- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Spherical Invasion Assay: A Novel Method to Measure Invasion of Cancer Cells
球形侵袭测定:一种测量癌细胞侵袭的新方法
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2022年02月20日第12卷第4期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4320 浏览次数: 5282
评审: Gal HaimovichAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The invasion of tumor cells into the neighboring blood vessels and lymph nodes is a vital step for distant metastasis. Traditionally, the invasive activity of growth factors (or the anti-invasive activity of drugs) is measured with the Boyden chamber assay. However, this assay has a few disadvantages like poor physiological relevance of transwell inserts and an inability to control chemokine gradients. The Boyden chamber assay is one of the most prevalent methods to measure the invasion of cancer cells. It would be advantageous to develop another assay that could validate the results of the Boyden chamber assay. With this in mind, our laboratory developed the spherical invasion assay (SIA) to measure the pro-invasive activity of human cancer cells. The SIA also circumvents some of the drawbacks of the Boyden chamber assay. The present manuscript measures the anti-invasive activity of the Src kinase inhibitor PP2 in A549 human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) cells using the SIA. The SIA protocol is comprised of two steps. In the first step, A549 human NSCLC cells (treated or not with PP2) were mixed with Matrigel and seeded in the middle of an eight-well chamber slide. After 24 h, a second layer of Matrigel was overlaid over the first layer. Over the course of the next 24 h, the A549 cells invade from the primary to the secondary Matrigel layers. Subsequently, the cells are visualized by phase-contrast microscopy and the images obtained are quantified using ImageJ to calculate the anti-invasive activity of PP2 in A549 cells. The results of the SIA correlate well with Boyden chamber assays. The SIA may be adapted for multiple experimental designs, such as drug screening (to combat invasion and metastasis), measuring the pro-invasive activity of growth factors, and elucidating the signaling pathways underlying the pro-invasive/anti-invasive activity of biological modifiers.
Graphic abstract:
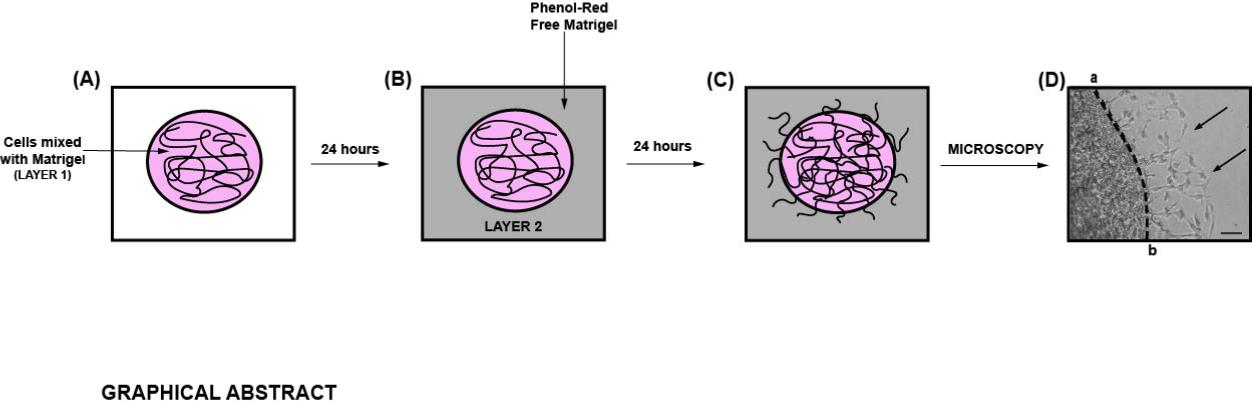
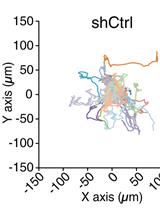
Diagrammatic illustration of the spherical invasion assay (Hurley et al., 2017). A. The first layer is comprised of human cancer cells mixed in a 1:1 suspension with Phenol Red containing Matrigel (represented as LAYER 1 in the figure). After 24 h, the cancer cells grow and extend up to the boundary of this first layer. B. A second layer of 1:1 solution Phenol Red-free Matrigel, in Phenol Red-free RPMI (represented as LAYER 2 in the figure) is added on top of the first Matrigel spot. The cells are incubated for 24 h at 37°C. C. Over these 24 h, the cancer cells invade from the primary layer into the secondary Matrigel layer. The chamber slides are observed by phase-contrast microscopy. D. A representative photograph of the images obtained by the SIA is shown. The black arrow indicates the cancer cells invading into the second layer of Matrigel. The dotted line represents the interface between the two layers. The distance to which the cells have traveled (into the secondary Matrigel layer) is measured at ten sites (for each photograph) in a randomized double-blind fashion by three independent observers, using NIH ImageJ Version 1.47. This process is repeated for three separate photographic fields per sample.
