- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Determination of Cellular Uptake and Endocytic Pathways
细胞摄取和内吞途径的检测
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2019年02月20日第9卷第4期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3169 浏览次数: 11572
评审: Chiara AmbrogioMauro Sbroggio'Muhammad Aslam
Abstract
Efficiency of drug and gene delivery via nonviral vehicles is contingent on proper cellular uptake and intracellular release. Further, various cargos, such as nucleases for gene editing or inhibitors for endosomal receptors, require transport to specific compartments of the cell. Hence, characterization of cellular uptake and endocytic pathways is crucial for the optimization of any nanoparticle-mediated intracellular delivery system. Previous work on endocytic pathways looks at the effect of various pathway inhibitors on the uptake efficiency of nanoparticles carrying fluorescently-labeled cargo. While this helps attribute particle uptake to specific pathways like caveolae-mediated or clathrin-mediated endocytosis, this does not provide a holistic picture of the delivery process. Here, we provide a general protocol that combines systematic studies of inhibitor effects on efficiency with quantification of particle-induced cell membrane permeability. By applying this methodology to a nucleic acid delivery system, for example a helical polypeptide-based nanoparticle for plasmid and guide RNA delivery, we gain understanding of the endocytic mechanisms and cell uptake for intelligent design of intracellular delivery.
Keywords: Endocytosis (内吞)Background
While nonviral delivery has made significant progress over the past decade, from the initial inert nanoparticle design to biofunctional and ligand-targeting nanocarriers with improved delivery efficiency, these novel delivery vehicle systems still lack viral delivery’s high transduction efficiency. Because of this inadequacy, a large portion of research has been dedicated to determining the limiting factors restricting nonviral delivery through mapping the cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of delivery vehicles. Further, in the field of nucleic acid therapeutics, where the success of nanoparticle delivery is measured through a secondary mechanism such as gene-cleavage detection or quantitative PCR, developing an analytical platform to resolve and quantify vehicle uptake, intracellular trafficking and endosomal escape is crucial. Previous work applies fluorescently-tagged nanoparticles, fluorescent protein gene expression and flow cytometry to explore uptake of the delivery vehicle as a whole (Dausend et al., 2008). More recently, researchers investigated cellular trafficking by employing image-based analysis for colocalization of fluorescently-tagged vehicles with lysotracker and application of uptake pathway inhibitors (Gilleron et al., 2013). This protocol builds on this breadth of research, to provide a robust method (Figure 1) to characterize the specific uptake and trafficking characteristics of any nucleic acid therapeutic in a nonviral delivery system (Wang et al., 2018). By the characterization of the intracellular transport of the therapeutic load, regardless of nanoparticle size, charge, material, and target cell type, the field can begin to pinpoint the weaknesses in nonviral genetic delivery and improve upon them (Iversen et al., 2011). As a broader spectrum of cell types and delivery vehicles are interrogated using this protocol, various genetic and alternative therapeutic cargos can be delivered through intelligently designed vehicles for optimized on-target effects (Douglas et al., 2008).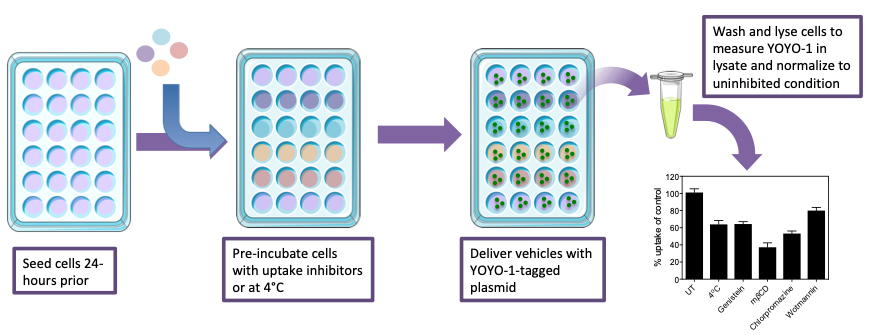
