- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Radioactive-free Kinase Inhibitor Discovery Assay Against the Trypanosoma brucei Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 short (TbGSK-3s)
一种无放射性布氏锥虫糖原合成酶激酶-3抑制剂探究实验
发布: 2020年01月20日第10卷第2期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3493 浏览次数: 4573
评审: Alexandros AlexandratosYing FengOmar Akil
Abstract
The identification of small molecules possessing inhibitory activity in vitro, against a given target kinase, is the first step in the drug discovery process. Herein, we describe a non radioactive protocol using luciferase-based ATP assay for the identification of inhibitors for the short isoform of the Trypanosoma brucei’s Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (TbGSK-3s). TbGSK-3s represents a potential drug target as it is essential for parasite survival. Small molecules used in our study are indirubin analogues possessing substitutions in different positions in the bis-indole backbone. Presently, the standard laboratory practice for the kinase assays is the incorporation of radiolabeled phosphate from [gamma-32P]ATP as the efforts for developing non-radioactive assays (ELISA-based assays, fluorescence quenching assays, etc.) exhibit limitations such as lack in sensitivity or limitations for broad applications. This protocol can be a useful starting point for lead discovery, as it surpasses the drawbacks of radioactive kinase assays and it allows for relatively sensitive measurements of kinase inhibition for TbGSK-3s.
Keywords: Kinase assay (激酶分析)Background
Kinases are enzymes that play a crucial role in biological processes including differentiation, cell proliferation and apoptosis, by putting in motion signaling pathways upon catalyzing the transfer of the γ-phosphate from ATP to substrate (Jia et al., 2008; Efstathiou et al., 2019). Deregulation of kinases can frequently lead to a variety of diseases (Ways and Sheetz, 2000; Cohen and Goedert, 2004; Mazitschek and Giannis, 2004; Resnick and Fennell, 2004) and therefore, they are considered one of the largest classes of drug targets (Cohen 1999; Manning et al., 2002). The first step of the lead kinase inhibitor discovery is the establishment of an in vitro kinase assay. The radioactive assays are the standard laboratory practice due