- EN - English
- CN - 中文
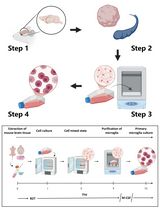
Isolation and Culture of Murine Hepatic Stellate Cells
小鼠肝星状细胞的分离培养
发布: 2019年11月05日第9卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3422 浏览次数: 10286
评审: Gal HaimovichSara JohnsonAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), alternatively known as liver pericytes, can differentiate into myofibroblasts and secrete extra-cellular matrix components, thereby promoting wound healing and fibrosis. Studying HSCs can provide insights into the pathological mechanisms governing these processes. HSC isolation methods typically comprise of enzymatic digestion followed by density gradient centrifugation and/or Fluorescent Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) mediated sorting. In this protocol, we describe a step-wise method for HSC isolation that utilizes Pronase and Collagenase for enzymatic tissue dissociation, followed by an Optiprep based density gradient centrifugation. The isolation can be performed using common media and buffers, and without the use of any special equipment for liver perfusion and HSC isolation. The technique yields ex vivo HSCs, suitable for use in assays.
Keywords: Hepatic stellate cells (肝星状细胞)Background
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) harbor in the perisinusoidal space amidst the endothelial cells and hepatocytes. Under homeostatic conditions, HSCs assume a quiescent state comprising about 15% of the liver resident cells (Friedman, 2008). Upon activation, HSCs can differentiate into myofibroblasts producing copious amount of extra-cellular matrix components, such as collagen.
Originally, rat livers were utilized for HSC isolation during the 1980s (Knook et al., 1982; Friedman et al., 1985). Owing to the ability of quiescent HSCs to store vitamin A in lipid droplets, isolation was based on density gradient separation. On similar lines, vitamin A rich mouse HSCs localize in the upper layers in density gradients (Chang et al., 2014, Maschmeyer et al., 2011). Subsequently developed FACS based methods explore the inherent vitamin A fluorescence to sort HSCs (Mederacke et al., 2015).
Our method was implemented in our recent studies on pericyte induced wound healing (Minutti et al., 2019) and is advantageous as a rapid, inexpensive method to yield around 2 x 105 HSCs and takes about 3.5 h. HSCs isolated using our method can be used in gene expression studies, in vitro differentiation assays and can be applied to wild type as well as genetically modified mice.
Materials and Reagents
- Culture hood for sterile work
- Dissection scissors (Any available dissection scissors can be used)
- Forceps- 2 pairs (preferably blunt forceps from any manufacturer are preferred)
- Ice box
- Tissue culture treated T75 flask (Corning, catalog number: S430641)
- 0.22 μm sterile syringe filters (Millex/Millipore Sigma, catalog number: SLGP033RS)
- 10 ml syringes (BD Plastipak, catalog number: 302188)
- 30 ml Universal Containers (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12511299)
- 27 G needles, disposable, ½ ‘’ (BD, catalog number: 305109)
- Nybolt mesh or 70 µm Cell Strainer (Falcon, catalog number: 352350)
- 15 ml tubes (Sarstedt 62.554.502)
- 50 ml tubes (Sarstedt 62.548.004)
- Disposable 5 ml and 10 ml pipettes
- 100 mm x 20 mm (D x H) Tissue-culture treated culture dishes (Corning, catalog number: 430167)
- Taqman probes, used for Acta2 (Mm00725412_s1) and Rn18s (Mm03928990_g1) from Applied Biosystems for validation in Figure 4
- 4 x Mice
- DNase 1, Grade II, from bovine pancreas (Roche, catalog number: 10104159001)
- Collagenase B (Roche, catalog number: 11088807001)
- Protease from Streptomyces griseus (Pronase) (Sigma, catalog number: P5147)
- Hanks Balanced Salt Solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9394)
- Axis-Shield Density Gradient Media OptiPrepTM (Abbott Diagnostics Technologies AS, catalog number: 1114542)
- Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with high glucose, pyruvate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 41966)
- Fetal Bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 10500064)
- Penicillin-Streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15140122)
- L-Glutamine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25030081)
- Trypsin 0.25% EDTA (Gibco, catalog number:25200056)
- Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8537)
- Red Blood Cell Lysing Buffer Hybri-Max (Sigma, catalog number: R7757)
- Ethanol absolute > 99.8% (VWR, 20821.330P)
- Enzymes (see Recipes)
- Complete DMEM (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Milligram Balance
- CO2 chamber for mouse asphyxiation (Any available apparatus approved by the animal ethics committee and the animal facility may be used.)
- Incubator-shaker or water bath (Grant W28)
- Refrigerated centrifuge for 15- and 50-ml tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5810R)
- Inverted microscope (Zeiss Primovert)
- Incubator for culturing cells (Wolflabs, Binder CB160)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Modak, R. V. and Zaiss, D. M. (2019). Isolation and Culture of Murine Hepatic Stellate Cells. Bio-protocol 9(21): e3422. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3422.
分类
发育生物学 > 细胞生长和命运决定 > 分化
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link