- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Electrophysiological Measurements of Isolated Blood Vessels
离体血管的电生理测量
发布: 2022年03月20日第12卷第6期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4359 浏览次数: 3053
评审: Andrea PuharWendy Leanne Hempstock

相关实验方案
基于人外周血单个核细胞(PBMCs)和浆细胞样树突细胞(pDCs)的宿主靶向抗病毒药物(HTA)筛选方案
Zhao Xuan Low [...] Pouya Hassandarvish
2025年03月05日 3059 阅读
Abstract
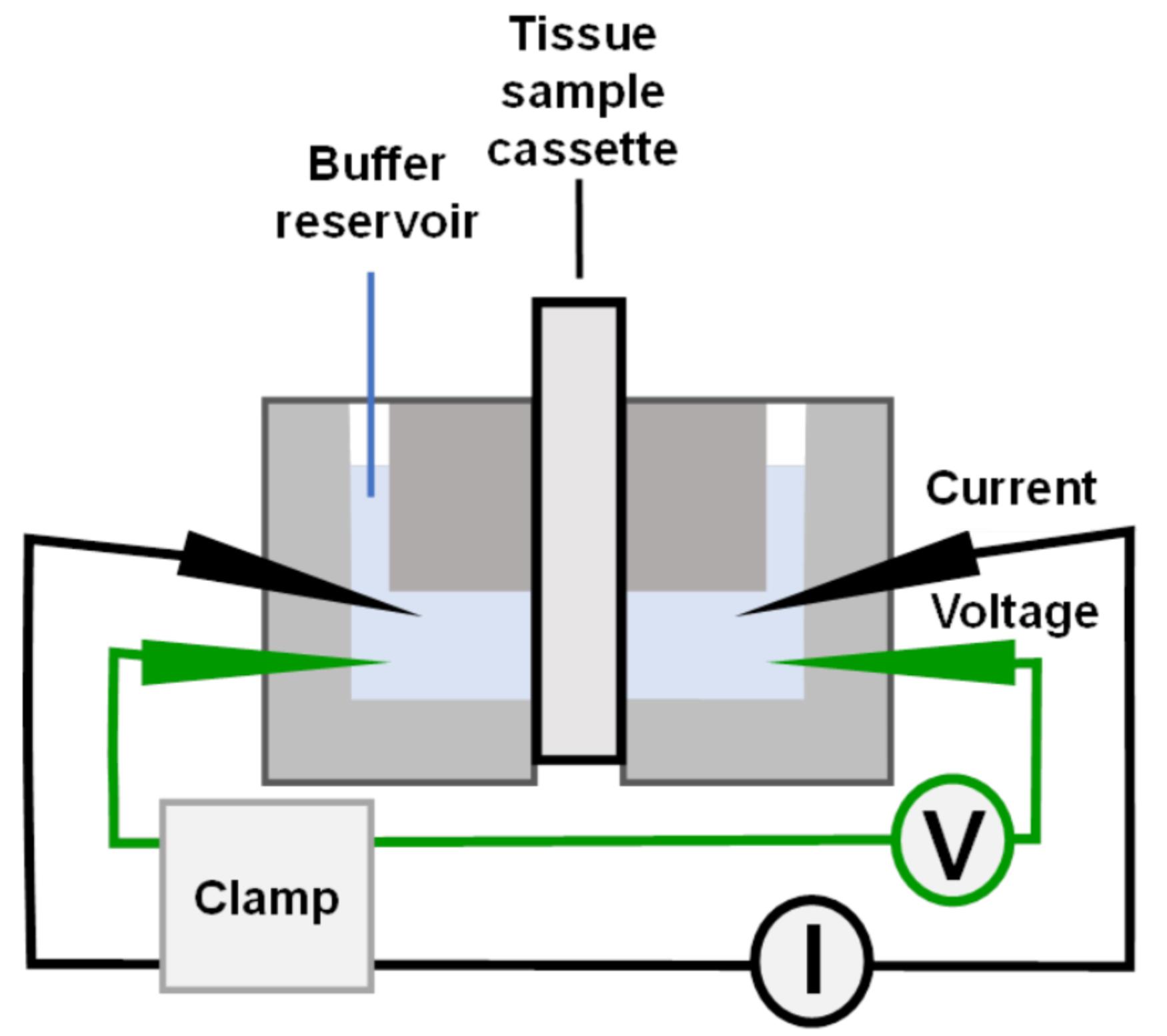
The lumen of blood vessels is covered by endothelial cells, which regulate their permeability to ions and solutes. Endothelial permeability depends on the vascular bed and cell phenotype, and is influenced by different disease states. Most characterization of endothelial permeability has been carried out using isolated cells in culture. While analysis of cultured cells is a valuable approach, it does not account for factors of the native cell environment. Building on Ussing chamber studies of intact tissue specimens, here we describe a method to measure the electrophysiological properties of intact arteriole and venule endothelia, including transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) and ion permselectivity. As an example, vessels isolated from the mesentery were treated ex vivo, then mounted in a custom-made tissue cassette that enable their analysis by classical approaches with an Ussing chamber. This method enables a detailed analysis of electrophysiological vessel responses to stresses such as proinflammatory cytokines, in the context of an intact vessel.
