- EN - English
- CN - 中文
APEX-mediated Proximity Labeling of Proteins in Cells Targeted by Extracellular Vesicles
APEX 介导的细胞外囊泡靶向细胞中蛋白质的邻近标记
发布: 2021年11月05日第11卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4213 浏览次数: 5021
评审: Pavan VedulaFarah HaqueAnthony FlamierChao Wang
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are thought to mediate intercellular communication through the delivery of cargo proteins and RNA to target cells. The uptake of EVs is often followed visually using lipophilic-dyes or fluorescently-tagged proteins to label membrane constituents that are then internalized into recipient cells (Christianson et al., 2013; De Jong et al., 2019). However, these methods do not probe the exposure of EV cargo to intracellular compartments, such as the cytoplasm and nucleus, where protein or RNA molecules could elicit functional changes in recipient cells. In this protocol, we employ an EV cargo protein-APEX fusion to detect proximity interactions with recipient cell cytoplasmic/nuclear targets. This approach results in the biotinylation of proteins in close contact with the reporter fusion and thus permits profiling of biotinylated proteins affinity purified on immobilized streptavidin beads.
Graphic abstract:
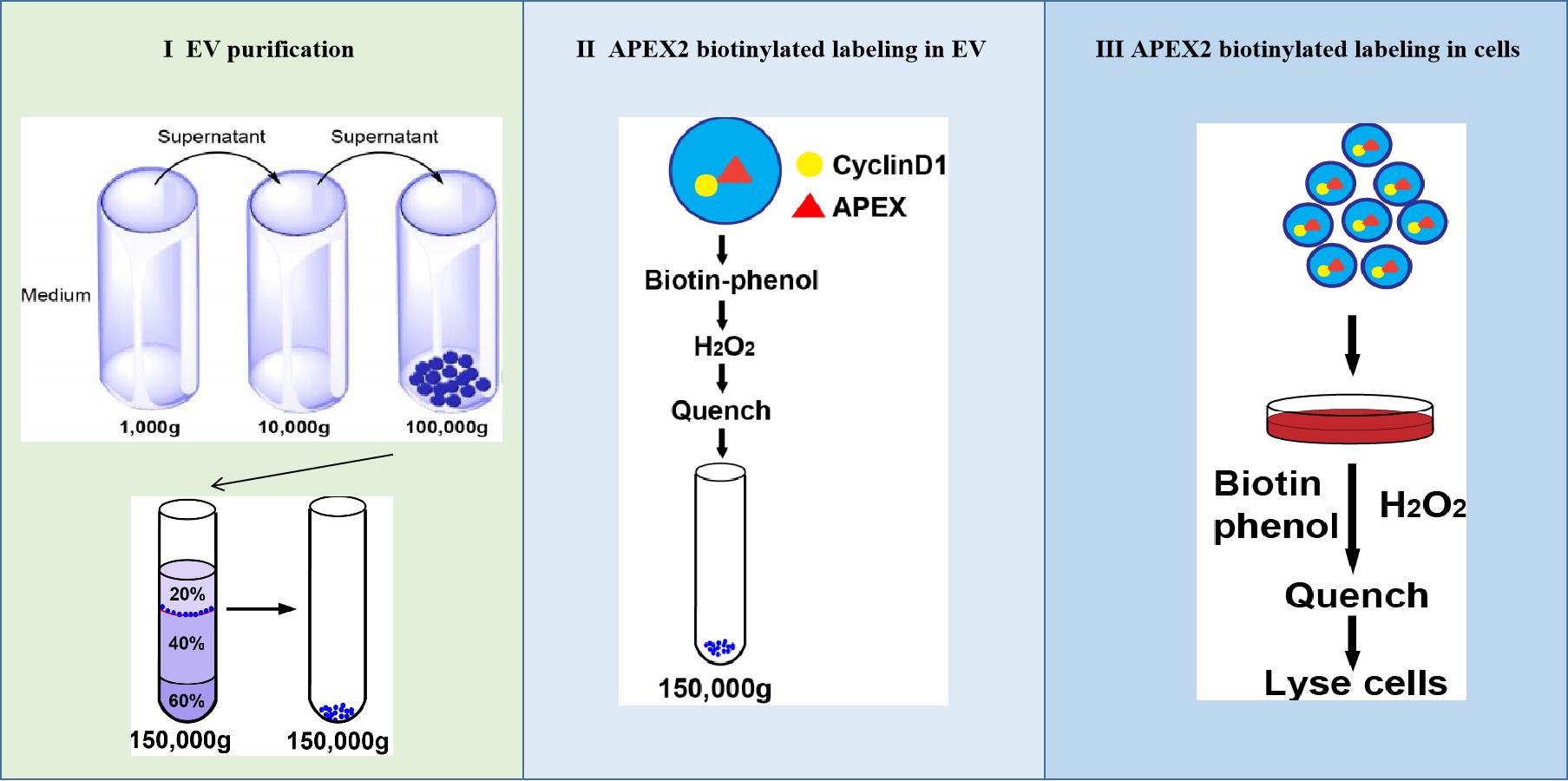
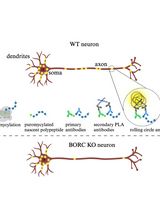
Schematic showing three steps of APEX-mediated proximity labeling of proteins in cells targeted by EVs.
Background
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are secreted by cells, circulate in body fluids, and ultimately generate functional changes through interaction with or uptake into recipient cells (Raposo and Stoorvogel, 2013). Protein, RNA, and possibly DNA are packaged by EVs and may be delivered into target cells to elicit changes in gene expression and cell behavior (Budnik et al., 2016; Van Niel et al., 2018; Shurtleff et al., 2016; Temoche-Diaz et al., 2019; Song et al., 2021). Most of the current methodologies used to visualize EV uptake, however, do not identify the molecular targets of molecules released into recipient cells. An approach to define such targets should be of broad utility.
