- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Classic Labyrinth Test for Neurobehavioral Evaluation in Wistar Rats
利用经典迷宫实验对大鼠进行神经行为功能评价
发布: 2018年09月20日第8卷第18期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3007 浏览次数: 6802
评审: Pengpeng LiUdita UpadhyayAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The Classic Labyrinth Test (CLT) is a simple way to evaluate behaviors in rodents such as learning ability, memory, and anxiety. The protocol presented here describes the procedure for use with rats, but the protocol can also be adapted for use in mice if a smaller device is used. In short, the CLT uses a square-shaped maze with a starting point and a stopping point. After the animal is trained, the animal is allowed to view and explore the labyrinth freely for 10 min. During this time, all of the animal's vertical and horizontal movements within the labyrinth are recorded. This is a very challenging task because it requires the animal to remember the quickest path between the starting points and the end. In cases where the labyrinth is designed so that the animal only needs to walk forward, it is quite easy for healthy rats, but for rats exposed to neuro-xenobiotics (drugs, pesticides) there will be disturbances in their path. Researchers use many different versions of this test and the procedure for each version can vary significantly. Here, we present a working protocol that enables the detection of traces of some toxic substances that may be exposed to individuals over a long period and in very small amounts under specific conditions such as drugs, medicines and pesticides.
Keywords: Classic labyrinth (经典迷宫测试)Background
We set out to elucidate how animals memorize and learn when they are challenged with stress utilizing the classical labyrinth test. The CLT is performed in a square-shaped plastic enclosure (125 x 125 x 40 cm) with several labyrinth passages of identical width and height (25 x 35 cm), but with variable length (Figure 1). Usually, this labyrinth is placed on a table 90 cm high. Control rats can quickly move through the labyrinth between the starting point and the ending point. When the animal explores the maze, it increases the time it spends in the maze's passages, which will be considered as aversive or anxiety-provoking for the stressed animal; while the leak behavior will be observed when the animal spends more time in the starting point or corners, which will be associated with a refuge (Leo and Pamplona, 2014; Gasmi et al., 2017b). There are many tests similar to this test, but this test is unique because it is concerned with measuring the impact of environmental pollutants on the behavior and psychology of animals, especially rats (Serchov et al., 2016). Some advantages of this approach are that this test is inexpensive, and it is quick; the test usually takes about 10 min, and after cleaning the labyrinth with 70% ethanol, it can be used to test the next animal (Gasmi et al., 2017a and 2018).
