- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Isolation of First-Trimester and Full-term Human Placental Hofbauer Cells
妊娠早期和足月人胎盘霍夫鲍尔细胞的分离
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2021年06月05日第11卷第11期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4044 浏览次数: 4653
评审: Luis Alberto Sánchez VargasWilliam C. W. ChenAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The placenta is the crucial organ that regulates the health of both mother and fetus during pregnancy. The human placenta is composed of villous tree-like structures that embed into the maternal decidua. Within the stroma of the villi resides a population of fetally-derived macrophages, the Hofbauer cells (HBC). HBC are the only fetal immune cells found within the placenta in the steady-state and are thought to play a crucial role in placental function. From the 10th week of gestation, maternal blood flow into the intervillous space begins, resulting in the placental villi becoming bathed in maternal blood. To study HBC it is necessary to develop techniques that allow for their specific isolation and distinction from maternal blood monocytes and decidual macrophages. Here, we describe a protocol that explains step-by-step the strategy we have developed that allows the specific isolation of HBC.
Keywords: Placenta (胎座)Background
The human placenta is a highly specialized organ that is crucial for both maternal and fetal health during pregnancy. It is made up of highly branched villous tree-like structures that are bathed in maternal blood from approximately the 10th week of gestation (Jauniaux et al., 2000). Anchoring villi attach the placenta to the endometrium, which is transformed during placentation into the decidua. A population of fetal tissue-resident macrophages, the Hofbauer cells (HBC), are abundant within the stroma of placental villi. Early studies determined that these cells are of fetal origin based on Y-chromosome detection in pregnancies with male fetuses (Kim et al., 2008). HBC are the only immune cell population on the fetal side of the placental barrier in the steady-state (Thomas et al., 2021). Accordingly, they are thought to have important roles in the regulation of placental growth and homeostasis and to act as immune sentinels, protecting the fetus from infection in utero. However, compared to other adult tissue-resident macrophages, HBC remain poorly understood. A range of protocols has been used to isolate HBC, as excellently reviewed elsewhere (Tang et al., 2011). However, a standard technique has not been established across the field. Many of the protocols used are suboptimal for the isolation of tissue macrophages. For example, unnecessarily long digestion times (sometimes up to 3 h) and the failure to use DNase I greatly affect HBC viability. Furthermore, HBC are typically isolated as total CD14+ cells from placental tissue for phenotypic and functional analysis. However, we have previously shown that maternal cells can comprise up to 30% of CD14+ cells isolated from first-trimester placental digests (Thomas et al., 2021). By adding common HLA allotype antibodies to our flow cytometry panel, we can distinguish maternal from fetal cells and ensure the isolation of a pure population of HBC. Therefore, in all future research of HBC using in vitro assays, additional steps that are described here should be performed to ensure that true fetally-derived HBC are studied with optimal viability.
In this article, we provide step-by-step protocols to isolate HBC from first-trimester and full-term human placental tissue with high purity. Procedures B and C describe how to obtain single-cell suspensions from first-trimester and full-term placental tissue, respectively. Procedure D describes how to obtain HBC from placental digests with high purity by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Following these protocols allows investigating HBC properties with downstream in vitro assays to understand their functional properties further. A scheme of the overall procedure of HBC isolation from first-trimester and full-term placenta is shown in Figure 1.