Figure 1. Schematic showing the process for determination of the contribution of each endocytosis pathway to particle uptake. Beginning from the seeding of cells, to the treatment with inhibitors, followed by delivery vehicle application and then analysis of the lysate.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips
- Microscope slides
- Cover slips (0.17 to 0.25 mm thickness)
- 24-well cell culture plates
- 1.5 ml tubes
- FITC-labeled in vitro transcribed single guide RNA, sgRNA (synthetic can also be used)
- pSPCas9 (Addgene, px165)
- Opti-MEM reduced serum medium (Thermo Fisher, Gibco, catalog number: 31985062)
- Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium, DMEM (Thermo Fisher, Gibco, catalog number: 11960077)
- Fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher, Gibco, catalog number: 16000044)
- Penicillin-streptomycin (Thermo Fisher, Gibco, catalog number: 15140148)
- Phosphate buffered saline, or PBS (Fisher Scientific, Corning, catalog number: 21040CV)
- Delivery vehicle such as a helical nanoparticle (HNP) formulated from poly(γ-4-((2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethyl)aminomethyl) benzyl-L-glutamate (PPABLG) (see Recipes) or a lipid nanoparticle like Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher, catalog number: 300001)
- Heparin (Stemcell Technologies, catalog number: 07980)
- RadioImmunoPrecipitation Assay (RIPA) lysis buffer (Thermo Fisher, Pierce, catalog number: 89900)
- BCA protein assay (Thermo Fisher, Pierce, catalog number: 23225)
- Paraformaldehyde (Thermo Fisher, ACROS, catalog number: 28906)
- DAPI (Thermo Fisher, Invitrogen, catalog number: D1306)
- Lysotracker Red (Thermo Fisher, Invitrogen, catalog number: L12492)
- Mounting medium (Sigma-Aldrich, Fluoromount, catalog number: F4680)
- Trypsin-EDTA 0.25% (Thermo Fisher, Gibco, catalog number: 25200056)
- Genistein (Sigma-Aldrich, Sigma, catalog number: G6649)
- Chlorpromazine hydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, Sigma, catalog number: C8138)
- Wortmannin (Sigma-Aldrich, Sigma, catalog number: W1628)
- Methyl-β-cyclodextrin or mβCD (Sigma-Aldrich, Sigma, catalog number: C4555)
- FITC (Thermo Fisher, Invitrogen, catalog number: F2181)
- Tris buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, Sigma, catalog number: 21685)
- YOYO-1 Iodide (Thermo Fisher, Invitrogen, catalog number: Y3601)
- HiScribe T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis Kit (New England Biolabs, HiScribe, catalog number: E2040S)
- Fluorescein-12-UTP (Sigma-Aldrich, Roche, catalog number: 11427857910)
- γ-(4-vinylbenzyl)-L-glutamate N-carboxyanhydride (VB-L-Glu-NCA)
- Anhydrous dimethyl formamide (DMF)
- Hexamethyldisilazane
- Nitrobenzene
- Hexane
- Ether
- Chloroform
- O3 gas
- Methanol
- 1-(2-aminoethyl) piperidine
- Borane-pyridine complex
- Cell culture medium (see Recipes)
- 4% paraformaldehyde (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator
- Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences, BD FACSCalibur, catalog number: 342975)
- Microcentrifuge
- Confocal laser scanning microscope with 40x objective (Zeiss, model: LSM 700)
- 4 °C fridge
- Vortexer
- Glovebox
- Laminar flow hood
- Fluostar Optima (BMG, Fluostar Optima, catalog number: 0413B0001J) or any fluorescence plate reader with excitation wavelength of 485 nm and an emission wavelength of 530 nm
Software
- Computer running Flowjo (Flowjo LLC, https://www.flowjo.com/) or any flow cytometry data analysis software
- Computer running BMG Optima Windows (BMG, https://www.bmglabtech.com/discontinued-microplate-readers/) or any other fluorescence plate reader software
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Gong, J., Wang, H. and Leong, K. W. (2019). Determination of Cellular Uptake and Endocytic Pathways. Bio-protocol 9(4): e3169. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3169.
分类
细胞生物学 > 基于细胞的分析方法 > 内吞作用
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link