- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Eye Drops for Delivery of Bioactive Compounds and BrdU to Stimulate Proliferation and Label Mitotically Active Cells in the Adult Rodent Retina
滴眼液运输生物活性物质和BrdU促进成年啮齿动物视网膜中有丝分裂活跃细胞的增殖和标记
(*contributed equally to this work) 发布: 2018年11月05日第8卷第21期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3076 浏览次数: 5902
评审: Vivien Jane Coulson-ThomasRumen IvanovAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
一种改良的酰基-RAC方法分离视网膜棕榈酰蛋白质组,并通过LC-MS/MS进行后续检测
Sree I. Motipally [...] Saravanan Kolandaivelu
2023年04月20日 2565 阅读
Abstract
Eye drop treatments are typically used to apply drugs to the anterior structures of the eye. Recently, however, studies have demonstrated that eye drops can reach the retina in the back of the eye if pharmacological agents are carried in appropriate vehicles. Here, we introduce an eye drop procedure to deliver a drug (PNU-282987), in combination with BrdU, to stimulate cell cycle re-entry and label dividing cells in the retinas of adult rodents. This procedure avoids potential systemic complications of repeated intraperitoneal injections, as well as the retinal damage that is induced by repeated intravitreal injections. Although the delivery of PNU-282987 and BrdU is the focus of this article, many different proliferating compounds could be delivered to the retina using this procedure.
Keywords: BrdU (BrdU)Background
Although eye drop applications are not considered innovative, they are typically used to generate effects in the anterior portion of the eye (Patel et al., 2013; Sung et al., 2015). For instance, eye drop medications used in glaucoma patients decrease the production of aqueous humor or affect drainage of fluid through the trabecular meshwork in the anterior chamber of the eye (Dikopf et al., 2017). However, others have begun to use agents that are dissolved in vehicles to exert their effects in the back of the eye at the retina. For instance, the neuropeptide pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide [PACAP] provides a well-established neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects in the eye against different retinopathies. Although the route of delivery is usually intravitreal, a recent study that used PACAP dissolved in benzalkonium-chloride was able to cross the ocular barriers and exert protection in ischemic conditions (Werling et al., 2017). Other studies showed that the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor specific agonist, PNU-282987 (Bodnar et al., 2005; Hajos et al., 2005; Iwamoto et al., 2014), was able to cross ocular barriers and induce neurogenesis of adult mammalian neurons when delivered as eye drops, made by diluting a stock solution of PNU-282987 in lipophilic vehicle, DMSO, in PBS. (Webster et al., 2017). Previous dose and time-dependent studies showed that PNU-282987 was detectable in the retina by HPLC MS/MS after eye drop delivery. PNU-282987 levels were detected in the retina after topical application of the nAChR agonist to the bulbar conjunctiva (Mata et al., 2015).
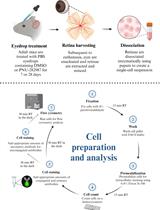
BrdU is a synthetic nucleoside that is an analog of thymidine and is commonly used in the detection of proliferating cells in living tissues. To label mitotically active cells with BrdU, well-established methods for delivery in rodents is via intraperitoneal or intraocular injection (Karl et al., 2008; Lee et al., 2015; Xie et al., 2016). However, more robust labeling of mitotically active cells in the retina occurs if BrdU is added into the PNU-282987 eye drop solution (Webster et al., 2017) (Figure 1). Eye drop applications of agents that reach the retina are much less invasive than either intraperitoneal or intravitreal injections and have the added advantage that they can be introduced several times each day or week without the disadvantage of multiple injections. Here, the procedure for labeling mitotically active cells in the adult rodent retina with BrdU eye drops is provided after stimulation with the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor specific agonist, PNU-282987. However, this method also has broader implications and can be used to deliver other proliferating agents in the retina. 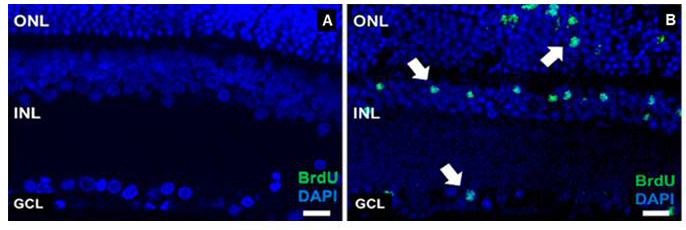
Figure 1. Evidence of successful BrdU labeling. A. A confocal retinal section obtained from an adult SVJ 129 mouse treated only with PBS containing BrdU for 3 days. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). No evidence of BrdU positive cells when the retina is processed with antibodies against BrdU. B. A confocal retinal section obtained from an eye treated with PNU-282987/BrdU eye drops for 3 days. BrdU positive cells are observed in all nuclear layers of the retina (green). ONL: outer nuclear layer, INL: inner nuclear layer, GCL: ganglion cell layer. Arrows point to BrdU positive retinal cells. Scale bars represent 50 µm.
Materials and Reagents
- 3 ml disposable transfer pipettes (VWR, catalog number: 414004-037)
- 0.2 µm sterile syringe filter (VWR, catalog number: 28145-477)
- Latex exam gloves (VWR, catalog number: 414004-429)
- Lab coat (VWR, catalog number: 37000-922)
- 3 month female adult SVJ 129 mouse
- 3 month adult female Sprague Dawley rat
- PNU-282987 (N-[(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-4-chlorobenzamide hydrochloride) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6499) (desiccate, store at 4 °C)
- BrdU (5-Bromo-2’-deoxyuridine) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 19-160) (store for up to 2 years at -20 °C)
- PBS (Phosphate buffered saline 10x concentrate) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5493) (store at room temperature)
- DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8418) (store at room temperature)
- Cheerios (Local grocery store, store at room temperature)
- PNU-282987/BrdU solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 30 ml clear glass bottles (VWR, catalog number: 10862-356)
- 4 °C refrigerator
- Fume hood
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Linn, C. L., Webster, S. E. and Webster, M. K. (2018). Eye Drops for Delivery of Bioactive Compounds and BrdU to Stimulate Proliferation and Label Mitotically Active Cells in the Adult Rodent Retina. Bio-protocol 8(21): e3076. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3076.
分类
神经科学 > 感觉和运动系统 > 视网膜
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 生理学
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link