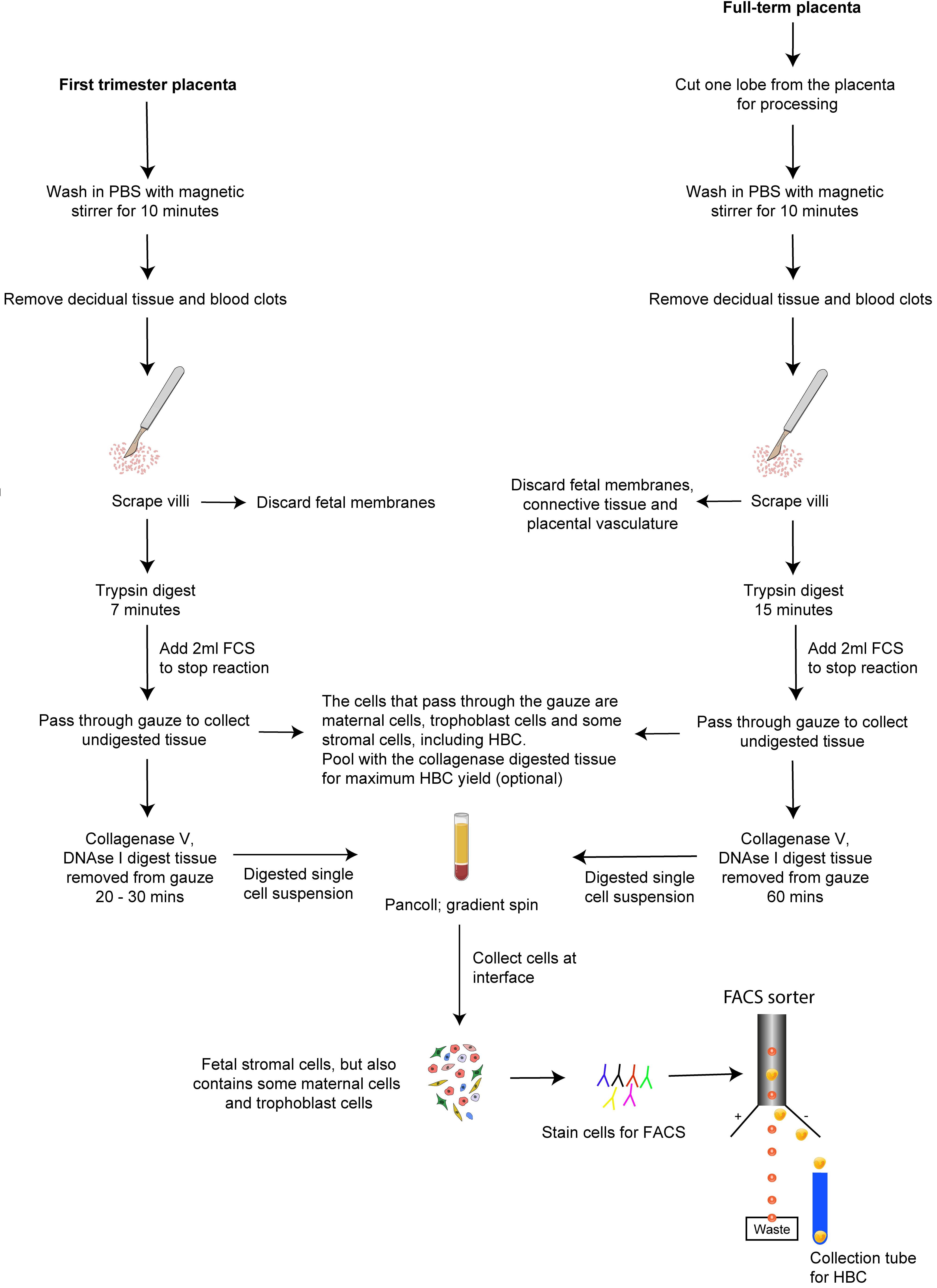
Figure 1. Isolation of HBC from human placenta. A schematic outlining the procedure for isolating HBC from first-trimester and full-term placenta.
