- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Direct-TRI: High-throughput RNA-extracting Method for all Stages of Zebrafish Development
Direct-TRI: 斑马鱼发育各阶段高通量RNA提取方法
发布: 2021年09月05日第11卷第17期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4136 浏览次数: 4719
评审: Pilar Villacampa AlcubierreMikiko NagashimaGülçin ÇAKAN AKDOĞAN
Abstract
Recent popularization of next-generation sequencing enables conducting easy transcriptome analysis. Nevertheless, substantial RNA isolation work prior to RNA sequencing, as well as the high cost involved, still makes the routine use of large-scale transcriptome analysis difficult. For example, conventional phenol-chloroform RNA extraction cannot be easily applied to hundreds of samples. Therefore, we developed Direct-TRI, a new cost-effective and high throughput RNA-extraction method that uses a commercial guanidine-phenol-based RNA extraction reagent and a 96-well silica column plate. We applied Direct-TRI to zebrafish whole larvae and juvenile samples and obtained comparable RNA qualities by several different homogenization methods such as vortexing, manual homogenizing, and freezing/crushing. Direct-TRI enabled the extraction of 192 RNA samples in an hour with a cost of less than a dollar per sample. Direct-TRI is useful for large-scale transcriptome studies, manipulating hundreds of zebrafish individuals, and may be used with other animal samples.
Keywords: Zebrafish (斑马鱼)Background
RNA-sequencing (RNA-Seq) is one of the standard methods in various fields of biology (Cheng et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2021) because it provides comprehensive information about gene expression. Recently, several researchers have developed cost-effective and high-throughput RNA-Seq library preparation protocols such as Lasy-Seq (Kamitani et al., 2019), BRB-Seq (Alpern et al., 2019), and Decode-Seq (Li et al., 2020). Although these techniques and the lower cost of massive parallel sequencing have enabled large-scale RNA-Seq analyses (Hoang et al., 2020; Miller et al., 2013), the RNA extraction process prior to RNA-Seq remains laborious and time-consuming. For example, a conventional RNA extraction method using phenol-chloroform (Peterson et al., 2009) requires careful liquid handling and a number of steps. Another method using silica columns, the RNeasy of Qiagen, provides easy and time-saving operation but is costly. In addition, the lysis solutions included in the kit do not contain phenol and, thus, are less effective in disrupting cells and tissues than phenol-containing lysis solutions. Recently, a new easy and time-saving method, Direct-zol (Sosanya et al., 2013), has been developed by combining these two methods. In the Direct-zol protocol, samples are lysed in phenol-containing solution and subsequently subjected to silica column-based RNA purification. However, the kit is costly (approximately 7 dollars per sample) for a large number of samples. From the viewpoint of high throughput, low cost, and robustness, the aforementioned methods are not feasible for large-scale sampling. Here, we introduce Direct-TRI, a high-throughput, cost-effective, and reliable RNA-extraction method using TRI Reagent-LS and 96-well silica column plate. This protocol consists of two steps: homogenization of samples in phenol-containing TRI Reagent-LS followed by the direct isolation of RNA from the phenol lysate with handmade washing solutions. Direct-TRI makes it possible to simultaneously process hundreds of RNA samples individually with a simple procedure and at an affordable cost. We show an example of a Direct-TRI application using whole zebrafish samples. Zebrafish is a model organism to study development, behavior, and disease in vertebrates (Goldsmith et al., 2012; Gore et al., 2018; Maeta et al., 2020). The large-scale gene expression analysis of zebrafish is a powerful tool for investigating the molecular basis underlying developmental events and diseases (Lee et al., 2020; Scholz, 2013). The combination of Direct-TRI and the cost-effective and high throughput RNA-Seq library preparation methods will make large-scale transcriptome analysis more useful not only for zebrafish samples but also for other organisms.
Materials and Reagents
1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube (Rikaken, catalog number: RSV-MTT1.5)
Transfer pipet, 3 ml (Falcon, catalog number: 357575)
8-strip tube, dome type (Rikaken, catalog number: RS-PCR-8D)
Cell culture dish, 100 mm (Nippon Genetics, catalog number: FG-2090)
Cell culture dish, 35 mm (Nippon Genetics, catalog number: TR4000)
Gemma Micro ZF 75 (Skretting)
Otohime B2 (Marubeni Nisshin Feed)
Kimwipe (Kimberly Clark)
AcroPrep Advance 96-well Long Tip Filter Plate for Nucleic Acid Binding (Pall, catalog number: 8133)
A reservoir for AcroPrep Advance (Merck, catalog number: BR701340-50EA)
Eppendorf twin.tec 96 well LoBind PCR plates (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030129512)
DuraCross zebrafish breeding tank with divider (Laboratory Product Sales, catalog number: T233795)
Zebraifsh (Danio rerio)
TRI Reagent-LS (Molecular Research Center, catalog number: TS120)
Notes:
TRIzol-LS Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10296028) or ISOGEN-LS (Nippon Gene, catalog number: 311-02621) can also be used.
Sepasol-RNA II Super (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 30487-46), an equivalent product, could not be used for RNA extraction from adult zebrafish because a precipitate was produced during the freezing and crushing processes.