APEX biotinylation labeling is a newly-developed technique that reveals the subcellular proteomes of many landmarks in the nucleus and cytoplasm (Chen and Perrimon, 2017). Using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as an electron donor, the enzyme APEX catalyzes the oxidation of the substrate biotin-phenol (BP) (Hung et al., 2016). The biotin-phenoxyl radical is a highly reactive, short-lived (<1 ms) species that conjugates to other proteins that are proximal to the APEX active site. Biotinylated protein products may then be isolated by streptavidin affinity purification and identified using conventional mass spectrometry (MS) techniques (Lobingier et al., 2017).
We used this approach to investigate the contacts made by the protein cyclinD1 when it is delivered to mouse embryonic cells (mESCs) from EVs produced by differentiating neural progenitor cells (Song et al., 2021). The use of a fusion of APEX to other EV cargo proteins should prove useful to identify molecular contacts within target cells.
Materials and Reagents
Syringe, 10 ml (BD, catalog number: 302995)
Syringe filter (0.45 µm; Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 44525-PP)
Falcon tube (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 08-771-23)
35 mm dishes (tissue culture dish) (Corning, catalog number: CLS430165)
10 cm dishes (tissue culture dish) (Corning, catalog number: CLS430167)
15 cm dishes (tissue culture dish) (Corning, catalog number: CLS430597)
Open-Top Thinwall Ultra-Clear Tube (38.5 ml), 25 × 89 mm (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 344058)
Note: On text "38.5 ml ultra-clear tube".
Open-Top Thinwall Ultra-Clear Tube (13.2 ml), 14 × 89 mm (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 344059)
Note: On text "13.2 ml ultra-clear tube".
Open-Top Thinwall Ultra-Clear Tube (5 ml), 13 × 51 mm (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 344057)
Note: On text "5 ml ultra-clear tube".