to their high sensitivity (Jia et al., 2008; Lilienthal et al., 2010). However, drawbacks of kinase-based radioactivity assays include the need of special handling and the restriction in flexibility because of the short half-life of 32P. To resolve these limitations, new non-radioactive technologies have been created that are based on fluorescence or luminescence (Jia et al., 2008). Herein, we describe a non radioactive protocol using luciferase-based ATP assay, for the identification of inhibitors for the short isoform of the Trypanosoma brucei’s Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (TbGSK-3s). In the bloodstream form of T. brucei, TbGSK-3s is essential for survival (Ojo et al., 2008) and therefore it is a molecular target for the discovery of new anti-trypanosomal agents (Ojo et al., 2008; Oduor et al., 2011; Woodland et al., 2013; Urich et al., 2014; Swinney et al., 2016). Mammalian GSK-3 has been related to a wide range of diseases and thus small molecular weight GSK-3 inhibitors has been developed (Woodland et al., 2013; Gaboriaud-Kola et al., 2015; Masch and Kunick, 2015). Amongst GSK-3 inhibitors, there are the indirubins, a family of natural bis-indole derivatives (Hoessel et al., 1999, Polychronopoulos et al., 2004, Vougogiannopoulou et al., 2008, Myrianthopoulos et al., 2013). In this protocol, a luminescent kinase assay based on the Kinase-Glo® reagent of Promega, is described. This method is straightforward, radioactive-free, fast and it doesn’t lack sensitivity. While the protocol described below is specific for the recombinant TbGSK-3s expressed in baculovirus system as described before (Efstathiou et al., 2019), it can be applicable to any kinase with the appropriate alterations for the specific kinase (substrate, ATP concentration, buffer, etc.).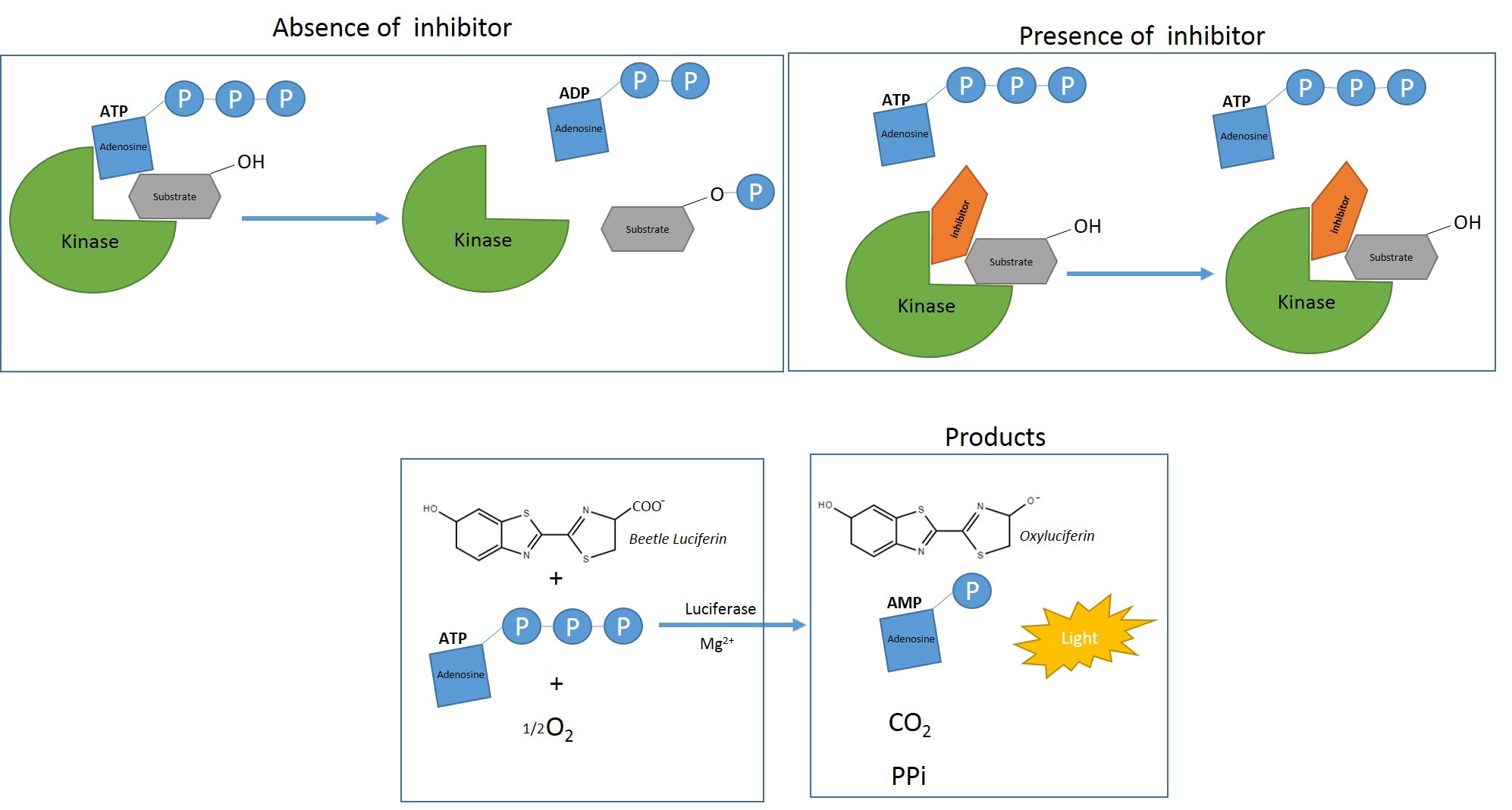
Figure 1. Scheme for the luminescent kinase assay based on the Kinase-Glo® reagent. The kinase reaction is conducted under the appropriate conditions with or without inhibitors. The remaining ATP at the time that the reagent is added, is used as a substrate by the Kinase-Glo® Luciferase to catalyze the mono-oxygenation of luciferin. The luciferase reaction produces one photon of light per turnover. Luminescence is inversely related to kinase activity (Promega).
