- EN - English
- CN - 中文
cDNA Display Mediated Immuno-PCR (cD-IPCR): A Novel PCR-based Antigen Detection Method
cDNA免疫PCR:一种新的基于PCR的抗原检测方法
发布: 2019年12月20日第9卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3457 浏览次数: 6505
评审: Alessandro DidonnaTanxi CaiRubul Mout
Abstract
Immuno-PCR (IPCR) is a powerful method in antigen detection where a PCR-amplifiable DNA reporter is conjugated to a specific antibody or an aptamer for the target molecule. In the development and application of IPCR, successful conjugation of a protein (an antibody) with a reporter DNA becomes challenging. To address this issue, we recently demonstrated the feasibility of IPCR based on cDNA display, a 1:1 covalent complex of a polypeptide and its encoding cDNA at the single molecule level. The cDNA display molecule for IPCR is generated first by transcribing the DNA that encodes the detection antibody into an mRNA by in vitro transcription. A puromycin DNA linker is then ligated to the mRNA and then in vitro translation and reverse-transcription are performed to generate the cDNA display molecule. The molecule is then directly used in antigen detection and subsequent qPCR. This method can be applied to detect various antigens in biological samples, if sequences of their single-domain antibodies (VHHs) or peptide aptamers are known.
Keywords: Immuno-polymerase chain reaction (免疫聚合酶链反应)Background
Immuno-PCR, often abbreviated as IPCR, is an extremely powerful method in detection and quantification of low abundance biomarkers that exist in biological samples (e.g., serum and urine). It acts as a bridge between immuno-reaction and signal amplification. In most cases, IPCR relies on the use of a detection antibody which has been conjugated to a reporter oligonucleotide, followed by the quantification of the analytes using real-time PCR of the reporter (Sano et al., 1992). However, in the development and application of IPCR, the difficulty associated with appropriately conjugating antibodies to oligonucleotides has become the most challenging issue (van Buggenum et al., 2016). Strategies available to conjugate the antibody and the DNA include non-covalent conjugation such as coupling via biotin-streptavidin (Sano et al., 1992) and covalent conjugation using chemical crosslinkers (Hendrickson et al., 1995). However, the tetrameric nature of streptavidin leads to the formation of heterogeneous DNA-antibody conjugates, which may decrease the reproducibility of IPCR. At the same time, conventional crosslinking chemistry reacts with the cysteine/lysine in the antibody, and the modification may compromise binding affinity of the antibody.
To avoid these problems, Guo et al. developed a new immuno-assay protocol with the aid of phage display: phage display mediated immuno-PCR (PD-IPCR) (Guo et al., 2006). In PD-IPCR, an engineered recombinant phage particle which expresses a single-chain antibody for the analyte is used as a ready reagent for IPCR instead of a monoclonal antibody (mAb) and chemically bound DNA. However, in PD-IPCR, the specificity of the DNA-protein linkage is compromised due to the difficulty in controlling of the number of exposed engineered coat proteins on the phage surface. Further, since these bacteriophages are genetically engineered viruses, experiments must be performed under strict legal regulations, which may be a hurdle for real-world applications.