Transfer pipettes (Fisherbrand, catalog number: 13-711-7M)
293T cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3216)
N2A cells (ATCC, catalog number: CCL-131)
mESCs (R1, ATCC, catalog number: SCRC-1011)
Retinoic acid (RA) (Sigma, catalog number: R2625)
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (VWR, catalog number: 89510-194)
Exosome-depleted FBS (System Biosciences (SBI), catalog number: EXO-FBS-250A-1)
Puromycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8833-100MG)
pcDNA3 APEX-nes (Addgene, catalog number: 49386)
XPack CMV-XP-MCS-EF1α-Puro Cloning Lentivector (System Biosciences)
psPAX (Addgene, catalog number: 12260)
pMD2.G (Addgene, catalog number: 12259)
Lipofectamine 2000 (Life Technologies, catalog number: 11668019)
OPTI-MEM (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 31985062)
Sucrose (Fisher Chemical, catalog number: S5-3)
Biotin-phenol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: SML2135)
Protease inhibitor cocktail (100×) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8340)
Streptavidin-HRP (Thermo Fisher Scientific; catalog number: 21130)
H2O2 (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 34062)
Sodium ascorbate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7631)
Sodium azide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 26628-22-8)
Trolox (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 238813-5G)
Biotin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 29129)
DTT (Gold Biotechnology, catalog number: DTT25)
DPBS (Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline; Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 14190144)
Streptavidin-agarose beads (Sigma, catalog number: 16-126)
NovexTM WedgeWellTM 10% Tris-glycine mini gels, 10-well (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: XP10200BOX)
Ponceau S (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: XP00100PK2)
Coomassie G250 (Sigma, catalog number: 1.15444)
DMEM/F12 culture medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11320033)
DMEM culture medium (Life Technologies, catalog number: 10566-024)
Neurobasal culture medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 21103049)
B-27TM Supplement (50×) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 17504044)
N-2 Supplement (100×) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 17502048)
L-glutamine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25030081)
Non-essential amino acids (100×) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11140050)
β-mercaptoethanol (0.1 M) (Sigma, catalog number: M3148)
DMEM + 10% FBS (see Recipes)
RA (10 μM) + 1% exosome-depleted FBS in DMEM (see Recipes)
Buffer C (see Recipes)
Quencher solution (see Recipes)
4× Loading buffer (20 ml) (see Recipes)
N2B27 medium (1 L) (see Recipes)
RIPA (see Recipes)
Buffer D (see Recipes)
TBS-T (see Recipes)
Equipment
Sorvall RC 6+ centrifuge (Thermo Scientific, model: 46910)
Fixed angle rotor F14S-6X250y FiberLite (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 78500)
Ultracentrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Optima XE-90, catalog number: A94471)
Swinging-bucket rotor SW 32 Ti and bucket set (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 369694)
Swinging-bucket rotor SW 28 Ti and bucket set (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 342204)
Swinging-bucket rotor SW 55 Ti and bucket set (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 342194)
Swinging-bucket rotor SW 41 Ti and bucket set (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 331362)
ChemiDoc MP Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: ChemiDoc MP 10)
NanoSight NS300 instrument equipped with a 405-nm laser (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, United Kingdom)
Refractometer (Fisher Scientific)
Bath sonicator (Covaris, model: S220)
Software
Nanosight NTA 3.1 software (Malvern Instruments)
Excel (Microsoft, 2016)
GraphPad Prism 7
ImageLab software v4.0
PEAKS Studio X+
Vsn R package
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Song, L., Chen, J., Sun, A. and Schekman, R. (2021). APEX-mediated Proximity Labeling of Proteins in Cells Targeted by Extracellular Vesicles. Bio-protocol 11(21): e4213. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4213.
- Song, L., Tian, X. and Schekman, R. (2021). Extracellular vesicles from neuronal cells promote neural induction of mESCs through cyclinD1. J Cell Biol 220(9): e202101075.
分类
发育生物学 > 细胞生长和命运决定 > 分化
干细胞 > 胚胎干细胞 > 细胞分化
细胞生物学 > 细胞工程
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link