Graphic abstract:
Background
The endothelial barrier regulates the passage of ions, water, and proteins across blood vessels. The vasculature is heterogeneous, with veins being generally more permeable than arteries (Crone and Christensen, 1981; Durán et al., 2008; Hilfenhaus et al., 2018). Several diseases, including sepsis, stroke, and hypertension are exacerbated by a failure in endothelial barrier function (Wang et al., 2002; Granger et al., 2010; Rosenberg, 2012; Schoknecht and Shalev, 2012). Thus, it is critically important to understand the molecular regulation of vascular function in general, and of the endothelium in particular.
Ussing chambers enable the most detailed analysis of the electrophysiological properties of barrier-forming cells (Clarke, 2009; Herrmann and Turner, 2016). Originally developed to measure sodium permeability across frog skin (Ussing and Zerahn, 1951; Lindemann, 2001), Ussing chambers have been used to measure ion permeability in systems ranging from epithelial cells cultured on Transwell permeable supports (Molina et al., 2015) to intact tissues, such as the intestine (Laukoetter et al., 2007). The vast majority of Ussing chamber measurements have been performed on epithelial cells. By contrast, Ussing chamber analysis of cultured endothelial cells is much more difficult, although there are some examples where the approach was used to measure endothelial ion channel activity (Wigham et al., 2000; Hatou et al., 2010). The barrier function of cultured endothelial cells is generally characterized with other techniques, including cells cultured on Transwells with the EndOhm/ Millicell-ERS system, measuring flux with fluorescent tracers, and/or cells cultured on gold electrodes using electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) (Dubrovskyi et al., 2013; Adil and Somanath, 2021; Maier-Begandt et al., 2021).
Here, we describe a method for Ussing chamber analysis of the electrophysiological properties of semi-intact blood vessels, which have been dissected and longitudinally cut. This method can be applied to veins and arteries, and avoids difficulties encountered when measuring intact perfused blood vessels (Crone and Christensen, 1981). Several parameters can be measured, including transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER), short circuit current (Isc), and determination of relative ion permeability. Each of these measurements reflects both transcellular and paracellular ion transport, where transcellular ion transport is largely mediated by plasma membrane ion channels and the paracellular component is mediated through tight junctions (Anderson and van Itallie, 2009; Clarke, 2009). Together, the transcellular and paracellular pathways regulate tissue barrier function, a parameter that can be impacted by several pathophysiological conditions, such as sepsis (Joffre et al., 2020).
The ability to analyze an intact vascular barrier enables electrophysiological analysis of the endothelium in a native context that complements and validates measurements done with cultured cells or isolated perfused vessels. Native tissues also have better tissue integrity than endothelial cells in culture, and are more amenable to Ussing chamber analysis. Here, we describe techniques needed for electrophysiological analysis of intact vessels, and how these were applied to analyze the effect of a proinflammatory cytokine called TNFα on vein barrier function and ion permselectivity.