Materials and Reagents
Materials
- Pipettes tips: 0.5-10 μl, 10-200 μl, 200-1,000 μl (Greiner Bio-One, catalog numbers: 771291, 739290, 740290)
- Eppendorf tubes (Greiner Bio-One, catalog number: 616201)
- Amicon® Ultra-4 centrifugal filters
Reagents
- GSK-3 peptide substrate YRRAAVPPSPSLSRHSSPHQ(pS)EDEEE (HQ), 1 mg (Biaffin GmbH & Co KG, proteinkinase.de, catalog number: PEP-GSK-001, storage temperature: -20 °C)
- Kinase-Glo® Luminescent Kinase Assay, 10 ml (Promega, catalog number: V6711, storage temperature: -20 °C)
- Kinase Glo® Substrate, 1 vial (lyophilized) (Promega, catalog number: V378A)
- Kinase Glo® Buffer, 10 ml (Promega, catalog number: V379A)
- Adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) disodium salt hydrate, 1 mg (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: FLAAS, storage temperature: -20 °C)
- TbGSK-3s expressed in a baculovirus expression system as previously described (Efstathiou et al., 2019) (storage temperature: immediate usage after expression or glycerol stock at -80 °C)
Notes:- TbGSK-3s is not available commercially. In order to use it, it must be expressed in the laboratory following the protocols described in bibliography (Efstathiou et al., 2019). Briefly, as mentioned in Efstathiou et al., 2019, the pTriEx-1.1-TbGSK3s plasmid was cotranfected with the BaculoGold DNA into Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) insect cells and upon production of the TbGSK3s, the kinase was purified on Ni2+-nitrilotriacetate (Ni-NTA) resin according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen).
- Kinase fractions should be used immediately to ensure maximum activity. If they are stored as glycerol stocks at -80 °C, they should be used up to 3-5 days upon isolation to avoid complete loss of the kinase activity.
- 32 indirubin analogs that were synthesized as previously described (Meijer et al., 2003; Polychronopoulos et al., 2004; Ferandin et al., 2006; Vougogiannopoulou et al., 2008), (storage temperature: 4 °C, away from sunlight)
- MOPS (3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid) (Applichem, catalog number: A2947, storage temperature: RT)
- MgCl2 (Magnesium chloride hexahydrate) (Applichem, catalog number: A1036, storage temperature: RT)
- EGTA (Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E4378, storage temperature: RT)
- PierceTM DTT (Dithiothreitol) (ThermoFisher Scientific, catalog number: 20290, storage temperature: 4 °C)
- Ni-NTA Agarose (25 ml) (QIAGEN, catalog number: 30210, storage temperature: 4 °C)
- Amicon® Ultra-4 Centrifugal Filter Unit (Merck-Millipore, catalog number: UFC801008, storage temperature: RT)
- Imidazole for molecular biology (Applichem, catalog number: A1378,0050, storage temperature: RT)
- Kinase assay solution (10x) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Water bath (Julabo, ED-13 Open Heating Bath Circulator/discontinued product)
- GloMax® 20/20 Luminometer (Promega, model/catalog number: 2030-100/E5311)
- Eppendorf 5417R Refrigerated Centrifuge (Marshall Scientific, Product code: EP-5417R)
Software
- Microsoft® Office Excel 2013
- GraphPad Prism v6 software
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2020 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Efstathiou, A. and Smirlis, D. (2020). A Radioactive-free Kinase Inhibitor Discovery Assay Against the Trypanosoma brucei Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 short (TbGSK-3s). Bio-protocol 10(2): e3493. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3493.
分类
微生物学 > 抗微生物试验 > 杀寄生虫药试验
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
分子生物学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link