- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Analysis of Indole-3-acetic Acid (IAA) Production in Klebsiella by LC-MS/MS and the Salkowski Method
利用液相色谱-串联质谱法和萨尔科夫斯基氏法分析克雷伯菌中吲哚乙酸的产生
发布: 2019年05月05日第9卷第9期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3230 浏览次数: 23979
评审: Dennis J NürnbergManish Kumar PatelDarrell Cockburn

相关实验方案
细菌病原体介导的宿主向溶酶体运输的抑制:基于荧光显微镜的DQ-Red BSA分析
Mădălina Mocăniță [...] Vanessa M. D'Costa
2024年03月05日 2893 阅读
通过制备连续聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳和凝胶酶谱分析法纯化来自梭状龋齿螺旋体的天然Dentilisin复合物及其功能分析
Pachiyappan Kamarajan [...] Yvonne L. Kapila
2024年04月05日 2080 阅读
Abstract
Many rhizobacteria isolated from plant rhizosphere produce various phytohormones in the form of secondary metabolites, the most common of which is Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Here, we detail analytical protocols of IAA detection and quantification, in vitro and in situ, as recently applied to Klebsiella SGM 81, a rhizobacterium isolated from the rhizosphere of Dianthus caryophyllus (a commercially important flower across the globe). Specifically, we describe a detailed protocol for a colorimetric assay using the Salkowski reagent method, which can be used to screen for the presence of Indole compounds. To further detect and quantify IAA, a highly accurate analytical approach of LC-MS/MS is used. To detect the presence of IAA around the root system of Dianthus caryophyllus, in situ staining of plant roots is done using Salkowski reagent.
Keywords: Indole-3-acetic acid (吲哚乙酸)Background
The bacterial auxin in the form of Indole-3 Acetic Acid (IAA) is a product of L-tryptophan metabolized by bacteria (Lynch, 1985). The group of bacteria known as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) specifically residing in the vicinity of the roots depend on tryptophan being present in the root exudates of plants (Kravchenko et al., 2004; Kamilova et al., 2006). These PGPR use IAA as a signal to interact with plant roots and to colonize the plant parts. This signaling feature of IAA is thought to effect on the physiology of the bacteria (Spaepen et al., 2007).
Different methods are found in the literature to detect the biosynthesis of IAA. Gordon and Weber (1951) were the first to provide a colorimetric assay using Salkowski reagent for the detection of IAA. This method has since been widely used for detecting IAA from microorganisms. Salkowski reagent is a mixture of 0.5 M ferric chloride (FeCl3 ) and 35% perchloric acid (HClO4) which upon reaction with IAA yields pink color, due to IAA complex formation with and reduction of Fe3+ (Kamnev et al., 2001). The color developed by positive reaction indicates the presence of various indole compounds as a product of tryptophan metabolism. Apart from the colorimetric assay, other methods for IAA estimation from bacteria and plant are High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) (Perrig et al., 2007), Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometric (LC-ESI-MS/MS) (Chiwocha et al., 2003), and by High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography HPTLC (Goswami et al., 2015). Liquid Chromatography (LC) is the preferred approach to determine the concentration of IAA and to confirm its purity with high accuracy and standardization. LC coupled with various mass spectrometry detectors are powerful tools for IAA analysis. Because of the high sensitivity and selectivity, Mass Spectrometry detectors are most commonly coupled with LC. One of the important benefits of LC-MS is that analysis and separation of compounds can be achieved in a continuous manner eliminating the step of purification (Kallenbach et al., 2009).
