- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Optical Clearing and 3D Analysis Optimized for Mouse and Human Pancreata
小鼠和人胰腺的光学清除和三维分析优化
发布: 2021年08月05日第11卷第15期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4103 浏览次数: 5631
评审: Gal HaimovichSarajo MohantaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The pancreas is a heavily innervated organ, but pancreatic innervation can be challenging to comprehensively assess using conventional histological methods. However, recent advances in whole-mount tissue clearing and 3D rendering techniques have allowed detailed reconstructions of pancreatic innervation. Optical clearing is used to enhance tissue transparency and reduce light scattering, thus eliminating the need to section the tissue. Here, we describe a modified version of the optical tissue clearing protocol iDISCO+ (immunolabeling-enabled three-dimensional imaging of solvent-cleared organs) optimized for pancreatic innervation and endocrine markers. The protocol takes 13-19 days, depending on tissue size. In addition, we include protocols for imaging using light sheet and confocal microscopes and for 3D segmentation of pancreatic innervation and endocrine cells using Imaris.
Keywords: Pancreas (胰腺)Background
The pancreas and islets of Langerhans are heavily innervated by the autonomic nervous system and sensory nerves (Ahren, 2000; Rodriguez-Diaz et al., 2011; Rodriguez-Diaz and Caicedo, 2014). The autonomic nervous system consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is activated by decreased blood glucose and is essential in initiating the counter-regulatory responses to hypoglycemia (Ahren and Holst, 2001). The parasympathetic nervous system mediates the cephalic phase insulin secretion and is activated in response to feeding (Louis-Sylvestre, 1978; Strubbe and Steffens, 1993; Teff and Townsend, 1999). The roles of sensory innervation in pancreatic function remain poorly understood, but sensory islet innervation is implicated in hormone release and glucose homeostasis (Ahren, 2000). Parasympathetic intrapancreatic ganglia, consisting of aggregates of neuronal cell bodies, are scattered throughout the pancreas and act as neuronal networks that integrate intrinsic and external nerve inputs to modulate pancreatic functions (Li et al., 2019). Metabolic pathologies, including type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D), remodel the pancreatic environment in mice and humans, including islet morphology and endocrine and exocrine innervation (Giannulis et al., 2014; Mundinger et al., 2016; Lundberg et al., 2017; Butterworth et al., 2018; Alvarsson et al., 2020). However, the mechanisms behind the remodeling of pancreatic innervation in diabetes, and the functional consequences, remain poorly understood.
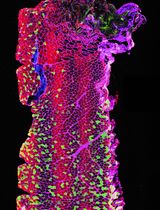
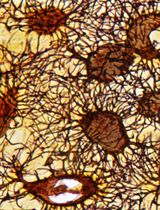
The pancreas is a highly heterogeneous organ, which in the mouse macroscopically consists of three diffuse lobes: the duodenal, splenic, and gastric lobes, separated by adipose, lymphatic, and connective tissue (Dolenšek et al., 2015). Pancreatic innervation is difficult to comprehensively assess using conventional histological methods due to its filamentous structure and the long-range projections of pancreatic nerves (Fasanella et al., 2007). Therefore, there is a need for 3-dimensional high-resolution organ-wide pancreatic imaging techniques. Recent advances in optical clearing techniques, including immunolabeling-enabled three-dimensional imaging of solvent-cleared organs (iDISCO+) (Renier et al., 2016), allow the visualization of intact organs, including dispersed neuronal networks, in 3D (Video 1). The purpose of optical clearing is to render tissue transparent by reducing light scattering and absorption and by equilibrating its refractory index with that of an imaging medium, thus allowing full penetration of light during imaging and eliminating the need to section the tissue. This approach readily allows detailed analyses of tissue architecture, spatial relationships between structures, and regional differences in three dimensions. This provides an ideal approach to study the architecture of innervation across the pancreas. Here, we describe a modified version of iDISCO+ optimized for pancreatic innervation (Alvarsson et al., 2020), which takes 13-19 days to complete depending on sample size (Figure 1). We also describe basic protocols for imaging optically cleared pancreata using light sheet microscopy and confocal microscopy and protocols for the segmentation of 3-dimensional pancreatic structures.

