- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Visualization of Plant Cell Wall Epitopes Using Immunogold Labeling for Electron Microscopy
利用电子显微镜免疫金标记法进行植物细胞壁表位的可视化观察
发布: 2019年04月05日第9卷第7期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3205 浏览次数: 7224
评审: Amey RedkarGongjun ShiSmita Nair
Abstract
Plant cell walls consist of different polysaccharides and structural proteins, which form a rigid layer located outside of the plasma membrane. The wall is also a very dynamic cell composite, which is characterized by complex polysaccharide interactions and various modifications during cell development. The visualization of cell wall components in situ is very challenging due to the small size of cell wall composites (nanometer scale), large diversity of the wall polysaccharides and their complex interactions. This protocol describes immunogold labeling of different cell wall epitopes for high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM). It provides a detailed procedure for collection and preparation of plant material, ultra-thin sectioning, specimen labeling and contrasting. An immunolabeling procedure workflow was optimized to obtain high efficiency of carbohydrates labeling for high-resolution TEM. This method was applied to study plant cell wall characteristics in various plant tissues but could also be applied for other cell components in plant and animal tissues.
Keywords: Cell walls (细胞壁)Background
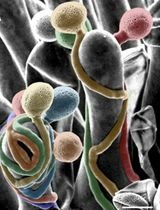
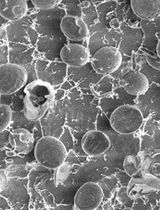
Plant biomass is mainly composed of cell walls, which are widely used as an energy source in our daily life (Loqué et al., 2015). At the microscopic scale, cell walls consist of cellulose microfibrils embedded in complex matrix polysaccharides (hemicelluloses, pectins) and structural proteins. Cellulose microfibrils (CMFs) are the largest wall polymers with a radius of 3-5 nm and many micrometers long (Cosgrove, 2005). The orientation of CMFs determines the direction of growth and cell anisotropy (Baskin, 2005), but the CMFs also interact with other wall components all together modifying the wall properties (reviewed in Majda, 2018; Majda and Robert, 2018). The study of cell wall composition has a long history, going back to when different chemicals were applied to bind to the wall composites; however, many of them had a wide range of targets (Wallace and Anderson, 2012; Voiniciuc et al., 2018) and could be observed only via light microscope resolution. In contrast, the immunogold labeling is characterized by a high specificity of antibodies and high-resolution imaging, which can precisely localize the wall epitopes across the wall matrix (e.g., Majda et al., 2017). Despite electron microscopy being a relatively old method, it is not broadly used for plant cell walls. The reason could be that it is time-consuming, requires long training and extensive preparation time. In this protocol, I will walk you through all the steps concerning sample preparation, specificity for all the reagents and troubleshooting.
Materials and Reagents
- Adhesion slides, Polysine, 25 x 75 x 1.0 mm (VWR, catalog number: 631-0107)
- Aluminum foil
- Centrifuge tubes 15 ml (PluriSelect, catalog number: 05-00002-01)
- Centrifuge tubes 50 ml (sterile) (PluriSelect, catalog number: 05-00001-01)
- Compressed air in the can (e.g., air duster PRF 4-44)
- Disposable pH indicator paper (universal indicator paper) (Johnson, catalog number: 101.3C)
- Disposable plastic Pasteur pipettes (BRAND, catalog number: 747750)
- Double-edged razor blades (Personna, catalog number: 171930)
- Embedding capsules (8 mm flat, polypropylene capsules) (TAAB, catalog number: C095)
- Filter papers (circles, 150 mm Ø), (Whatman, catalog number: 1001150)
- Glass vials with plastic snap-cap (ca. 41 x 24 mm) (Karl Hecht, catalog number: 2783/3), or clear glass vials with snap-cap (closed top, PE transparent, 18 mm, 500 ml 20 x 40 mm) (VWR, catalog number: 548-0555)
- Grids for transmission electron microscopy, e.g., grid size 100 mesh x 250 μm pitch, nickel or copper (TAAB, maxtaform HF4, catalog number: GM021N; Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G1528; Agar Scientific, catalog number: G2500C)
- Light-duty 3-Ply tissue wipers (VWR, catalog number: 82003824-CS)
- Metal needle or dissection needle (VWR, catalog number: 10806-330)
- Microcentrifuge tubes 1.5 ml (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z606340)
- Microscope slides, 25 x 75 x 1.0 mm (VWR, catalog number: 48300-025 or Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 10144633CF)
- Paper tags
- Parafilm (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7543)
- Pencil
- Pipette tips
- Plastic Petri dishes (Fisherbrand, catalog number: S33580A)
- Protective gloves (Honeywell, catalog number: Dermatril 740)
- Round silicone rubber (TAAB, catalog number: G082)
- Single edge razor blades with aluminum spine (VWR, catalog number: 233-0156)
- Slide labels (Agar Scientific) or one side adhesive paper
- Square Petri dish (120 mm) (Corning, catalog number: BP124-05)
- Transparent tape (e.g., scotch)
- Waste containers
- Agar, plant agar (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: 9002-18-0)
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA), lyophilized powder ≥ 96% (agarose gel electrophoresis) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 9048-46-8)
- Disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4) (store in ambient temperature: room temperature, approx. 21 °C) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 7558-79-4)
- Distilled water
- Ethanol laboratory reagent, absolute, ≥ 99.5% (flammable, stored in designated place) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 64-17-5)
- Formaldehyde (FA) (10 ml ampule of 16% methanol-free FA) (health hazards, store closed in ambient temperature, or open in cold room/refrigerator 4 °C) (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: 28908) or paraformaldehyde (PFA) for histology (CH2O)n, (store in cold room/refrigerator 4 °C) (J.T. Baker, catalog number: S898-07)
- Formvar solution (1% formvar in dichloroethane, for microscopy) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 63148-64-1)
- Glutaraldehyde (GA) (grade I, 1 ml ampule of 25% GA in H2O, specially purified for use as an electron microscopy fixative, linear formula: OHC(CH2)3CHO (health hazards, store closed in ambient temperature, or open in cold room/refrigerator 4 °C) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 111-30-8)
- Hydrogen chloride (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 7647-01-0)
- LR white resin medium grade–catalyzed (health hazards, store in cold room/refrigerator 4 °C) (TAAB, catalog number: L012)
- Monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 7778-77-0)
- Monosodium phosphate (NaH2PO4) (store in ambient temperature) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 7558-80-7)
- Murashige and Skoog basal medium (MS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5519)
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 7447-40-7)
- Primary antibodies (PlantProbes: www.plantprobes.net or the University of Georgia: www.ccrc.uga.edu)
- Secondary antibodies, e.g., EM Goat anti-Rat IgG (H+L): 10 nm Gold (BBI Solutions, catalog number: 014990) or EM Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) 10 nm Gold (BBI Solutions, catalog number: EM.GMHL10)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 7647-14-5)
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 1310-73-2)
- Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 57-50-1)
- Toluidine blue for microscopy (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 6586-04-5)
- TopVision low melting point agarose (LMP agarose) (store in ambient temperature) (Thermo Scientific, catalog number: R0801)
- Tween 20 (Signa-Aldrich, catalog number: P1379)
- Uranyl acetate (UA) (health hazardous, store in ambient temperature) (VWR, catalog number: 541-09-3)
- Half strength MS basal medium (see Recipes)
- Paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde (4% PFA and 0.05% GA) fixative solution (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffer (PB), 0.1 M solution (pH = 7.2) (see Recipes)
- Low melting point (LMP) agarose 1% solution (see Recipes)
- Different ethanol concentrations 10%-95% (see Recipes)
- Different LRW resin concentrations 10%-75% (see Recipes)
- Toluidine blue solution (see Recipes)
- Blocking Reagent (BR) 1% (see Recipes)
- Antibodies solutions (see Recipes)
- Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS), 0.1 M solution (pH = 7.2) (see Recipes)
- Uranyl acetate solution (5%) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Analytical balance
- Autoclave (YPO, model: D66161)
- Centrifuge (Marshall Scientific, Eppendorf, model: 5417C)
- Conical flask
- Desiccator (Thermo Fisher, model: 5311-0250)
- Diagonal cutting pliers e.g., stanley diagonal cutting pliers, 5 (Robosource, catalog number: 15-11)
- Diamond knife, e.g., ultra 45° (Diatome)
- Flat beaker or crystallizer (with a wide diameter)
- Forceps
- Freezer (-20 °C)
- Fume hood
- Glass baker (50 ml)
- Glass knife strips (Agar Scientific, catalog number: AGG336)
- Glass knifemakers for histology knives (LKB, catalog number: LKB 7801B; or Agar Scientific, catalog number: AGL4158)
- Grid storage box (LKB/Leica catalog number: G133, or TAAB Gilder G062)
- Lab oven/incubator (60 °C)
- Light microscope
- Magnetic hotplate stirrer with magnetic stir bar
- Metal 1.5 ml Eppendorf rack
- Microtome (Reichart Ultracut)
- Microwave oven
- pH meter
- Pipettes
- Protective clothes and mask
- Refrigerator (4 °C)
- Rotary shaker or orbital shaker (IKA KS 130 Basic)
- Slide drying rack or slide staining jar (e.g., DWK Life Sciences Wheaton)
- Small bench clamp workshop
- Thin painting brush
- Transmission Electron Microscope (JEOL, model: JEM-1230)
- Tweezers: negative-action style: thin curved tips (Dumont, catalog number: 0203-N7-PO) or thin tips (Dumont, catalog number: 0302-N0-PO-1)
- Tweezers: straight with Geneva pattern, thin tips (Dumont, catalog number: 0103-0-PO)
- Vortex mixer (Vortex-Genie 2)
- Warming plate, or slide drying hotplate (Agar Scientific, model: AGL4384) or spirit lamp burner
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Majda, M. (2019). Visualization of Plant Cell Wall Epitopes Using Immunogold Labeling for Electron Microscopy. Bio-protocol 9(7): e3205. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3205.
分类
植物科学 > 植物细胞生物学 > 细胞壁
植物科学 > 植物发育生物学 > 形态建成
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 电子显微镜
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link