- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Assessing Classical Olfactory Fear Conditioning by Behavioral Freezing in Mice
通过小鼠冻结行为检测经典嗅觉条件恐惧
发布: 2018年09月20日第8卷第18期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3013 浏览次数: 6224
评审: Andrew L. EagleArnau Busquets-GarciaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Classical fear conditioning typically involves pairing a discrete cue with a foot shock. Quantifying behavioral freezing to the learned cue is a crucial assay for neuroscience studies focused on learning and memory. Many paradigms utilize discrete stimuli such as tones; however, given mice are odor-driven animals and the wide variety of odorants commercially available, using odors as conditioned stimuli presents advantages for studies involving learning. Here, we describe detailed procedures for assembling systems for presenting discrete odor cues during single-day fear conditioning and subsequent analysis of freezing behavior to assess learning.
Keywords: Classical conditioning (经典条件作用)Background
Associative fear learning, the root of several anxiety disorders, involves pairing a neutral stimulus with an aversive outcome. This pairing produces robust behavioral fear responses, in the form of freezing (LeDoux, 2003), to the conditioned stimulus, which can be quantified as a measure of fear learning and memory. Discrete stimuli, such as tones, are often used as conditioned stimuli for fear conditioning; however, olfactory cues are also highly effective at inducing learned freezing (Pavesi et al., 2012; Ross and Fletcher, 2018). This method of associative fear learning differs from those utilizing predator odors, which produces instinctive behaviors rather than learned behaviors, making it ideal for rapidly assessing olfactory learning. Behavioral freezing, defined as absence of all voluntary movements (Blanchard and Blanchard, 1969; Fanselow, 1980), can be measured through automated software that compares pixel differences on a frame-by-frame basis. We developed a protocol that uses the automated FreezeFrame software to deliver discrete olfactory cues during training and testing. This protocol supports standard fear conditioning and subsequent testing but also provides flexibility for expansion to fit broad experimental needs such as extinction, discriminate conditioning, and generalization paradigms or experimental manipulations (e.g., optogenetics or chemogenetics). In addition, olfactory fear conditioning provides a rapid method of studying mechanisms of olfactory associative learning given that training requires few trials in a single day with learning assessed the next day.
Materials and Reagents
- Parafilm
- Tubing
- 1/16” ID Kflex tubing (United States Plastic, catalog number: 65170 )
- 1/16” ID Tygon tubing (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-171-129 )
- 1/8” ID Masterflex Tygon E-Lab (E-3603) Pump Tubing (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-06509-16 )
- 1/4” ID Tygon tubing (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 14-171-221 )
- Luers and connectors
- Stopcock 1-way male lock (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-30600-00 )
- Male Luer x 1/16” hose barb (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-45518-00 )
- Male Luer Lock Plug (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-30800-30 )
- Female Luer x 1/8” hose barb (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: SI-30800-08 )
- Masterflex Y-connector (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-30614-04 )
- Female Luer 1/16” x 1/16” hose barb (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-45508-00 )
- (2) 1/4” straight barbed connectors (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-30612-13 )
- 1/8” NPT male adapter to 1/16” barb (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-06365-41 )
- 1/8” NPT male adapter to 1/4” barb (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-30704-09 )
- 1/2” NPT Male adapter to 1/4” Hose Barb (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-30704-17 )
- Pipette tips (Eppendorf, catalog numbers: 0030073061 , 0030073100 )
- 20 ml glass scintillation vial with polypropylene cap (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z190535 )
- 16 G 1½ needle (Surgo Surgical Supply, catalog number: 150-305198)
Manufacturer: BD, catalog number: 305198 . - Mice (C57BL/6J; THE JACKSON LABORATORY, catalog number: 000664 ), preferably > 6 weeks old
Notes:- This protocol is suitable for use with other strains, but we recommend users test and determine suitability with their strains.
- If using fear conditioning in conjunction with other techniques, e.g., optogenetics, prepare mice in advance and allow sufficient recovery time prior to training.