cDNA display is one of the simplest genotype-phenotype linking methods, where cDNA is covalently fused to its coding polypeptide (which can act as the affinity probe for the target) via a uniquely designed puromycin linker (Yamaguchi et al., 2009; Mochizuki et al., 2011). So far, we and others have successfully applied cDNA display for in vitro selection of high affinity peptides/proteins against various targets (Suzuki et al., 2018; Terai et al., 2019). Stimulated by PD-IPCR, we envisioned that cDNA display molecules can also be regarded as antibody-DNA conjugates that are used for IPCR. Thus, we recently demonstrated the feasibility of IPCR based on cDNA display (cD-IPCR, Anzai et al., 2019). The cD-IPCR, which takes advantage of the structural characteristics of cDNA display, proved to work in detection of target proteins both in direct and sandwich-type formats. The cD-IPCR method offers several merits over the conventional IPCR and PD-IPCR, which include 1) based on a covalent homogeneous DNA-antibody conjugation, 2) non-viral, and 3) almost a ready to use reagent, 4) easy to perform by biologists without expertise in organic chemistry. The overall procedures for cD-IPCR are shown in Figure 1. Refer to the original paper "Anzai et al. (2019)" for further clarifications about the newly developed method. Here in this article, we describe step by step preparation of cDNA display molecule and its application in detecting analytes in a sandwich-type manner, which should be most general. To demonstrate the above steps, sandwich-type detection of green fluorescent protein (GFP) using anti-GFP VHH (Single variable domain on a heavy chain antibody) (Fridy et al., 2014) and commercially available polyclonal anti-GFP antibody is explained here. Of course, the readers can detect other target proteins with this method if appropriate VHH or peptide aptamers as well as their immobilization antibodies are available. Current article takes advantage from our previously published "Anzai et al. (2019)" but different from original paper as this article includes all the experimental details that even novices could easily reproduce the experiment. We hope this article will help to ensure the high reproducibility of our newly developed protocol, and also lend a helping hand to researchers who are interested in the procedures and want to use themselves.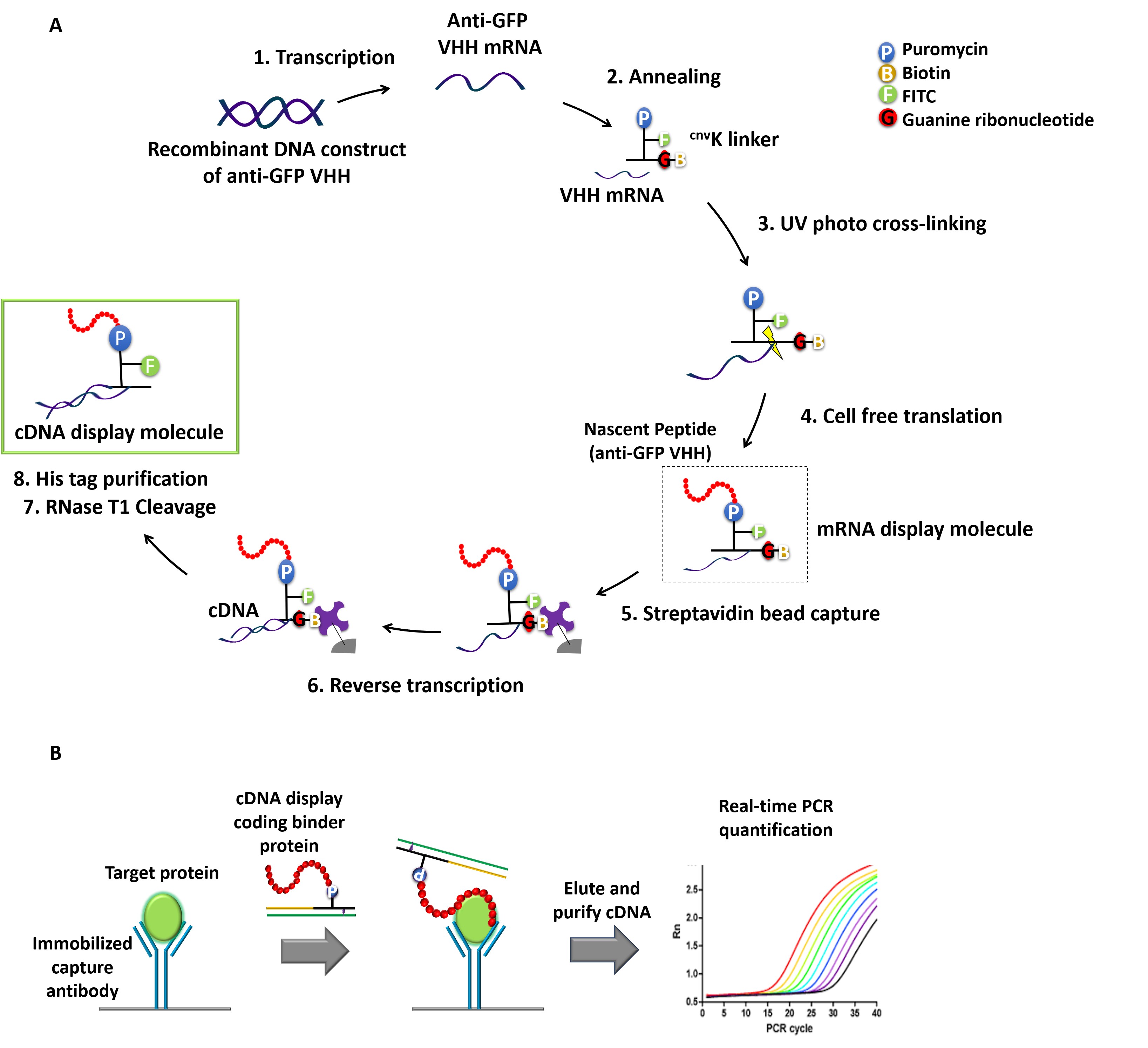
Figure 1. Schematic representation of cDNA displays mediated immuno-PCR (cD-IPCR). A. Preparation of cDNA display (schematic representation). B. Schematic diagram of cD-IPCR (sandwich-type detection). A target protein in a biological sample is captured on solid phase using a capture antibody. After washing, cDNA display of a polypeptide/VHH that has affinity to the target is added. Unreacted display molecules are washed away, and resulting cDNA is quantified by qPCR.
