- EN - English
- CN - 中文
pNP Transgenic RNAi System Manual in Drosophila
果蝇中pNP RNAi 转基因系统手册
发布: 2019年02月05日第9卷第3期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3158 浏览次数: 7336
评审: Gal HaimovichPradeep Kumar BhaskarAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Much of our knowledge about the mechanisms underlying biological processes relies on genetic approaches, whereby gene activity is reduced and the phenotypic consequences of perturbation are analyzed in detail. For functional genomic studies, a specific, systematic, and cost-effective manner is critical. Transgenic RNAi system is the top priority choice to study gene functions due to its simple and practical characteristics in Drosophila. We established a novel system that works well in both soma and germ cells which is efficient and specific. With this system, we can precisely and efficiently modulate highly expressed genes, and simultaneously knock down multiple genes in one step. In this study, we provide a detailed protocol of the pNP system, which replaces other transgenic systems, and expect it can provide some help to researchers who are using this system.
Keywords: Drosophila (果蝇)Background
Drosophila melanogaster is easy to culture, and has a short life cycle, clear genetic background, and abundant research tools. More importantly, most genes in Drosophila are highly homologous to human genes, which over the past century made Drosophila a powerful model to study the genes in vivo.
RNAi technology can specifically reduce gene expression, which is efficient and easy to operate, so it has been widely used in different model organisms to study gene functions (Dietzl et al., 2007; Ni et al., 2008, 2009 and 2011; Perrimon et al., 2010). In Drosophila, transgenic RNAi approach is a binary system, where UAS-hairpin is controlled by GAL4 to achieve tissue- or developmental stage-specific gene knockout (Brand and Perrimon, 1993). Without Gal4, the hairpin downstream of the UAS will not be transcribed, thus transgenic hairpin lines behave similar to wild type. That is why we can keep thousands of transgenic RNAi lines. However, current RNAi systems exhibit many limitations, such as off-target effects, leaky expression of the basal promoter, poor efficiency to highly expressed genes and the unsolved challenge of simultaneously targeting multiple genes.
We developed a new transgenic RNAi system based on pNP vector, which has an intergenic linker between miR-2a-1 and miR-2b-2 and a modified promoter (Qiao et al., 2018). The pNP transgenic RNAi system can efficiently target highly expressed genes and produce expected severe phenotypes, which overcomes the poor efficiency of current RNAi systems (Ma et al., 2006; Markstein et al., 2008). Furthermore, the pNP transgenic RNAi system can innovatively knock down multiple genes simultaneously in one step, for example simultaneously depleting all the core components of PRC1 in the eye using the pNP system led to smaller eyes (Qiao et al., 2018). The efficiency of multiple mRNA depletion was further confirmed by qRT-PCR, which showed reduced expression levels of these targeted genes. Moreover, the loss-of-function phenotypes produced by targeting multiple genes simultaneously are more robust than the effect of sequentially depleting the genes. The following protocol details the steps from vector construction to transgenic RNAi flies’ screening, which gives us the approach to study the autonomous or non-autonomous roles of genes, including protein complexes or redundant genes.
Materials and Reagents
- 1.5 ml MaxyClear Microtubes (Axygen, catalog number: MCT-150-C)
