- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Isolation of Primary Leydig Cells from Murine Testis
从小鼠睾丸中分离出原发性睾丸间质细胞
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2021年11月20日第11卷第22期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4223 浏览次数: 3595
评审: Giusy TornilloAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
In males, Leydig cells are the primary source of testosterone, which is necessary for testis development, masculinization, and spermatogenesis. Leydig cells are a valuable cellular model for basic research; thus, it is important to develop an improved method for isolation and purification of Leydig cells from testes. The available methods for Leydig cell isolation have some drawbacks, including the need for sophisticated instruments, high cost, tediousness, and time consumption. Here, we describe an improved protocol for isolation of primary Leydig cells from testicular tissue by digestion with collagenase IV.
Keywords: Primary Leydig cell (原发性淋巴细胞)Background
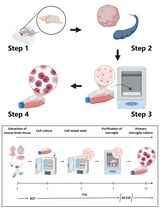
Leydig cells, located in the interstitial tissue of testis, are steroidogenic cells that contribute to testosterone synthesis and secretion. Leydig cell steroidogenesis is strictly regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) secreted by the pituitary gland. LH binds luteinizing hormone receptor (LHCGR) located on the surface of Leydig cells to activate adenylyl cyclase and increase the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). The cAMP signaling cascade stimulates the expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR), which transports cholesterol from cytoplasm into the inner membrane of mitochondria. Cholesterol is converted to pregnenolone by a P450 side-chain cleavage enzyme (CYP11A1) and translocated to the endoplasmic reticulum. Finally, pregnenolone is converted to testosterone by a series of lyase reactions. Male hypogonadism is characterized by testosterone deficiency and affects approximately 6% of males, with an increasing incidence and prevalence in recent years. However, the mechanisms of testosterone deficiency are far from clear. Immortalized cell lines provide useful tools to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying testosterone deficiency. Characterized Leydig cell lines, such as MA-10, BLTK1, and TM3 (Engeli et al., 2018), are unable to produce testosterone due to a lack or low expression of testosterone synthase genes. In contrast, the expression level of these genes in primary Leydig cells is closer to the cells in vivo. Furthermore, primary Leydig cells feature a complete signaling pathway of testosterone synthesis and are widely used to investigate late-onset hypogonadism (LOH) and diseases of the reproductive system. Additionally, Leydig cell and stem Leydig cell transplantation have been developed as alternative therapies for the treatment of testicular damage, LOH, and sexual dysfunction, achieving good curative effects (Artyukhin et al., 2007; Sun et al., 2009; Jiang et al., 2014). Therefore, procedures for isolation and enrichment of Leydig cells from testes are vital for establishing the role of Leydig cells in hypogonadism. In recent years, various approaches have been used to isolate Leydig cells, but gradient centrifugation is the most frequently used (Conn et al., 1977; Gale et al., 1982). Therefore, these methods are complicated, costly, time-consuming, and provide low yield. Here, we describe a cost-effective and time-saving protocol for isolating Leydig cells via digestion with collagenase VI.
Materials and Reagents
Sterile 50 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430829)
40 μm cell strainers (Falcon, catalog number: 352340)
Sterile 100 × 20 mm cell culture dish (Corning, catalog number: 430167)
0.22 μm filters (Millipo, catalog number: GNWP02500)
8-week-old healthy Kunming (KM) mice
DMEM basic (1×) (Gibco, catalog number: C11995500BT)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (ExCellBio, catalog number: FSD500)
Collagenase IV (Biosharp, catalog number: C-5138)
NaCl (Guangzhou Chemical Reagent Factory, catalog number:7647-14-5)
KCl (Guangzhou Chemical Reagent Factory, catalog number: 7447-40-7)
Na2HPO4·12H2O (Guangzhou Chemical Reagent Factory, catalog number: 7558-79-4)
KH2PO4 (Guangzhou Chemical Reagent Factory, catalog number: 7778-77-0)
Penicillin G Potassium Salt (MDBio, catalog number: W627099)
Streptomycin Sulfate (Diamond, catalog number: G821BA0034)
100% ethyl alcohol (Sinopharm, catalog number: 64-17-5)
Nitrotetrazolium Blue chloride (NTB) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N6876-50G)
DHEA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 252805-10MG)
DMSO(Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2650-100ML)
β-NAD (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N1511-250MG)
I125-testosterone Coat-A-Count RIA kits (Beijing North Institute of Biological Technology, catalog number: 201202)
Luteinizing Hormone (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 869003)
HSD3B antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-515120)
StAR antibody (CST, catalog number: D1Z2A)
SF-1 antibody (CST, catalog number: D10H12)
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488) (Abcam, catalog number: ab150077)
Goat Anti-Mouse IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 647) (Abcam, catalog number: ab150115)
Primary & secondary antibody diluent for immunostaining (Yeasen, catalog number: 36323ES60)
Paraformaldehyde (Shanghai Lingfeng, catalog number: 30525-89-4)
1× PBS (see Recipes)
D-PBS (see Recipes)
Penicillin/streptomycin solution (see Recipes)
0.75 mM KCl hypotonic buffer (see Recipes)
75% ethyl alcohol (see Recipes)
10 mg/ml Collagenase IV solution (see Recipes)
HSD3B staining solution (see Recipes)
Complete medium (see Recipes)
4% paraformaldehyde solution (see Recipes)
StAR antibody dilution solution (see Recipes)
HSD3B antibody dilution solution (see Recipes)
SF-1 antibody dilution solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
Surgical Instruments:
Scissors (Yuyan instruments, catalog number: Y15103)
4× forceps (Yuyan instruments, catalog number: Y15201)
Pointed forceps (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11252-00)
Low-speed centrifuge (Zonkia, model: SC-3610)
Biological safety cabinet (Heal Force, model: HFsafe-I200LC)
Water bath kettle (Jing Hong, model: XMTD-8222)
Cell incubator (Thermo Fisher, model: 371)
Fully automatic autoclave sterilizer (STIK, model: MJ-78A)
Inverted microscope (Nikon, model: TS100)
Electronic analytical balance (Sartorius, model: BSA124S-CW)
Gamma radioimmunoassay counter (Anhui ustc zonkia scientific, model:GC -1200γ)
Hemacytometer (Marienfeld, catalog number: 0650030)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Liang, J., Tang, Y., Li, H., Mei, J., Cao, Z., Xia, H., Huang, R., Yang, Y. and Huang, Y. (2021). Isolation of Primary Leydig Cells from Murine Testis. Bio-protocol 11(22): e4223. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4223.
分类
发育生物学 > 细胞生长和命运决定 > 再生
发育生物学 > 繁殖
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link