Materials and Reagents
Note: All reagents should be of molecular biology grade to avoid contamination of ribonuclease.
- Polystyrene microtiter plate (MICROLON, 96 Well Single-Break Strip Plate, PS) (Greiner Bio-One, catalog number: 705071)
- PCR tubes (End point PCR tubes; TreffLab Laboratory Consumables, catalog number: 96.09852.9.01, qPCR strip tubes; SSIBio, catalog number: 3248-00)
- cnvK-rG Puromycin-linker, store at -20 °C
Note: The components of cnvK-rG puromycin-linker can be obtained from custom DNA synthesis service. Please refer (Nemoto et al., 2018 or Terai et al., 2019) for the detailed protocol of formation. - DNA oligos can be obtained from custom DNA synthesis service. Eurofins Genomics (Ota-ku, Tokyo, Japan), Tsukuba Oligo Service (Tsuchiura, Ibaraki, Japan), and Hokkaido System Science (Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan), store at -20 °C
- Nuclease-free ultra-pure distilled water (UPDW) (various suppliers)
- PrimeSTAR HS DNA polymerase (Takara, catalog number: R010A), store at -20 °C
- FavorPrep PCR Clean-Up Mini Kit (Favorgen), store at room temperature
- RiboMAXTM Large-Scale RNA Production System T7 (Promega, catalog number: P1300), store at -20 °C
- RNA Clean-Up Kit (Favorgen, catalog number: FAPCK001), store at 4 °C
- Nuclease treated Rabbit Reticulocyte Lysate System (Promega, catalog number: L4960). Amino acid mixtures for translation are included. Store at -80 °C
- RNasin® Ribonuclease Inhibitor (Promega; catalog number: N2111), store at -20 °C
- Dynabeads MyOne streptavidin C1 (VERITAS; catalog number: DB65002), store at 4 °C
- ReverTra Ace® (Toyobo, catalog number: TRT-101). 5x RT Buffer and 2.5 mM each dNTP mix are included. Store at -20 °C
- His Mag Sepharose Ni (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 2896390)
- RNase T1 (1,000 U/L) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EN0541)
- RNase H (Takara, catalog number: 2150A, 10 U) and 10x NE buffer 2 (NEB)
- DL-Dithiothreitol ≥ 99.0% (RT) (Sigma, catalog number: 4381)
- Quick-Load 100 bp DNA Ladder (Biolabs, catalog number: N0467), NEB
- SYBRTM Gold Nucleic Acid Gel Strain (Invitrogen, catalog number: S11494)
- THUNDERBIRD SYBR qPCR Mix (Toyobo, catalog number: QPS-201)
- 10x PBS (Phosphate-buffered saline-) (Wako, catalog number: 163-25265)
- Anti-GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) pAb (MBL Life Science, catalog number: 598)
- Skim milk (Wako, catalog number: 190-12865)
- NaCl (Wako, catalog number: 191-01665)
- Tris-HCl (Wako, catalog number: 208-14691)
- KCl (Wako, catalog number: 163-03545)
- MgCl2 (Wako, catalog number: 136-03995)
- EDTA (Invitrogen, catalog number: 15575-038)
- Urea (Wako, catalog number: 217-01215)
- Bromophenol Blue (BPB) (Wako, catalog number: 021-02911)
- Xylene Cyanol (XC) (Wako, catalog number: 244-00461)
- Sucrose (Wako, catalog number: 196-00015)
