- EN - English
- CN - 中文
ATAC Sequencing Protocol For Cryopreserved Mammalian Cells
哺乳动物冷冻保存细胞的ATAC测序方法
发布: 2022年01月20日第12卷第2期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4294 浏览次数: 5216
评审: Giusy TornilloYogita JethmalaniFernando A Gonzales-Zubiate

相关实验方案
利用OxiDIP-Seq方法对含8-氧代-2′-脱氧鸟苷的受损DNA进行全基因组图谱分析
Francesca Gorini [...] Stefano Amente
2022年11月05日 2883 阅读
Abstract
ATAC-seq (assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing) is a powerful method to evaluate chromatin accessibility and nucleosome positioning at a genome-wide scale. This assay uses a hyperactive Tn5 transposase, to simultaneously cut open chromatin and insert adapter sequences. After sequencing, the reads generated through this technique are generally indicative of transcriptional regulatory elements that are located in accessible chromatin. This method was originally developed by Buenrostro et al. (2013), and since then it has been improved by the same authors several times, until their last update called OMNI ATAC-seq (Corces et al., 2017). Here, we describe an ATAC-seq protocol based on the OMNI-ATAC method, with a special focus on the initial steps of thawing cryopreserved cells, and the final steps of library purification using magnetic beads. This protocol can be of interest for laboratories working in a fast-paced environment.
Graphic abstract:
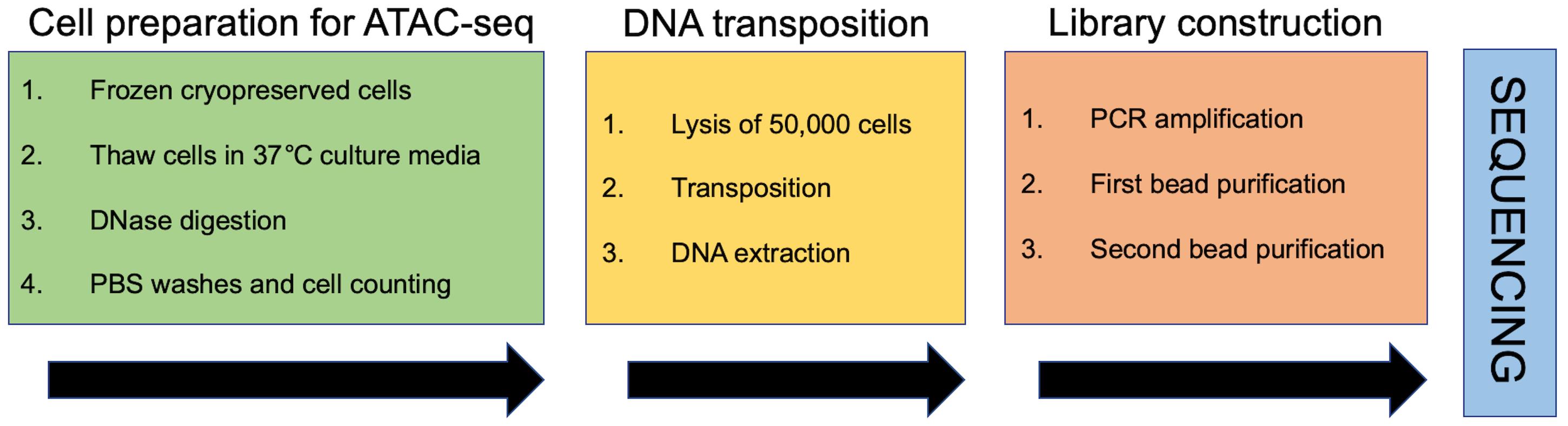
Flowchart of the protocol
Background
In eukaryotic organisms, the packaging of long DNA molecules into the nucleus is achieved by wrapping the DNA around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, and further compacting this structure into chromatin (Kornberg, 1974). The control of chromatin condensation is a major player in the regulation of gene expression. Since high DNA compaction restricts access for the transcriptional machinery, closed chromatin is usually associated with repressed gene expression. By contrast, open chromatin is associated with active gene expression, and the presence of regulatory elements like enhancers and promoters (Wegel and Shaw, 2005). The potential to reveal areas of high and low transcriptional activity has led to genome-wide mapping of chromatin accessibility becoming an area of broad interest.
Until now, several technologies for assessing the genomic profile of chromatin compaction have been developed. Some examples are micrococcal nuclease sensitivity (MNase-seq) (Zaret, 2005), formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE-Seq) (Giresi et al., 2007), and deoxyribonuclease I hypersensitivity (DNase-Seq) (Boyle et al., 2008). In 2013, Greenleaf and colleagues developed a new method to probe chromatin accessibility, called assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-seq). ATAC-seq is a technique that assesses open chromatin using a mutated hyperactive Tn5 transposase, which simultaneously cuts DNA and tags the resulting fragments with sequencing adaptors, preferentially in decondensed chromatin areas (Buenrostro et al., 2013). DNA sequencing libraries are then generated by PCR amplification and analyzed by high-throughput sequencing. The main advantages of ATAC-seq over the methods mentioned above are the low number of cells required as input and the length of the protocol (see Sun et al., 2019 for a full comparison between several chromatin accessibility assays).