Figure 1. Flowchart of the protocol
Materials and Reagents
Materials
5-ml Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030119401)
2-ml Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022363352)
1.5-ml Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022364111)
0.5-ml Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022363611)
Glass-bottomed μ-slides (Ibidi, catalog number: 80827)
Glass-bottomed μ-dishes (Ibidi, catalog number: 81158)
Neoprene gloves (Ansell, catalog number: 25-101)
Polystyrene Petri dishes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5731)
Reagents
16% paraformaldehyde (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: 15710-S)
Heparin sodium salt from porcine intestinal mucosa (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3393)
Dichloromethane (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 270997)
Dibenzyl ether (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 108014)
Dimethyl sulfoxide (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: D128-500)
Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787)
Glycine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7126)
Double distilled H2O
Tween-20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416)
Sodium azide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 58032)
Hydrogen peroxide solution (30%) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 216763)
Normal donkey serum (Jackson ImmunoResearch, catalog number: 017-000-121)
Methanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 322415-2L)
Agarose (Invitrogen, catalog number: 16520-050)
PBS (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP2944100)
Forane (Isoflurane, USP) (Baxter, Deerfield, IL, USA)
4% PFA buffer (see Recipes)
10% Sodium azide (NaN3) stock (see Recipes)
Modified PTxwH (see Recipes)
Permeabilization buffer (see Recipes)
Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
Fine tweezers (Dumont tweezers, WPI, catalog numbers: 14098 [#5]; 500234 [#5B])
Iris scissor (WPI, catalog number: 501758)
Blunt tweezers (e.g., Dressing Forceps 12.5 cm; WPI, catalog number: 501217)
Single edge razor blade or scalpel (e.g., Single edge razor blade #12, Titan, Seattle, WA, USA; Disposable scalpel #20, WPI, catalog number: 500352)
Cyanoacrylate glue (e.g., Gorilla super glue, Loctite super glue, Starbond EM-02, Krazy glue all purpose)
Absorbent pads (e.g., Medline, catalog number: DDPAD1724Z)
Peristaltic pump (Gilson, catalog number: F155005)
Dissection microscope (United Scope LLC, model: SM-2T-6WB-V331)
Nutating shaker (Benchmark Scientific, model: B3D5000)
Incubator (37°C, no CO2 required) with space for a shaker or rotary mixer inside, or with a built-in shaker/mixer
Centrifuge (no refrigeration required) (Labnet International, model: C2400)
Standard household microwave (e.g., Westinghouse, model: WCM660W)
Light sheet microscope (Ultramicroscope II, LaVision Biotec, Bielefeld, Germany, or similar instrument)
Confocal microscope (Inverted Zeiss LSM, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany, or similar instrument equipped with standard 10× objective, red and far-red filters)
Image analysis computer (Suggested specifications: Motherboard: Gigabyte X299 Designare EX; CPU: Intel Core i7 7800X 3.5GHz Six Core 8.25MB 140W; RAM: 32GB; Video Card: Nvidia Quadro P4000 8GB; Hard drive: 512GB SSD plus 1TB SSD; Power supply: 850W; Cooling: Noctua NH-U12DX i4 CPU Cooling and Arctic MX-2 thermal compound paste; Operating system: Windows 10 64-bit)
Software
Image analysis software for 3D segmenting (e.g., Imaris, Bitplane, Zürich, Switzerland)
Spreadsheet software (e.g., Excel, Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA)
Data analysis software (e.g., GraphPad Prism, GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Alvarsson, A., Jimenez-Gonzalez, M., Li, R., Rosselot, C., Tzavaras, N., Wu, Z. and Stanley, S. A. (2021). Optical Clearing and 3D Analysis Optimized for Mouse and Human Pancreata. Bio-protocol 11(15): e4103. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4103.
- Alvarsson, A., Jimenez-Gonzalez, M., Li, R., Rosselot, C., Tzavaras, N., Wu, Z., Stewart, A. F., Garcia-Ocana, A. and Stanley, S. A. (2020). A 3D atlas of the dynamic and regional variation of pancreatic innervation in diabetes. Sci Adv 6(41): eaaz9124.
分类
神经科学 > 周围神经系统
神经科学 > 神经解剖学和神经环路 > 荧光成像
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 组织成像
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link