Materials and Reagents
Mice (at least 10 weeks of age)
Isofluorane
Rapid flow bottle top filter, 0.2 μm (ThermoFisher, catalog number: 291-4520)
Parafilm (Bemis)
1 mL slip tip syringe (BD, catalog number: 309659)
Gel-Loading tips (Fisher, catalog number: 02-707-138 or Bio-Rad, catalog number: 223-9915)
Copper bell wire
35 mm tissue culture dish (BD, Falcon Easy Grip, catalog number: 353001)
1.5 mL tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022363204)
50 mL conical centrifuge tubes (BD, catalog number: 352098)
Absolute ethanol
KCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3911)
Noble Agar, Ultrapure (ThermoFisher, catalog number: AAJ1090736)
Sodium hypochlorite, 5% (Clorox Chlorine Bleach)
NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9888)
CaCl2·2H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C3306)
MgCl2·6H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M2393)
Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7021)
HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H4034)
Lysine-Cl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L8662)
Na Aspartate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A6683)
Mannitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9647)
Dow Corning High Vacuum Grease
Wet or dry 600 grit ultrafine sandpaper (3M, catalog number: 1077259)
Extra sharp uncoated single edge razor blade (GEM, catalog number: 121-2)
5% CO2/95% O2 medical-grade gas mixture
DMSO, tissue culture grade (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2650)
Recombinant murine TNFα (R&D Systems, catalog number: 410-MT)
3 M KCl (100 mL) (see Recipes)
Agar solution (100 mL in 3 M KCl) (see Recipes)
70% ethanol (see Recipes)
10 M NaOH solution (100 mL) (see Recipes)
1 M HEPES (100 mL) (see Recipes)
Ringer’s Saline (500 mL) (see Recipes)
Ringer’s Mannitol (500 mL) (see Recipes)
Diluted Ringer’s Saline/Mannitol (1:4) (see Recipes)
Ringer’s Lysine-Cl (500 mL) (see Recipes)
Ringer’s Na-Aspartate (500 mL) (see Recipes)
1,000× TNFα (50 μg/mL) (see Recipes)
Equipment
Mouse Dissecting Kit (World Precision Instruments, catalog number: MOUSEKIT)
Dissecting Pan, Aluminum, with Vinyl Dissecting Pad (Carolina Supply, catalog number: 629004)
Silicone Dissecting Pad Kit (World Precision Instruments, catalog number: 501986)
Olympus SZX12 Dissecting Microscope or equivalent
Dual-channel, self-contained Ussing chamber (Warner Instruments, catalog number: U2500)
Custom made plug-in cassette, slot size: 175 μm in width and 1,500 μm in length (Emory Department of Physics Machine Shop), external dimensions comparable to Warner Instruments cassette, catalog number: U9924C-05.
Ussing Electrode Set (2 Ag/AgCl pellets and 2 Ag wires) (ADInstruments, catalog number: U9975A)
Ussing Electrode Bridge Fitting Kit (12 Fittings & 6 Adapters) (ADInstruments catalog number: U9565SC)
Bunsen burner
500 mL Erlenmeyer flask connected to in-house vacuum line
Multimeter Ohmmeter/voltmeter (Kosmos FKV-1025 or equivalent)
Lab stand with a 3 prong clamp
Multichannel Voltage/Current Clamp controller (Physiological Instruments, catalog number: VCC-MC2)
Circulating water bath (Haake DC10 or equivalent)
Fisherbrand accumet AB315 pH meter with electrode (13636AB315A)
Nutating platform (VWR, catalog number: 82007-202)
Software
Acquire & Analyze software ver 2.3 (Physiological Instruments)
Excel (Microsoft)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Molina, S. A., Maier-Begandt, D., Isakson, B. E. and Koval, M. (2022). Electrophysiological Measurements of Isolated Blood Vessels. Bio-protocol 12(6): e4359. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4359.
- Maier-Begandt, D., Comstra, H. S., Molina, S. A., Kruger, N., Ruddiman, C. A., Chen, Y. L., Chen, X., Biwer, L. A., Johnstone, S. R., Lohman, A. W., et al. (2021). A venous-specific purinergic signaling cascade initiated by Pannexin 1 regulates TNFalpha-induced increases in endothelial permeability. Sci Signal 14(672): eaba2940.
分类
生物物理学 > 电生理
免疫学 > 免疫机理 > 体外模型
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 电生理学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link