Materials and Reagents
Disposable scalpels, No. 22 (Swann Morton, catalog number: 508)
Pasteur pipette (ELKay, catalog number: 127-P503-STR)
Muslin gauze (Winware food grade, catalog number: E948)
Cell strainers 30 µm (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-041-407)
Cell strainers 70 µm (BD Falcon, catalog number: 352350)
Cell strainers 100 µm (BD Falcon, catalog number: 352360)
Cell strainers 400 µm (Pluriselect, catalog number: 43-50400-50)
Petri dishes 140 mm (Sterilin, catalog number: SC269)
Falcon 50 ml round bottom polypropylene test tubes (Corning, catalog number: 352070)
Polypropylene round-bottom FACS tubes 5 ml (Falcon, catalog number: 352063)
Dissection forceps (Scientific Laboratory Supplies, catalog number: SR04010)
Surgical straight scissors (SAMCO, catalog number: E101/01)
250-ml glass Duran bottles (Scientific Laboratory Supplies, catalog number: F151164 )
Funnel (Scientific Laboratory Supplies, catalog number: FUN1260)
Collagenase type V (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C9263)
DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8417)
DNase I (Roche, catalog number: 10104159001)
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E9884)
Fetal calf serum (heat inactivated) (Biosera, catalog number: FB -1001)
Flow cytometry antibodies (see Table 1)
Table 1. Flow cytometric antibodies
Antibody Company Dilution Antibody CD3 FITC, clone: UCHT1 Biolegend, catalog number: 300406 1:100 Antibody CD14 PE-Dazzle 594, clone: HCD14 Biolegend, catalog number: 325634 1:100 Antibody CD19 FITC, clone: SJ25C1 Biolegend, catalog number: 363008 1:100 Antibody CD20 FITC, clone: 2H7 Biolegend, catalog number: 302304 1:100 Antibody CD45 PerCp-Cy5.5, clone: 2D1 Biolegend, catalog number: 368503 1:40 Antibody CD66b FITC, clone: G10F5 Biolegend, catalog number: 305103 1:100 Antibody CD335 FITC, clone: 9E2 Biolegend, catalog number: 331921 1:100 Antibody FOLR2 APC, clone: 94b/FOLR2 Biolegend, catalog number: 391705 1:1,000 Antibody HLA-A2 APC-Cy7, clone: BB7.2 Biolegend, catalog number: 343310 1:50 Antibody HLA-A3 BV650, clone: GAP.A3 BD Biosciences, catalog number: 747774 1:100 Antibody HLA-B7 PE, clone: BB7.1 Biolegend, catalog number: 372404 1:100 Pancoll (density 1.077 mg/ml) (Pan Biotech, catalog number: P04-601000)
Penicillin/streptomycin solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0781)
RPMI-1640 Medium (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R7388)
Trypsin-250 (Pan Biotech, catalog number: P10-025100P)
Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D9434)
NaCl (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 151944)
KCl (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 194738)
Disodium hydrogen orthophosphate (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S/4520/53)
Potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P/4800/53)
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) 1× concentration
Human serum (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H4522)
Mouse serum (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5905)
Rat serum (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R9759)
Brilliant stain buffer (BD Horizon, catalog number: 563794)
Trypsin/EDTA, 0.2% solution (see Recipes)
The RF10 medium (see Recipes)
The FACS buffer (see Recipes)
Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
BD FACSAriaTM III Cell Sorter (or similar), 4-laser cell sorter for containment level 2 samples fitted with a 100 µm nozzle (BD Biosciences, model: FACSAriaTM III)
Temperature controlled centrifuge with lids for buckets (Eppendorf Centrifuge 5810R, catalog number: F151380)
Hot plate magnetic stirrer (DLAB, catalog number: DL2255-380H)
Waterbath (VWR, catalog number: 462-0557)
Haemocytometer (VWR, catalog number: BR718605)
Light microscope (Leica, catalog number: 11964479)
Software
BD FACSDivaTM software
A collection of tools for flow cytometer and application setup, data acquisition, and analysis. It runs on the Microsoft® Windows 10 64-bit operating system.
FlowJoTM (Becton, Dickinson, and Company; 2019) software
A package for analyzing flow cytometry data. Files produced by modern flow cytometers are written in the Flow Cytometry Standard format with a .fcs file extension. FlowJo will import and analyze cytometry data regardless of which flow cytometer is used to collect the data. It is available for both Mac and PC.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Appios, A., Thomas, J. R. and McGovern, N. (2021). Isolation of First-Trimester and Full-term Human Placental Hofbauer Cells. Bio-protocol 11(11): e4044. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4044.
分类
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离
发育生物学 > 细胞生长和命运决定 > 增殖
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link