Background
Tumor invasion refers to the process by which cancer cells penetrate the basement membrane into surrounding stroma, neighboring blood vessels, and lymph nodes (Stuelten et al., 2018; Baghban et al., 2020). Tumor invasion is an essential step for metastasis of human cancers (Baghban et al., 2020). Amongst the many steps of metastasis, the process of tumor invasion has been targeted by many therapeutic agents to suppress the distant spread of tumors (Gandalovicova et al., 2017). The Boyden chamber assay is the benchmark technique for measuring the invasion of cancer cells (Guy et al., 2017). This assay involves the movement of a single-cell suspension through a microscopic mesh (8 micrometers in pore size) coated with an extracellular matrix. However, this assay suffers from several caveats. The physiological relevance of transwell inserts (to recapitulate invasion in vivo) is poor. The pore size of the membrane highly influences the number of cells that invade (Guy et al., 2017). In the Boyden chamber assay, a chemokine is added to the lower basolateral chamber to facilitate the invasion of tumor cells through the transwell membrane; however, it is very difficult to control the concentration of the chemokine gradient, and this may produce aberrant results (Guy et al., 2017). The Boyden chamber is one of the prevalent methods to measure tumor cell invasion. The “wound-healing assay” measures the migration (NOT THE INVASION) of human cancer cells. There are subtle differences between a “migration assay” and an “invasion assay”(Justus et al., 2014; Pijuan et al., 2019). In the migration assay, the movement of cells across a vacant area (like a scratch or wound) is measured. A second method to measure “cell migration” is to quantify the movement of cancer cells across a transwell filter (pore size of 8 µm) from the apical chamber to the basolateral chamber. Taken together, the migration assay measures the chemotactic capability of cells to travel toward a chemo-attractant or mixture of chemo-attractants (as observed with the use of conditioned medium). The invasion assay measures both cell chemotaxis and the invasion of cells through the layer of extracellular matrix proteins, a process that is commonly found in cancer metastasis. In the “invasion assay”, the transwell filters are coated with a thin layer of basement membrane (usually Matrigel). The first event in the “invasion assay” is that the cancer cells in the apical chamber secrete matrix metalloproteases to degrade basement membrane proteins, producing a gap in the basement membrane. Subsequently, the cancer cells travel through this gap in the basement membrane and pass through the transwell filter (pore size of 8 µm), to arrive at the basolateral chamber of the transwell filter. The process through which cancer cells degrade the basement membrane to penetrate the transwell insert is a unique feature of the “invasion assay”, which is not present in “migration assays”. The invasion assay faithfully recapitulates the process of “tumor invasion” during metastasis, where the neoplastic cells degrade the basement membrane to launch themselves into circulation in the neighboring blood vessel/lymph node. It would be useful to have a second invasion assay that could validate the results obtained with the Boyden chamber assay. All these considerations led us to develop a novel method of measuring tumor invasion namely the spherical invasion assay (SIA) in our laboratory. The SIA measures the invasion of human cancer cells as they migrate from the primary Matrigel layer, over the interface, and travel into a secondary Matrigel layer. The SIA mirrors the actual process of invasion under physiological conditions (Hurley et al., 2017). The cells that grow in extracellular matrix (ECM) retain biological characteristics of tumors, such as responsiveness to diffusion gradient of oxygen, nutrients, and pH. The growth of the cells inside the ECM allows for complex cell-cell and cell-matrix interaction. The SIA can be adapted to organoids, spheroids (Gunti et al., 2021), retinal angiogenic sprouts (Stitt et al., 2005), tumor stem cells (Atashzar et al., 2020), neurospheres (da Silva Siqueira et al., 2021), and cells grown on polymeric scaffolds (Stratton et al., 2016). In such cases, it is important to remember that the conditions for culturing normal cells are very different from cancer cells. In addition, normal cells should be used at a low passage number, so that they do not become senescent. For example, if the SIA is performed with retinal endothelial cells, then the assay should be performed between passages 3-6 (Stitt et al., 2005). Furthermore, these invading cells can be characterized by confocal laser microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Most importantly, the results of the SIA correlate with the data obtained in the Boyden chamber assay, so the SIA can be used to confirm the results obtained in Boyden chamber assays (Hurley et al., 2017). The present protocol examines the effect of the Src Kinase inhibitor PP2 (Hanke et al., 1996) (at a concentration of 10 µM) on the invasion of A549 human NSCLC cells. We hope that the SIA will be a useful tool for researchers working in the field of tumor microenvironment biology and cancer metastasis.