- Epoxy (Thorlabs, catalog number: G14250 )
- Mineral oil (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5904 )
- Odorants, e.g., Ethyl Valerate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 290866 )
- Alconox (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 242985 )
Equipment
- Single-channel pipettes (Eppendorf, catalog numbers: 3121000074 and 3121000120 )
- Training chamber (Figure 1B)
- Shock floor (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: H10-11M-TC-SF )
- Training cage (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: H10-11M-TC )
- Metal wall panels (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: H90-00M-M-KT01 )
- 25 ft shock cable (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: H93-01-25 )
- Precision animal shocker (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: H13-15 )
- Testing chamber (custom-made clear Plexiglas chamber, Figure 1C)
- Outer dimensions: 11” x 6” x 5.5” (L x W x H) with 1/2” thick walls.
- A 1/4” thick wall with 2 rows of 6 holes (1/2” dia) beginning ~1/2” from the top to allow air/odor diffusion across the middle wall divides the 11” chamber length in half, such that there are two inner compartments measuring 5” x 5” x 5.5”.
- The chamber has a 1/2” thick lid that can be secured to the chamber by screws.
- The chamber has one 1/2” dia hole on either side of the cage ~1/2” from the top for odor and vacuum lines, respectively.
- USB Cameras (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: ACT-VP-02 )
- Actimetrics USB Digital Interface (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: ACT-712 )
- FreezeFrame 4 adapter cable for Coulbourn hardware (Actimetrics, catalog number: ACT-INTF )
- Isolation cubicle (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: H10-24T )
- Infrared illuminator (Stoelting, catalog number: 60540 )
- Acrylic Flowmeter, 0.1-1 LPM (Cole-Parmer Instrument, catalog number: EW-32460-42 )
- Aquarium air pump, non-UL (Spectrum Brands, Tetra, Whisper®, catalog number: 77851 )
- 2-Channel SPDT Relay Board (Winford Engineering, catalog number: RLY102-12V-DIN )
- 12 V wall power supply for 2-Channel SPDT Relay Board (Winford Engineering, catalog number: WSD050-10-0 )
- Pinch Valves
- 1 Tube Normally Open pinch valve (NResearch, catalog number: 225P021-21 )
- 1 Tube Normally Open pinch valves (NResearch, catalog number: 648P021-82 )