Materials and Reagents
- 100-1,000 μl pipette tips (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Test tube racks (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z334146)
- Screw-cap tubes and caps (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: AXYSCT10MLS)
- Pyrex test tube 20 ml (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CLS980016)
- UV quartz cuvette semi-micro square, 1.4 ml, PTFE stopper (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z276707)
- Sterile syringe filters with a pore size of 0.2 μm (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 720-1230)
- Centrifuge tube with screw cap, capacity 10 ml (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: SIAL301NN10R)
- Pyrex glass serological pipettes, capacity 5 ml (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z653829)
- Amber storage bottles (Sigma-Aldrich, Supelco, catalog number: 23230-U)
- Klebsiella SGM 81 strain (isolated from the rhizosphere of Dianthus caryophyllus)
- Distilled water
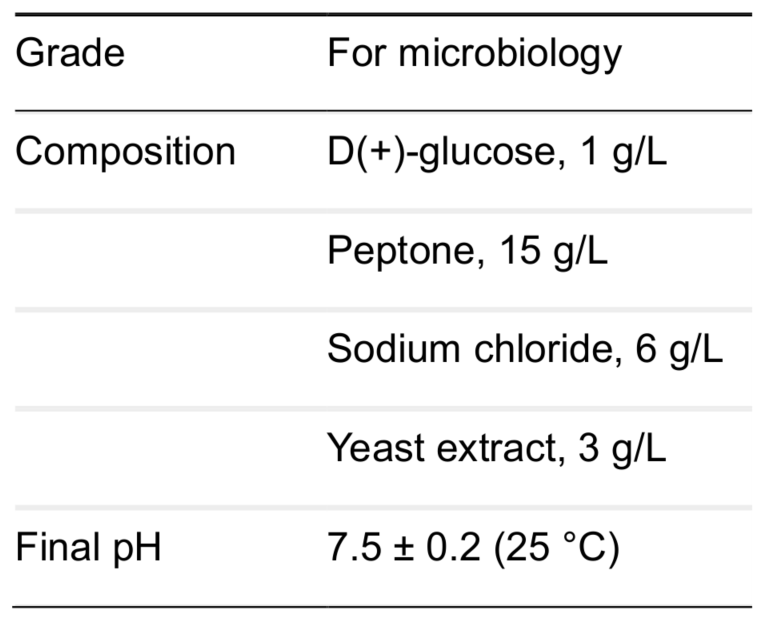
- Nutrient broth (Microbiology grade) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 70122-500G), its composition and final pH see below:
- FeCl3 reagent grade (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 7705-08-0)
- Perchloric acid 70% (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 7601-90-3)
- Methanol (laboratory grade) (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 67-56-1)
- HCl (ACS grade) (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 7647-01-0)
- L-tryptophan (traceCERT grade) (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 73-22-3)
- Acetic acid glacial (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 64-19-7)
- Ethyl acetate (grade anhydrous) (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 141-78-6)
- Indole-3-Acetic acid (IAA) (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS: 87-51-4)
- Murashige and Skoog medium (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Acetonitrile
- Ammonium formate
- CH3CN
- Formic acid
- Ethanol
- Agarose
- Culture media (see Recipes)
- Salkowski reagent (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Spatula (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: F36711-0012)
- Nichipet Eco pipette, 100-1,000 μl volume (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z710199)
- Measuring cylinder (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z324361-2EA)
- 250 ml conical flask (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z723088-1EA)
- Rotary Vacuum Flash Evaporator (Buchhi Type) (Jain Scientific Glass, 1188)
- Balance
- Agilent 1100 LC system and an ABSciex 6500 Qtrap MS [Chromatography was on a Phenomenex Luna C18 column (100 mm x 2 mm x 3 μm)]
- UV-spectrophotometer (Systronics, 166)
- Microcentrifuge (Thermo scientific, Pico 17)
- Magnetic stirrer (Remi, 1 MLH)
- Vortex cyclo mixer (Remi, CM 101)
Software
- Analyst 1.6.1 (AB Sciex)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Gang, S., Sharma, S., Saraf, M., Buck, M. and Schumacher, J. (2019). Analysis of Indole-3-acetic Acid (IAA) Production in Klebsiella by LC-MS/MS and the Salkowski Method. Bio-protocol 9(9): e3230. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3230.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物-宿主相互作用 > 细菌
生物化学 > 其它化合物 > 植物激素
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 植物激素
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link