- UltraPure DNase/RNase-Free Distilled Water (UPDW) (Invitrogen, catalog number: 10977-015)
- Ammonium persulfate (Wako, catalog number: 012-20503)
- Acrylamide (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 00807-05)
- Tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) (Wako, catalog number: 205-06313)
- Boric acid (Wako, catalog number: 021- 02195)
- Tween20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416)
- Dibasic sodium phosphate (Wako, catalog number: 042-29445)
- Imidazole (Wako, catalog number: 095-05392)
- Glycine (Wako, catalog number: 077-00735)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 320331)
- Tris-borate-EDTA (TBE) Buffer (10x) (Invitrogen, catalog number: B52)
- Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer (Invitrogen, catalog number: AM9849)
- Tris base (Wako, catalog number: 011-20095)
- SDS (Wako, catalog number: 194-13985)
- APS (Wako, catalog number: 016-08021)
- BIS (N, N’-Methylene-bis (acrylamide) (Wako, catalog number: 130-06031)
- 1x SYBR Gold Nucleic Acid Gel Strain (stored at 4 °C, see Recipes)
- 2x loading dye (see Recipes)
- 4% Denaturing urea polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) 10 ml (see Recipes)
- 5x TBE buffer 1 L (see Recipes)
- 2x Binding buffer (see Recipes)
- Ni-NTA binding/wash buffer (see Recipes)
- Ni-NTA elution buffer (see Recipes)
- SDS-page gel (prepare and allow to set 2-3-hour prior to the experiment) (see Recipes)
10 ml of 6% separating gel and 5 ml of 4% stacking gel - 0.2 M Glycine-HCl buffer (see Recipes)
- 40% (w/v) Acrylamide (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Thermal cycler (Biometra, Model: TRIO48)
- Biomolecular imager (GE Healthcare, Model: Typhoon FLA9500 )
- NanoDrop Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Model: 1000 V3.3)
- NanoDrop Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Model: 3300 V2.7, FITC)
- Heat block (ANATECH, Model: cool stat 5200)
- UV Crosslinker (UVP, Model: CL-1000)
- Vortex mixer (IWAKI, Model: TM 2000)
- Magnetic separator (Invitrogen, Model: 12320D)
- Thermo block rotator (NISSIN, Model: SNP 24B)
- StepOne Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Model: 4376600)
- High speed refrigerated microcentrifuge (Tomy Tech, Model: KITMAN MX-301)
- Gel electrophoresis apparatus (PAGE/SDS-PAGE) (ATTO, Model: AE 6510)
- Pipettes (Gilson Pipetman, Model P2- P1000)
Software
- Quantity One 1-D Analysis Software (Bio-Rad, Version 4.6.6)
- Primer Express (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Version 3.01)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Jayathilake, C., Terai, T. and Nemoto, N. (2019). cDNA Display Mediated Immuno-PCR (cD-IPCR): A Novel PCR-based Antigen Detection Method . Bio-protocol 9(24): e3457. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3457.
分类
免疫学 > 抗体分析 > 抗体检测
癌症生物学 > 癌症生物化学 > 癌代谢
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link