Ethanol, 99.5% (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 08948-25)
Nuclease-free water (Merck, catalog number: H20MB1006)
BioMasher II (Nippi, catalog number: 320102; Figure 1)
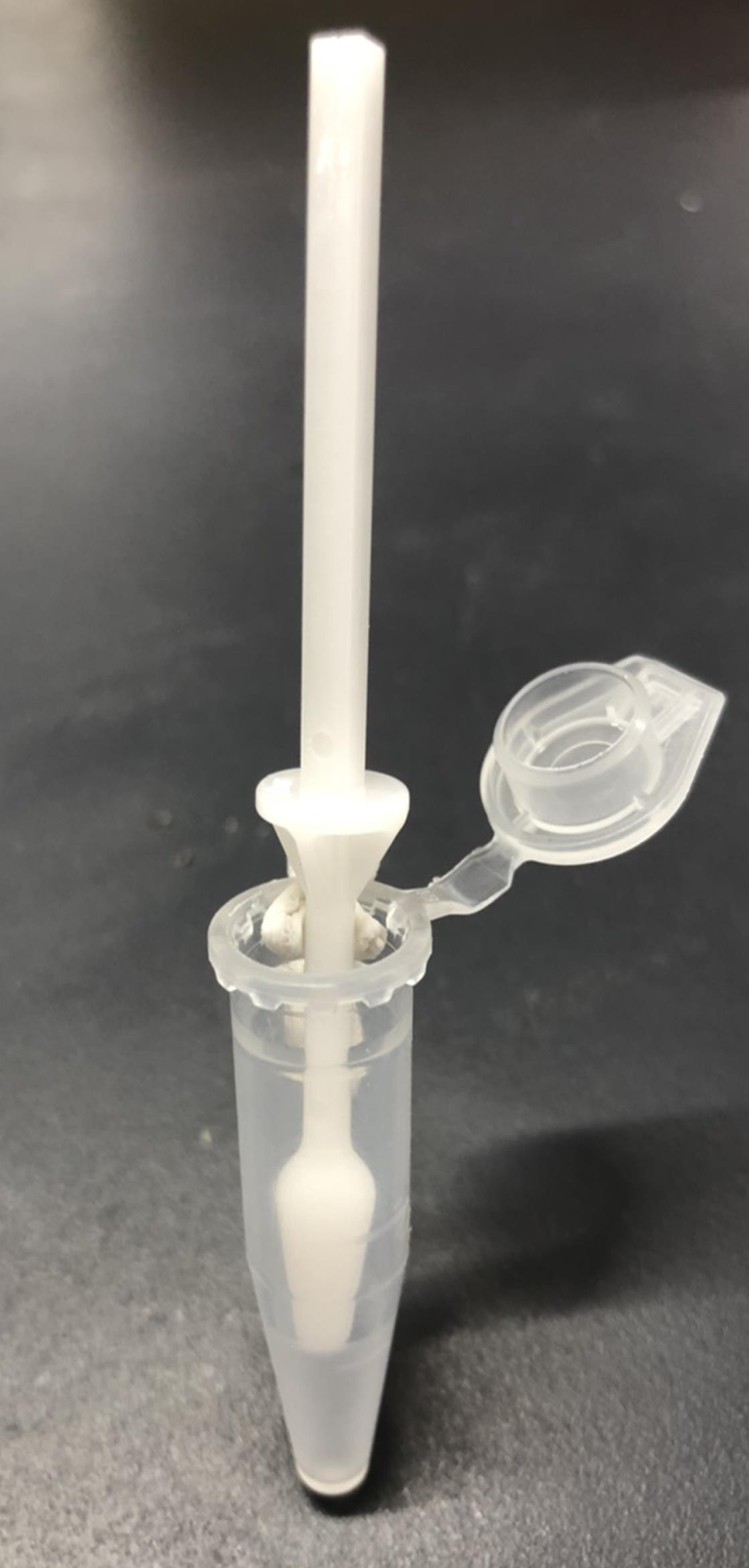

Figure 1. Image of BioMasher IILiquid nitrogen
Pronase (Merck, catalog number: 53702)
QuantiFluor RNA System (Promega, catalog number: E3310)
Agilent RNA 6000 Pico kit (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5067-1513)
10× Loading Buffer (Takara Bio, catalog number: 9157)
ExcelBand 1 KB (0.25-10 kb) DNA Ladder (Smobio, catalog number: DM3100)
Tricaine (Wako, catalog number: 051-06571)
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Rikaken, catalog number: RSP-THA500G)
Boric acid (Wako, catalog number: 021-02195)
EDTA-2Na (Wako, catalog number: 343-01861)
Agarose Powder (Rikaken, catalog number: RSV-AGRP-500G)
10 mg/ml Ethidium bromide (Nippon Gene, catalog number: 315-90051)
Ethanol, 80% (see Recipes)
1% agarose gel (see Recipes)
Tricaine (see Recipes)
E3 medium (see Recipes)
20 mg/ml Pronase (see Recipes)
5× TBE (see Recipes)
Equipment
Mortar and pestle, 120 mm (AsOne, catalog number: 6-549-03)
Vortex-Genie 2 (Scientific Industries)
PlateSpin II (Kubota)
Quantus Fluorometer (Promega, catalog number: E6150)
Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer System (Agilent, catalog number: G2939B)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Ujibe, K., Nishimura, K., Kashima, M. and Hirata, H. (2021). Direct-TRI: High-throughput RNA-extracting Method for all Stages of Zebrafish Development. Bio-protocol 11(17): e4136. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4136.
分类
分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 提取
发育生物学 > 形态建成 > 变态发育
发育生物学 > 细胞生长和命运决定 > 分化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link