- 0.2 ml Polypropylene PCR Tube (Axygen, catalog number: PCR-0208-C)
- Pipette tips (Corning, Axygen®)
- 0.22 μm Millipore filters (Biosharp, BS-QT-011)
- Petri dishes
- Drosophila lines (Tinghua Fly Center, http://fly.redbux.cn/)
- y[1] sc[1] v[1] p{y[+t7.7]}=nos-phiC31\int.NLS}X; P{y[+t7.7]=CaryP}attP40 (TB00016)
- y[1] sc[1] v[1] p{y[+t7.7]}=nos-phiC31\int.NLS}X; P{y[+t7.7]=CaryP}attP2 (TB00018)
- y[1] sc[1] v[1]; wg[Gla-1] Bc[1]/CyO (TB00023)
- y[1] sc[1] v[1]; Dr[1] e[1]/TM3, Sb[1] (TB00139)
- y[1] sc[1] v[1] (TB00077)
- pNP vector (Ampicillin resistant, plasmid map is shown in Figure 1. This vector is not commercial, but can be provided for free. If you want, please email your need to nijq@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn)
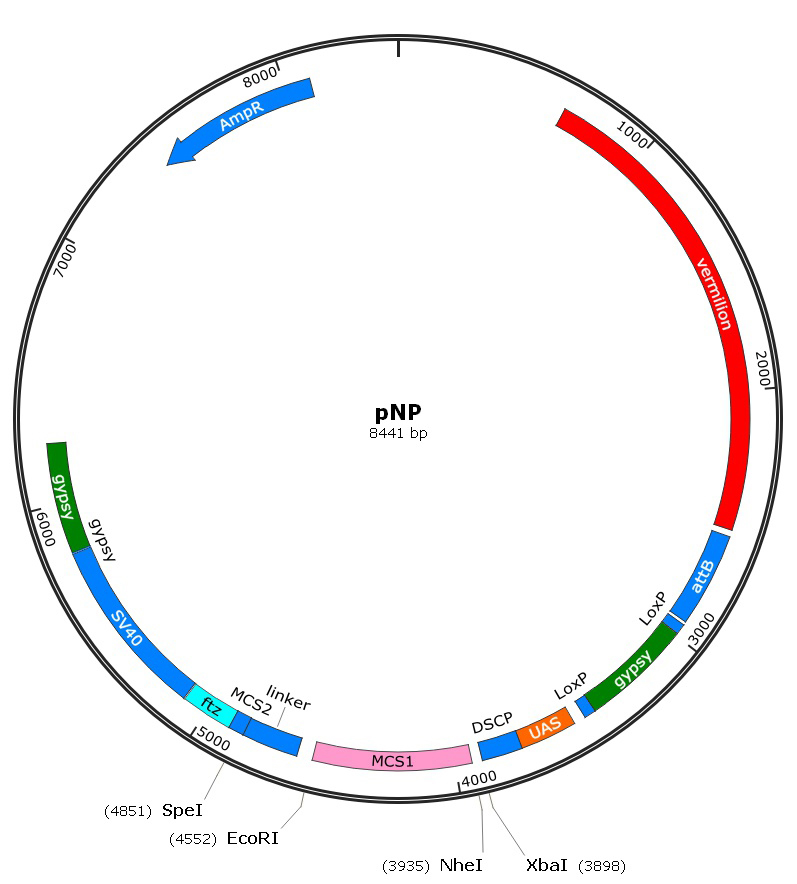
Figure 1. The map of pNP construct. Vermilion is a selectable marker. attB sequence is used for phiC31 targeted integration at genomic attP landing sites. MCS1 allows a single shRNA to be cloned in both orientations, while with the help of MCS2 and the linker it could simultaneously generate multiple shRNAs once. - EcoRI-HF (NEB, catalog number: R3101L)
- NheI-HF (NEB, catalog number: R3131L)
- SpeI (NEB, catalog number: R3133L)
- XbaI (NEB, catalog number: R0145L)
- Alkaline Phosphatase, Calf Intestinal (CIP, NEB, catalog number: M0290S)
- AxyPrepTM DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Corning, Axygen, catalog number: AP-GX-250)
- T4 DNA ligase (NEB, catalog number: M0202L)
- Trans5α Chemically Competent Cell (Transgen Biotech, catalog number: CD201-01)
- Go Tag Green Master Mix, 2x (Promega, catalog number: 000179370)
- AxyPrepTM Plasmid Miniprep Kit (Corning, Axygen, catalog number: AP-MN-P-250)
- PurePlasmid Mini Kit (CWBiotech, catalog number: CW0500M)
- Primers sequences:
U-F: 5’-GCTGAGAGCATCAGTTGTGA-3’; Ftz: 5’-TAATCGTGTGTGATGCCTACC-3’ - Buffer PB (QIAGEN, catalog number: 154051779)
- LB Broth, Miller (Luria Bertani) (Becton Dickinson)
- Agar (Beyotime)
- Ampicillin (Solarbio, catalog number: A8180)
- Tris-HCl (AMRESCO, catalog number: 1185-53-1)
- EDTA (AMRESCO, catalog number: 60-00-4)
- NaCl (AMRESCO, catalog number: 7647-14-5)
- KCl (AMRESCO, catalog number: 7447-40-7)
- Ethidium bromide (Sigma, catalog number: E8751)
- 50x TAE (Double Helix, catalog number: P0309A)
- Sodium phosphate buffer stock solution (pH 6.8) (see Recipes)
- 10x Annealing Buffer (see Recipes)
- Injection Buffer (see Recipes)
- LB (Luria Bertani) medium (see Recipes)
- LB/ampicillin plates (see Recipes)
- 1x TAE (see Recipes)
- 1.5% agarose gel (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipette (Eppendorf)
- Microwave (SANYO, model: EM-2509EB1)
- Autoclave (SANYO, model: MLS-3780)
- PCR Thermal Cycler (Eppendorf, Mastercycler nexus GSX1)
- Refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5417R)
- Stereo Microscope (Olympus Corporation)
- NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Scientific)
Software
- DSIR website: http://biodev.cea.fr/DSIR/DSIR.html
- FlyBase website: http://flybase.org/
- EMBOSS Needle: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/psa/emboss_needle/nucleotide.html
- Tsinghua Fly Center: http://fly.redbux.cn
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Wang, F., Qiao, H., Xu, R., Sun, J., Zhu, R., Mao, D. and Ni, J. (2019). pNP Transgenic RNAi System Manual in Drosophila. Bio-protocol 9(3): e3158. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3158.
分类
分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 干扰
分子生物学 > DNA > 基因表达
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link