-4,5-diphosphate; PIP3: phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate; DAG: diacylglycerol; IP3: inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate; Ca2+: cytosolic calcium ions; PMA: phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate; GMP/GDP/GTP: guanosine-mono/di/triphosphate.
Materials and Reagents
Plasmids and vectors
LentiCas9-Blast (Addgene, catalog number: 52962)
Cas9-reporter [pKLV2-U6gRNA5(gGFP)-PGKBFP2AGFP-W] (Addgene, catalog number: 67980)
psPAX2 (Addgene, catalog number: 12260)
pMD2.G (Addgene, catalog number: 12259)
pEGFP-N3 (Clontech, catalog number: 6080-1)
LentiGuide-Puro Brunello kinome library (Addgene, catalog number: 1000000082)
Cell culture, transfection, and transduction
6-well plate (Greiner, catalog number: 657160)
T175 flasks (Greiner, catalog number: 658170)
15 mL tubes (Falcon, catalog number: 734-0452)
0.45 µm filter (Millipore, catalog number: SLHA033SS)
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 41966-052)
Iscove’s modified Dulbecco’s medium (IMDM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12440-061)
Polyethylenimine, linear (PEI, Polysciences, catalog number: 24313-2)
HEK293T-17 (ATCC, catalog number: CRL11268)
Namalwa (DSMZ, catalog number: ACC24)
Cryovials (Costar, catalog number: 430488)
Puromycin (Invivogen, catalog number: ant-pr-1)
Blasticidin S hydrochloride (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: R210-01)
Supplements for cell culture medium (added before use; see Recipes)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (HyClone, catalog number: SH30071.03)
L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 59202C)
Penicillin-streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4333)
Library amplification
94 × 16 mm plates (Greiner, catalog number: 633181; other sizes can be used if desired)
EnduraTM electrocompetent cells (Lucigen, catalog number: 60242-1)
Agar (BD, catalog number: 214010)
Ampicillin (Sigma, catalog number: A5354)
NucleoBond Xtra midi prep kit (Macherey-Nagel, catalog number: 740420.50)
LB (BD, catalog number: 240230)
LB medium containing antibiotics (see Recipes)
SOC medium (see Recipes)
D-glucose (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1083371000)
Agar plates containing antibiotics (see Recipes)
Adhesion
96-well high binding, flat bottom plates (Greiner, catalog number: 655061)
Human plasma fibronectin (FN) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F2006)
Poly-L-lysine hydrobromide (PLL) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6282)
Bovine serum albumin fraction V (BSA) (Roche, catalog number: 10735094001)
Ibrutinib (SelleckChem, catalog number: S2680)
Goat F(ab’)2 anti-human IgM (Southern Biotech, catalog number: 2022-14)
Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8139)
Multichannel pipette reservoir (Corning, catalog number: 4870)
25% glutaraldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 354400)
Crystal violet (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C0775)
Ethanol (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1009831000)
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Fresenius Kabi, catalog number: M090001/13)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E9884)
0.5% crystal violet in 20% ethanol (see Recipes)
0.5 M EDTA, pH 8.0 (see Recipes)
Genomic DNA isolation
Quick DNA mini prep kit (Zymo Research, catalog number: D3024)
Qubit broad range kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: Q32850)
PCR and next-generation sequencing
PhusionTM high-fidelity DNA polymerase (contains 5× HF buffer) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: F530S)
10 mM dNTP mix (Sigma-Aldrich, 71004-3)
10 µM PCR1 barcoded forward primer (Sigma-Aldrich, Tables 1, 2)
10 µM PCR1 reverse primer (Sigma-Aldrich, Table 1)
10 µM PCR2 forward primer (Sigma-Aldrich, Table 1)
10 µM PCR2 indexed reverse primer (Sigma-Aldrich, Tables 1, 2)
Agarose (Meridian Biosciences, catalog number: BIO-41025)
Ethidium bromide (EtBr) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E1385)
NucleoSpin gel and PCR clean-up kit (Macherey-Nagel, catalog number: 740609.250)
Qubit high sensitivity kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: Q32851)
Tris base (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503)
Acetic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A6283)
PhiX Control v3 (Illumina, catalog number: FC-110-3001)
TAE buffer (see Recipes)
Agarose gel (see Recipes)
Table 1. Primers PCR1 and PCR2
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| PCR 1 barcoded forward | ACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTNNNNNNGGCTTTATATATCTTGTGGAAAGGACG |
| PCR 1 reverse | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTACTGACGGGCACCGGAGCCAATTCC |
| PCR 2 forward | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT |
| PCR 2 indexed reverse | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATNNNNNNGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCT |
The NNNNNN in the PCR1 forward and PCR2 reverse primers are replaced by the desired barcodes/ indexes listed in Table 2.
Table 2. Barcodes/indexes for PCR1 and PCR2 primers
| Catalog number | Barcode PCR1 | Index PCR2 |
| 1 | CGTGAT | ATCACG |
| 2 | ACATCG | CGATGT |
| 3 | GCCTAA | TTAGGC |
| 4 | TGGTCA | TGACCA |
| 5 | CACTGT | ACAGTG |
| 6 | ATTGGC | GCCAAT |
| 7 | GATCTG | CAGATC |
| 8 | TCAAGT | ACTTGA |
| 9 | CTGATC | GATCAG |
| 10 | AAGCTA | TAGCTT |
| 11 | GTAGCC | GGCTAC |
| 12 | TACAAG | CTTGTA |
Equipment
12-well multichannel pipette (Eppendorf Research, catalog number: 4926000069)
An electronic multichannel, which releases the fluid at a given speed, might be of interest, especially when a large number of 96-well plates are used for the screen. We used the Picus 1200 (Sartorius, catalog number: 735491)
Spectrophotometer (CLARIOstar Plus, BMG Labtech)
Fluorescence microscope (Olympus Lifesciences)
FACSCanto II (BD Biosciences)
37 °C, 5% CO2 incubators (cell culture)
Electroporation system (Bio-Rad, Gene Pulser)
37 °C incubator (bacteria)
100 mL erlenmeyers
Microcentrifuge (Hettich, MIKRO 220R)
Centrifuge (Hettich, ROTINA 420)
Vortex (Heidolph, Reax Top)
Qubit (ThermoFisher)
Thermal cycler (Westburg, Biometra TAdvanced)
Gel electrophoresis system (LKB Power supply; CBS scientific)
Sequencer (Illumina, HiSeq2000)
-80 °C freezer
-20 °C freezer
Software
FlowJo (BD Biosciences; https://www.flowjo.com/)
Perl (https://www.perl.org/) or Python (Anaconda) (https://www.anaconda.com/)
DESeq2 R-package (http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/htmL/DESeq2.htmL) (Love et al., 2014) and/or MAGeCK (only in Linux) (https://sourceforge.net/p/mageck/wiki/Home/) (Li et al., 2014)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Thus, Y. J., de Rooij, M. F. M., Beijersbergen, R. L. and Spaargaren, M. (2022). An Unbiased CRISPR-Cas9 Screening Method for the Identification of Positive and Negative Regulatory Proteins of Cell Adhesion. Bio-protocol 12(21): e4545. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4545.
分类
癌症生物学 > 侵袭和转移 > 药物发现和分析 > 细胞粘附
药物发现 > 药物筛选
细胞生物学 > 细胞运动 > 细胞粘附
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link