- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Mouse Mammary Gland Whole Mount Preparation and Analysis
小鼠乳腺的全胚胎准备和分析
发布: 2018年07月05日第8卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2915 浏览次数: 16931
评审: Vivien Jane Coulson-ThomasSudan PuriMindy Call
Abstract
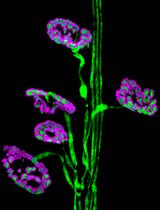
The mammary gland undergoes extensive remodeling during pregnancy and is also subject to neoplastic processes both of which result in histological changes of the gland epithelial structure. Since the mammary tree is a complex three-dimensional structure a method is needed that provides an overview of the entire gland. Whole mounts provide this information, are inexpensive and do not require specialized equipment. This protocol describes mammary gland isolation, whole mount preparation and analysis. Mammary gland tissue, which is removed postmortem, is stained with Carmine Alum, a nuclear stain, allowing detection of epithelial structures embedded in the adipose tissue of the mammary fat pad. Stained mammary glands are imaged by light microscopy or embedded and sectioned for histological examination. Image analysis software such as Image J can be used to quantify extensity of branching complexity, epithelial structure remodeling or hyperplastic changes.
Keywords: Mammary gland (乳腺)Background
Although development of the mammary gland begins during embryonic development and a rudimentary epithelial structure is present at birth, the epithelial mammary tree undergoes extensive expansion postnatally. In response to hormonal changes, mammary epithelial cells proliferate and invade the mammary fat pad. During pregnancy, the mammary gland epithelium undergoes further differentiation and remodeling to prepare for milk production. Subsequently, these epithelial structures involute in response to weaning. These remodeling processes are driven by hormones, growth factors, cytokines and the extracellular matrix. In addition to remodeling in response to physiological processes, the mammary gland is subject to pathological processes such as neoplastic transformation. This complex biology together with the relatively ease of isolation make the mammary gland a useful experimental model. Experimental studies analyzing mammary gland biology or neoplastic transformation often employ mouse models to quantify the effect of gene deletion or overexpression on mammary gland development, remodeling and neoplastic transformation. Mammary gland whole mounts allow routine examination of these normal and disease processes on the entire 3D epithelial structure of the mammary gland (Plante et al., 2011; Inman et al., 2015; Tucker et al., 2016 and 2017; Kolla et al., 2017; Tolg et al., 2017). Furthermore, injection of mice with potential therapeutic compounds combined with whole mount analysis allows in vivo testing of future cancer treatment strategies. This protocol provides details of the procedure starting with removal of the mammary gland and ending with image analysis. A video of mammary gland isolation, photos, figures and referenced literature make it more complete compared to existing whole mount protocol.
Materials and Reagents
- Glass slide (Micro Slides Superfrost Plus) (VWR, catalog number: 48311-703 )
- Micro cover glass (VWR, catalog number: 48393-081 )
- Glass Pasteur pipette (VWR, catalog number: 14672-380 )
- Glass Slide Staining Dish (DWK Life Sciences, WheatonTM, catalog number: 900200 )
- Coplin Staining Dish (Variety Glass, catalog number: 674EMD )
- 50 ml Crew Cap tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 62.547.254 )
- Mice
- 100% ethanol (Greenfield Global, Commercial Alcohols, catalog number: P016EAAN )
- Glacial acetic acid (Merck, catalog number: AX0073-9 )
- Carmine dye: Carmin Alum (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C579-25 )
- Aluminum potassium dodecahydrate (Merck, catalog number: 101042 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl, Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H1758 )
- Xylene (LabChem, catalog number: LC269704 )
- Permount SP15 (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SP15-100 )
- Carnoy’s solution (see Recipes)
- Carmine alum solution (see Recipes)
- Destaining solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Small scissors (Delicate dissecting scissors, Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 08-951-5 ; Sharp-pointed dissecting scissors, Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 08-940 )
- Forceps (Fisherbrand curved medium point general purpose forceps)
- Chemical hood (Fisher Scientific)
- Dissecting microscope with digital camera (Q color 3 camera, OLYMPUS, model: SZX 12 )
- Stirring Hotplate (Fisher Scientific)
- Weighing scale (Denver Instrument, model: XS-310D, catalog number: 8531.1 )
- pH meter (Fisher Scientific, Accumet Research, model: AR15 , catalog number: 13-636-AR15)
Software
- ImageJ: free download available at https://imagej.nih.gov/ij
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Tolg, C., Cowman, M. and Turley, E. A. (2018). Mouse Mammary Gland Whole Mount Preparation and Analysis. Bio-protocol 8(13): e2915. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2915.
分类
发育生物学 > 形态建成 > 器官形成
癌症生物学 > 通用技术 > 肿瘤形成
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 组织染色
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link