Since development of the ATAC-seq method, the original authors have advanced (Buenrostro et al., 2015) and improved (OMNI ATAC-seq, Corces et al., 2017) the protocol, to overcome some of the initial limitations of this technique. For example, to remove mitochondrial DNA from the transposition reaction, the OMNI ATAC-seq protocol includes a washing step with non-ionic detergent after the cell lysis. Another improvement is the addition of PBS in the transposition mix, to reduce the background noise. Other researchers from different laboratories have also helped to improve and optimize ATAC-seq protocols (Fujiwara et al., 2019), or have adapted them for specific organisms and cell lines (Doganli et al., 2017, Shashikant and Ettensohn, 2019).
Being a core sequencing facility, our group handles a large number of ATAC-seq projects on a regular basis. We have adopted the OMNI ATAC-seq protocol for most of the ATAC-seq experiments, with two main modifications: (i) to handle a large number of projects, cell samples from researchers are sent cryopreserved, to be stored and processed at a convenient time. In this protocol, we include a section focused on the process of thawing cryopreserved cells, which is very important to preserve cell viability, and therefore to the success of an ATAC-seq experiment. (ii) After the purification of the final PCR reaction with the different silica column DNA purification kits available in the market, it is very common to find primer dimers and unwanted DNA fragments, due to over/under transposase digestion or an excess of PCR cycles. Thus, instead of using silica column-based methods, we purify the ATAC-seq libraries with magnetic beads. In addition to the removal of impurities, this allows us to size select the DNA fragments as needed for different samples. The use of magnetic beads for this step also enables the integration of automation platforms for processing a large number of libraries (Hess et al., 2020).
In summary, we present here an ATAC-seq protocol adapted from Corces et al. (2017) that can be used by sequencing core facilities and other laboratories that routinely handle large quantities of samples.
Materials and Reagents
Solid Phase Reversible Immobilization (SPRI) select beads (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: B23318). Store at room temperature.
High Sensitivity DNA Chips and reagents (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-4626). Store reagents at 4°C and DNA Chips at room temperature.
Hanks Balanced Salt Solution (Sigma, catalog number: H6648-500ML). Store at room temperature.
Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) pH 7.4 (Gibco, Thermofisher, catalog number: 10010-023). Store at 4°C.
Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium (IMDM) (Gibco, Thermofisher, catalog number: 12440-053). Store at 4°C.
Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) (Gibco,Thermofisher, catalog number: 10082147). Store at -20°C.
1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.4 (Teknova, catalog number: T5074). Store at room temperature.
5 M NaCl (Teknova, catalog number: S5845). Store at room temperature.
1 M MgCl2 (Teknova, catalog number: M0308). Store at room temperature.
Digitonin (Promega, catalog number: G9441). Dilute the original 2% digitonin solution 1:1 in water. Make aliquots and store at -20°C.
Tween-20 (Sigma/Roche, catalog number: 11332465001). Store at 4°C.
NP40 (Sigma/Roche, catalog number: 11332473001). Store at 4°C.
Tagment DNA Enzyme (transposase) and 2× TD buffer (Illumina, catalog number: 20034197). Store at -20°C.
NEBNext 2× MasterMix (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0541S). Store at -20°C.
Zymo DNA Clean & ConcentratorTM-5 Kit (Zymo Research, catalog number: D4014). Store at room temperature.
DNase (Worthington, catalog number: LS002007)
20,000 Units/mL DNase stock solution (see Recipes)
ATAC-Resuspension buffer (ATAC-RSB) (see Recipes)
ATAC-RSB with detergents buffer (see Recipes)
Wash out lysis buffer (see Recipes)
Transposition mix (see Recipes)
Equipment
Pipettes (P1000, P200, P20, P10)
Cell counter (Nexcelom, model: Cellometer Auto 2000 Cell Viability Counter)
ThermoMixer (Eppendorf, model: C with heated lid)
Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, model: T100)
Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, model: 2100)
Software
Agilent Technologies 2100 Bioanalyzer 2100 Expert (Agilent Technologies, https://www.agilent.com/en/product/automated-electrophoresis/bioanalyzer-systems/bioanalyzer-software/2100-expert-software-228259)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Caravaca, J. M., Mehta, M., Gowda, S. and Tran, B. (2022). ATAC Sequencing Protocol For Cryopreserved Mammalian Cells . Bio-protocol 12(2): e4294. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4294.
- Krishna, S., Lowery, F. J., Copeland, A. R., Bahadiroglu, E., Mukherjee, R., Jia, L., Anibal, J. T., Sachs, A., Adebola, S. O., Gurusamy, D., et al. (2020). Stem-like CD8 T cells mediate response of adoptive cell immunotherapy against human cancer. Science 370(6522): 1328-1334.
分类
分子生物学 > DNA > 染色质可接近性
癌症生物学 > 癌症生物化学 > 癌代谢
生物化学 > DNA
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link