- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Improved HTGTS for CRISPR/Cas9 Off-target Detection
改进的HTGTS用于 CRISPR/Cas9脱靶检测
发布: 2019年05月05日第9卷第9期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3229 浏览次数: 6704
评审: Arif Md. Rashedul KabirMario RuizAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Precise genome editing is essential for scientific research and clinical application. At present, linear amplification-mediated high-throughput genome-wide translocation sequencing (LAM-HTGTS) is one of most effective methods to evaluate the off-target activity of CRISPR-Cas9, which is based on chromosomal translocation and employs a “bait” DNA double-stranded break (DSB) to capture genome-wide “prey” DNA DSBs. Here, we described an improved HTGTS (iHTGTS) method, in which size-selection beads were used to enhance reaction efficiency and a new primer system was designed to be compatible with Illumina Hiseq sequencing. Compared with LAM-HTGTS, iHTGTS is lower cost and has much higher sensitivity for off-target detection in HEK293T, K562, U2OS and HCT116 cell lines. So we believe that iHTGTS is a powerful method for comprehensively assessing Cas9 off-target effect.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9 (CRISPR/Cas9)Background
The CRIPSR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and CRISPR-associated proteins) has been widely used as a powerful genome editing tool (Cong et al., 2013; Jinek et al., 2013; Mali et al., 2013). However its off-target activity causes DNA DSBs at imperfectly matched loci. During the past few years, several methods based on next-generation sequencing have been published to detect off-target sites. LAM-HTGTS (Frock et al., 2015; Hu et al., 2016), which is based on chromosomal translocation, makes use of a “bait” DSB to capture “prey” DSBs to sensitively identify off-target hotspots; GUIDE-seq inserts a specific DNA oligo into break site and applies PCR to enrich DSBs (Tsai et al., 2015). In vitro methods such as Digenome-seq (Kim et al., 2015) and CIRCLE-seq (Tsai et al., 2017) are more sensitive but often need to be verified in vivo. Though LAM-HTGTS is very sensitive, there is still room for improvement.
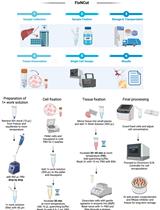
In the improved HTGTS (iHTGTS), we applied size-selection beads to deplete surplus biotinylated primer for the bridge adapter ligation efficiency enhancement. iHTGTS showed 4 times greater sensitivity than LAM-HTGTS. Also a new primer system was employed which can accommodate 150 bp x 2 Hiseq sequencing instead of 250 bp x 2 Miseq, so that the sequencing cost is much saved. Taken together, iHTGTS is a cost-effective and high efficient method. We believe iHTGTS can give researchers deeper insights into the off-target activity of CRIPSR/Cas9.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (Quality Scientific Plastics)
- 1.5 ml tube (Axygen, catalog number: MCT-150-C)
- 0.22 μm syringe filter (MILLEX, catalog number: PR03683)
- 200 μl PCR tubes (Axygen, catalog number: 14-222-261)
- Agarose (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: R0492)
- 1 kb DNA plus ladder (Transgen Biotech, catalog number: BM211)
- Streptavidin C1 beads (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 65001)
- AMPure XP beads (Axygen)
- Protease K (Sigma, catalog number: P8044)
- FastPfu (Transgen Biotech, catalog number: AP221-02)
- dNTPs (Transgen Biotech, catalog number: AD101-11)
- AxyPrep MAG PCR Clean-Up (Axygen, catalog number: MAG-PCR-CL)
- NaCl (VWR Life Sciences, catalog number: 97061-266)
- EDTA (Amresco, catalog number: BDH9232)
- Tris (VWR Life Sciences, catalog number: 97062-420)
- PEG 8000 (Sigma, catalog number: 89510-250G-F)
- T4 ligase (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: EL0011)
- EasyTaq (Transgen Biotech, catalog number: AP111-01)
- Gel extraction kit (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: K0691)
- 75% Ethanol (Beijing Chemical Works)
- Isopropyl (Beijing Chemical Works)
- EDTA-Na2·2H2O (Amresco, catalog number: BDH9232)
- NaOH (Sigma, catalog number: 221465)
- HCl (Sigma, catalog number: 7647-01-0)
- SDS (Sigma, catalog number: 72455)
- TAE (see Recipes)
- Proteinase K (see Recipes)
- 5 M NaCl (see Recipes)
- 0.5 M EDTA (pH 8.0) (see Recipes)
- 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) (see Recipes)
- Cell lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- TE buffer (see Recipes)
- 50% (wt/vol) PEG 8000 (see Recipes)
- 2x B&W buffer (see Recipes)
- Annealing buffer (see Recipes)
- 50 mM bridge adapter (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Foam floating tube rack
- 8-well magnet stand
- Pipettes (GILSON)
- Thermomixer C (Eppendorf)
- PCR Thermal Cyclers (Applied Biosystems)
- Covaris (M220 Focused-ultrasonicator)
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5418R)
- NanoDrop (DeNOVIX, DS11)
- Incubator (Thermo Fisher)
- Autoclave
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Yin, J., Liu, M., Liu, Y. and Hu, J. (2019). Improved HTGTS for CRISPR/Cas9 Off-target Detection. Bio-protocol 9(9): e3229. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3229.
分类
分子生物学 > DNA > DNA 测序
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link