- Olfactory stimulus control (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: H15-03 )
- True HEPA Air Purifier, 390 sq. ft. (Honeywell, model: 50250 )
- Cool Moisture Console Humidifier (Honeywell, model: HCM-6009 )
- Humidity and Temperature Monitor (such as FisherbrandTM TraceableTM Thermometer/Clock/Humidity Monitor, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 06-662-4 )
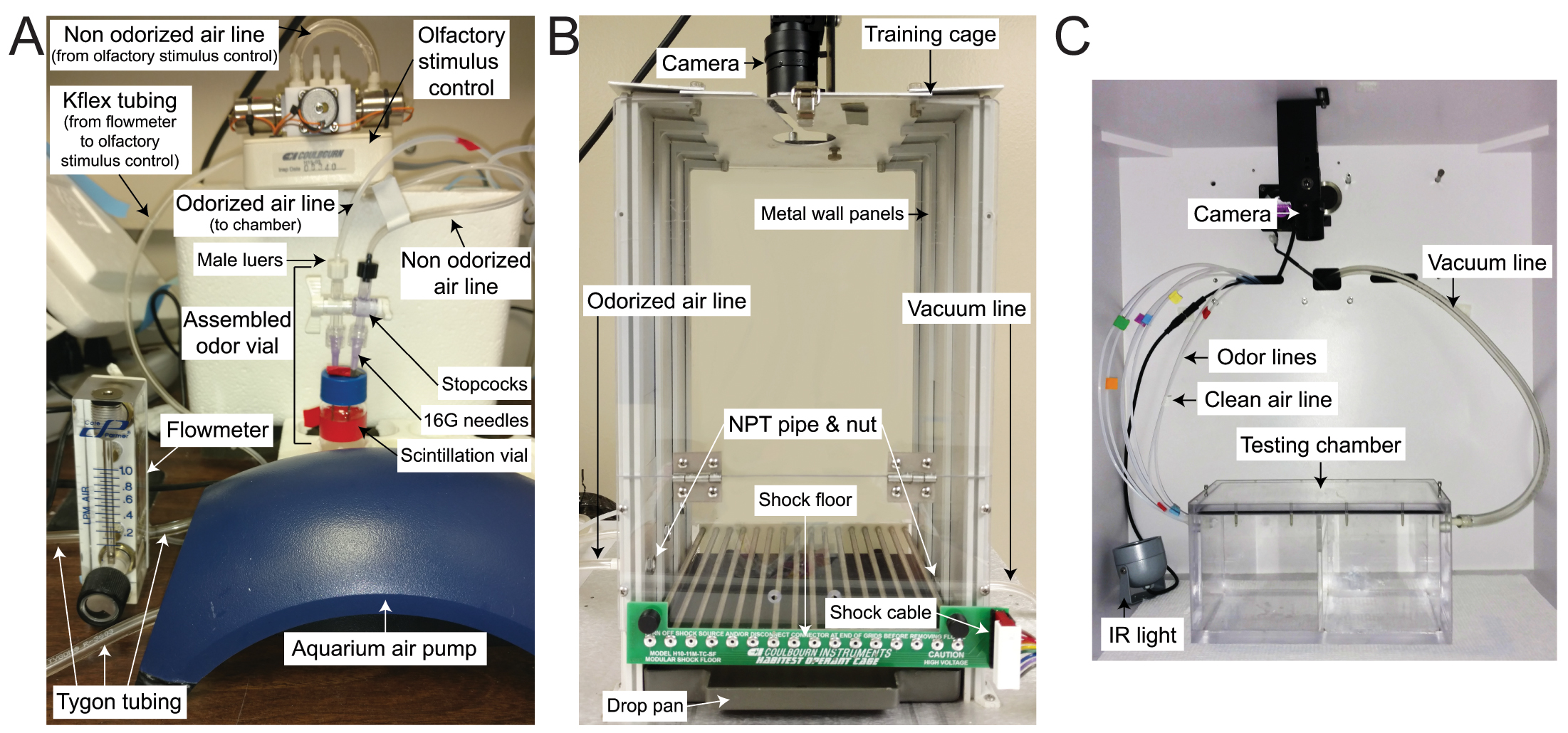
Figure 1. Odor delivery and behavioral chambers. A. The aquarium pump provides air to the flowmeter through Tygon tubing, which is then routed to the olfactory stimulus control for programming delivery. Kflex tubing is attached to the olfactory stimulus control and the non-odorized air stopcock to provide air flow to the assembled odor vial to make odorized air. The odorized air will flow out of the odorized air stopcock and to the attached chamber via additional Kflex tubing. B. The training chamber is modified to add small holes at the left and right of the cage. An NPT pipe is fitted through each hole and secured to the inside of the chamber with a nut. Odorized air lines are attached to the barbed end of the NPT pipe at the left of the cage while a vacuum line is attached to the barbed end of the NPT pipe at the right of the cage, just beneath the shock floor. A camera is positioned above the cage for recording. C. The testing chamber is placed inside the isolation cubicle with an infrared light source positioned on the right of the chamber and a camera mounted above the chamber. Separate tubing carrying clean and odorized air enter the chamber on the left and a vacuum is attached to the right of the chamber to facilitate odor clearance.
Software
- FreezeFrame 4 Software (Coulbourn Instruments, catalog number: ACT-100A)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Ross, J. M. and Fletcher, M. L. (2018). Assessing Classical Olfactory Fear Conditioning by Behavioral Freezing in Mice. Bio-protocol 8(18): e3013. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3013.
- Ross, J. M. and Fletcher, M. L. (2018). Learning-dependent and -independent enhancement of mitral/tufted cell glomerular odor responses following olfactory fear conditioning in awake mice. J Neurosci 38(20): 4623-4640.
分类
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 学习和记忆
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 嗅觉
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link