Materials and Reagents
- Paper towels
- Laboratory rats (3 months old and weight between 200 and 240 g)
The rats are housed in groups of 4 per cage and kept in an environment with temperature (23 ± 2 °C) and humidity control. The animals have a 12-12 h light-dark cycle and food and water ad libitum. - Ethanol (70%) for cleaning (CID: 702)
- Plastic sheets (PVC wall panel) (Dacheng, model: DCb-008 )
- Adhesive glue for plastics (SG300-05)
Equipment
- Home cage (Tecniplast, catalog number: 1291H001, EUROSTANDARD TYPE III H, 425 x 266 x 185 mm)
- Classic Labyrinth for rats [a square shaped plastic enclosure (125 x 125 x 40 cm) with several labyrinth passages of identical width and height (25 x 35 cm) but variable length according to the crossing. This Labyrinth can be assembled manually as shown in Figure 1, where it is made of white plastic sheets. These plates are smooth and solid and should be easy to clean and unbreakable or damaged by the animal. The maze is formed at 125 x 125 x 40 cm by welding the plastic sheets together with adhesive glue. According to Figure 1, after the maze is made, it is placed on a wooden table 90 cm high on the ground (Figure 1)]
- USB Camera Lenses (ITEM: 60528/ Lens for 60516, Vari-focal, 2.8-12 mm)
Note: It was placed directly in the middle above the Labyrinth at the height of 1.20 m so that only the labyrinth was exposed. - Chronometer (LCD Digital Portátil Reloj Alarma Temporizador by SYMTOP)
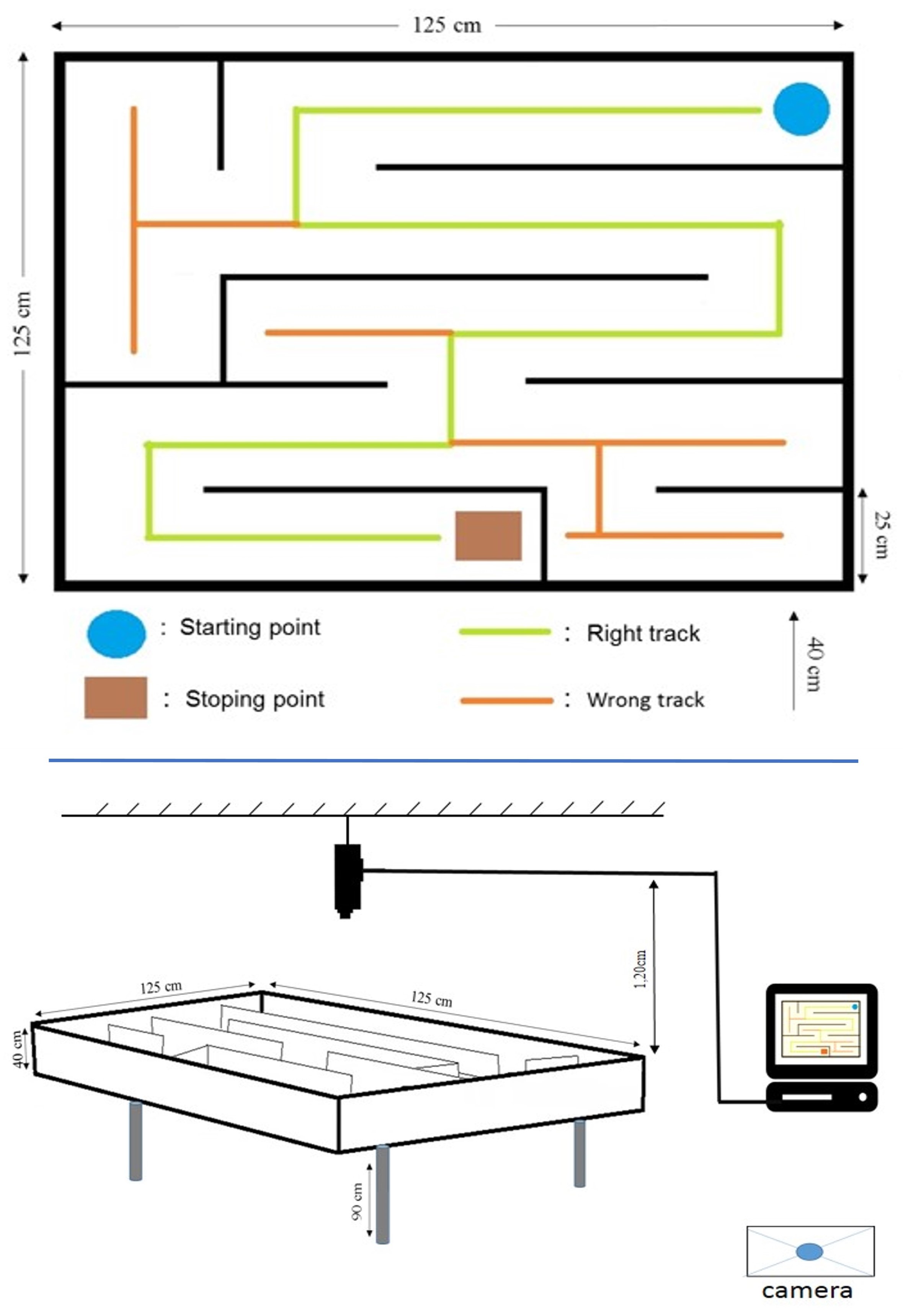
Figure 1. Classic Labyrinth and its dimensions
Software
- Ethovision video tracking system software (version 10, Noldus Information Technology, France)
- Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corp® 2016, USA)
- Minitab (Minitab® version 17.1, USA)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Gasmi, S. (2018). Classic Labyrinth Test for Neurobehavioral Evaluation in Wistar Rats. Bio-protocol 8(18): e3007. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3007.
分类
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 学习和记忆
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 实验动物模型 > 大鼠
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
提问指南
+ 问题描述
写下详细的问题描述,包括所有有助于他人回答您问题的信息(例如实验过程、条件和相关图像等)。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link