Materials and Reagents
Fisherbrand High Precision Sterile Scalpel Blade (Fisher, catalog number: 12-000-161)
NuncTM EasYFlaskTM T-75 Cell Culture Flasks (Fisher, catalog number: 12-565-349)
Tissue culture dishes (diameter 100 mm) may also be used (NuncTM EasYDishTM Dishes; Fisher catalog number: 12-600-003).
Ice cold 1.5 mL microfuge tubes (Fisher, catalog number: 05-408-129)
5 mL microfuge tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030119401)
Sterile 15 mL centrifuge tube (Thermo Scientific Nunc, Fisher, catalog number: 12-565-268)
Sterile 50 mL centrifuge tubes (ThermoScientific Nunc, Fisher, catalog number: 12-565-270)
Thermo Scientific Nunc Lab-Tek eight well Permanox plastic Chamber Slide System (Fisher, catalog number: 12-565-22)
A549 human NSCLC cells (ATCC, catalog number: CCL-185)
F-12K Medium (Kaighn's Modification of Ham's F-12 Medium; ATCC; catalog number: 30-2004). Store at 4°C
Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 medium with phenol-red (ATCC, catalog number: 30-2001). Store at 4°C
Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 medium without Phenol Red (Fisher, catalog number: 30-404-014). Store at 4°C
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (ATCC, catalog number: 30-2020)
Long-term storage for FBS is -20°C. In our laboratory, FBS is aliquoted into 50 mL centrifuge tubes and stored at -20°C. The FBS aliquot is stored at 4°C for immediate use.
Trypsin-EDTA (0.25% Trypsin, 0.53 mM EDTA, ATCC, catalog number: 30-2101)
Long-term storage for Trypsin-EDTA is stored at -20°C. However, Trypsin-EDTA is aliquoted and stored at 4°C for immediate use.
Dulbecco’s Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) without calcium and magnesium (Corning, Fisher, catalog number: 21-031-CM). Store at 4°C.
Matrigel membrane matrix (Fisher, catalog number: CB-40234)
Matrigel is a liquid at 4°C and it solidifies at 37°C. Matrigel is aliquoted and stored at -70°C for long-term storage. Before the experiment, Matrigel is kept overnight at 4°C for thawing. Matrigel is kept on ice throughout the experiment.
Phenol red-free Matrigel membrane matrix (Fisher, catalog number: CB-40234C)
PP2 (A potent and selective inhibitor of the Src family tyrosine kinases) was obtained from Enzo Biosciences (catalog number, 50-201-0681)
PP2 is a powder and is stored at -20°C. The PP2 is dissolved in DMSO (Corning DMSO, Fisher MT-25950CQC) at a final concentration of 10 mM. This stock solution of PP2 solution is aliquoted into microfuge tubes and stored at -20°C. Just before the SIA, the PP2 is thawed and diluted to the desired concentration using serum-free RPMI. After use, the remainder of the diluted PP2 solution (at a concentration of 10 µM) is discarded.
10 mM PP2 (see Recipes)
200 µM PP2 (see Recipes)
Equipment
NU-540 (LabGard® ES NU-540 Class II, Type A2) Laminar-Flow Biosafety Cabinet (NuAire, Plymouth, MN)
Cell culture incubator maintained at 37°C and 5% CO2 (Heracell VIOS 150i cell culture incubator, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA)
Leica DM IL LED Inverted Phase Contrast Microscope with a camera (Leica Microsystems, Welzar, Germany)
Corning Cell Counting Chamber (Fisher, catalog number: 07-200-988)
Labnet Hermle Z306 Universal Benchtop Centrifuge; 120V (Labnet International, Cary, NC)
Software
LAS Image Capture Software (Leica Microsystems)
Adobe Photoshop 2021 (Adobe Inc. for Windows)
Adobe Illustrator 2021 (Adobe Inc. for Windows)
NIH ImageJ Version 1.47 (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda)
GraphPad Prism Version 8
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Richbart, S. D., Merritt, J. C., Moles, E. G., Brown, K. C., Adeluola, A. A., Finch, P. T., Hess, J. A., Tirona, M. T., Miles, S. L., Valentovic, M. A. and Dasgupta, P. (2022). Spherical Invasion Assay: A Novel Method to Measure Invasion of Cancer Cells. Bio-protocol 12(4): e4320. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4320.
分类
癌症生物学 > 侵袭和转移 > 细胞生物学试验 > 细胞侵袭
药物发现
细胞生物学 > 细胞运动 > 细胞迁移
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link