- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Evaluating Human Natural Killer Cells Antibody-dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Using Plate-bound Anti-CD16 Antibodies
使用板结合抗 CD16 抗体评估人类自然杀伤细胞抗体依赖性细胞毒性 (ADCC)
发布: 2022年01月05日第12卷第1期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4285 浏览次数: 4574
评审: Gal HaimovichPorkodi PanneerselvamChris Tibbitt

相关实验方案

研究免疫调控血管功能的新实验方法:小鼠主动脉与T淋巴细胞或巨噬细胞的共培养
Taylor C. Kress [...] Eric J. Belin de Chantemèle
2025年09月05日 3543 阅读
外周血中细胞外囊泡的分离与分析方法:红细胞、内皮细胞及血小板来源的细胞外囊泡
Bhawani Yasassri Alvitigala [...] Lallindra Viranjan Gooneratne
2025年11月05日 1435 阅读
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that keep in check the health of neighboring cells through a large array of intrinsically expressed germline-coded receptors. Most importantly, CD16 is a low affinity Fc receptor for IgG that mediates the antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of NK cells, bridging the innate and adaptive immunities. There has been a significant interest in genetically engineering NK cells to enhance its ADCC, with the ultimate goal to produce off-the-shelf NK cell therapy products that can be combined with target-specific monoclonal antibodies to improve clinical outcomes. Previous protocols of ADCC assays use complex cell-based antigen-antibody models, which are both costly and time-consuming. This current protocol is devoid of target cells and uses plate-bound immobilized anti-CD16 antibodies as the trigger. It greatly shortens the experimental time, while faithfully evaluating NK cells ADCC.
Graphic abstract:
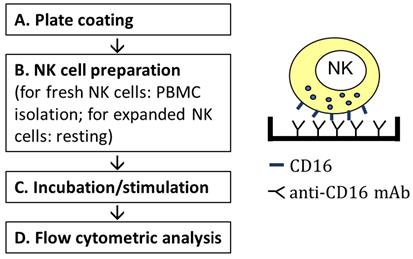
Workflow of stimulating NK cells via CD16 by plate-bound anti-CD16 mAb.
Background
Immunotherapies for cancer treatment are rapidly emerging, and many studies aim at increasing the safety and efficacy of anti-tumor immunotherapies. More research is being conducted on natural killer (NK) cells, as they have minimal risk of causing neurotoxicity in autologous settings (Gong et al., 2021), graft-versus-host disease in allogenic settings (Du et al., 2021), or cytokine release syndrome in general (Du et al., 2021). Other than being relatively safe in treatment, NK cells are effective in direct killing of target cells and regulating the immune system (Vivier et al., 2011).
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is an adaptive immune response largely mediated by NK cells through their CD16 (FCγRIII) receptor, which binds the Fc portion of IgG antibodies (Alderson and Sondel, 2011). However, this important aspect of NK cells remains underexplored. This can be ascribed to difficulties in establishing assay platforms. Previous protocols of ADCC assays use complex cell-based antigen-antibody models, such as the combination of SCC-4 cells and cetuximab (Kohrt et al., 2014), which is costly due to the low productivity of clinically relevant monoclonal antibodies, such as cetuximab. These target cell-based experiments also take a minimum of three days due to the need of culturing and maintaining target cells. The use of anti-CD16 antibody-opsonized P815 cells in reverse ADCC assays also evaluates NK cells ADCC (Euchner et al., 2021), but likewise requires time to culture and maintain the target cells.This current protocol is devoid of target cells, and uses plate-bound immobilized anti-CD16 antibodies as the trigger. Major steps include coating the plate with CD16 antibodies, preparing, and seeding the cells. It greatly shortens the experimental time to about 10 h, while faithfully evaluating NK cells ADCC. It can be used to quickly evaluate the ADCC aspect of any NK cell-based therapy product in vitro before subsequent in vivo testing, to facilitate the research and development (R&D) processes.
Materials and Reagents
1.5 mL Eppendorf (EP) tube (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022363204)
50 mL reagent reservoir (Corning, catalog number: CLS4870)
200 μL multi-channel pipette (Gilson, catalog number: FA10012)
Wide Mouthed Polypropylene Standard Spout Wash Bottle (SP SCIENCEWARE, catalog number: 46C798)
Paper towel (Skilcraft, catalog number: 5LA76)
Costar 96 well flat-bottom EIA plate (Bio-Rad, catalog number: 2240096)
12 × 75 mm FACS tube (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 342065)
DPBS, without calcium chloride and magnesium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8537)
RPMI medium 1640 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R8758-24X500ML)
Fetal bovine serum (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 16140089)
Penicillin-Streptomycin (Gibco, catalog number: 15-140-122)
L-glutamine (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 25030081)
Antibodies:
Ultra-LEAFTM Purified anti-human CD16 (Bioledgend, catalog number: 302050)
Anti-CD3-AF700 (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 557943)
Anti-CD14-APC/Cyanine7 (BioLegend, catalog number: 301820)
Anti-CD19-APC/Cyanine7 (BioLegend, catalog number: 302218)
Anti-CD56-PE/Cyanine7 (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: A51078)
Anti-CD107a-BV786 (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 563869)
Anti-IFN-gamma-APC (BioLegend, catalog number: 502512)
Anti-TNF-alpha-Pacific Blue (BioLegend, catalog number: 502920)
LIVE/DEADTM Fixable Far Red Dead Cell Stain Kit, for 633 or 635 nm excitation (Invitrogen, catalog number: L34973)
Brefeldin A Solution (1,000×) (BioLegend, catalog number: 420601)
BSA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 12133C)
Sodium Azide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71289)
Formaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F8775)
Saponin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 47036-250G-F)
R10 medium (see Recipes)
FACS Buffer (see Recipes)
Fixation buffer (see Recipes)
Perm buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
37°C 5% CO2 humidified incubator (Being Instrument)
Countess 3 Automated Cell Counter (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
LSR Fortessa flow cytometer (BD Biosciences)
Software
FlowJo Software (version 10.6.1)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2022 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Liu, W. (2022). Evaluating Human Natural Killer Cells Antibody-dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Using Plate-bound Anti-CD16 Antibodies. Bio-protocol 12(1): e4285. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4285.
分类
免疫学 > 免疫细胞功能 > 淋巴细胞
细胞生物学 > 基于细胞的分析方法 > 流式细胞术
细胞生物学 > 基于细胞的分析方法 > 炎症反应
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











