- EN - English
- CN - 中文
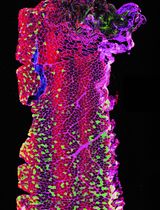
Imaging Cytokine Concentration Fields Using PlaneView Imaging Devices
使用PlaneView成像装置对细胞因子浓度视野进行成像
发布: 2018年04月05日第8卷第7期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2788 浏览次数: 7431
评审: Ivan ZanoniMarco Di GioiaAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
用于比较人冷冻保存 PBMC 与全血中 JAK/STAT 信号通路的双磷酸化 CyTOF 流程
Ilyssa E. Ramos [...] James M. Cherry
2025年11月20日 2328 阅读
Abstract
We describe here a method to visualize concentration fields of cytokines around cytokine-secreting cells. The main challenge is that physiological cytokine concentrations can be very low, in the pico-molar range. Since it is currently impossible to measure such concentrations directly, we rely on cell’s response to the cytokines–the phosphorylation of a transcription factor–that can be visualized through antibody staining. Our devices aim at mimicking conditions in dense tissues, such as lymph nodes. A small number of secreting cells is deposited on a polylysine-coated glass and covered by multiple layers of cytokine-consuming. The cells are left to communicate for 1 h, after which the top layers are removed and the bottom layer of cells is antibody labeled for the response to cytokines. Then a cross-section of cytokine fields can be visualized by standard fluorescence microscopy. This manuscript summarized our method to quantify the extent of cytokine-mediated cell-to-cell communications in dense collection of cells in vitro.
Keywords: Cytokine concentration (细胞因子浓度)Background
The mammalian immune system has evolved to identify and limit the spread of potential pathogens while minimizing collateral tissue damage caused by the immune system itself. To achieve this, immune cells rely on a network of cytokine mediators that enable cell-to-cell communications and broadcast information about the magnitude and nature of the pathogenic insult. Vast arrays of different cytokines bind strongly to their cognate receptors, often with characteristic binding affinities in the nano- or pico-molar range. Immunological niches are generated via cytokine communications. For example, in both the bone marrow and the thymus, secretion of Interleukin-7 (IL-7) by stromal cells supports the survival of proliferating B and T cell progenitors, respectively (Tokoyoda et al., 2004; Alves et al., 2009). The size of the cytokine niche controls the number of maturing progenitors, thereby keeping the blood cell compartments in equilibrium (Böyum, 1968; Weist et al., 2015).
We aim to collect information about the spatial and temporal dynamics of cytokines and how these two parameters influence the immune response. This is an area of immunology that is currently under-studied. Many assays test the effects of cytokines in tissue-culture dishes, where media is well-mixed, leading to homogeneous fields of growth and differentiation factors. The intricate and highly specialized architecture of the secondary lymphoid organs sets up niches where cells sense stimuli such as pathogen components and cytokines, proliferate, mature, differentiate, and die. Cytokine concentration gradients are formed within these niches such that some cells have greater or lesser access to cytokines than others (Liu et al., 2015). Measuring how far cytokines spread from their source, and the gradients they form, is key to unravelling the mechanism of the phenotypic heterogeneity of immune cells in differentiation, proliferation, and death (Feinerman et al., 2010; Busse et al., 2010; Höfer et al., 2012; Müller et al., 2012; Thurley et al., 2015).
Due to the typically low concentrations (pM range) of free cytokines in vivo, direct measurement of cytokine fields is difficult at best and maybe impossible. However, due to their high sensitivity to cytokine and graded, concentration-dependent response, the signaling levels of cells in response to cytokines can itself be used as a bio-sensor for cytokine concentrations (Oyler-Yaniv et al., 2017).
In this protocol, we describe how to directly image the signaling response generated around a cytokine producer in vitro, in conditions that mimic in vivo conditions: high cell density and no convection. Our method is general and can be applied to any cell type and any diffusible stimulus, and only depends on the existence of a specific antibody to target the downstream signaling molecule of interest and/or of live cell reporters.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (USA Scientific, catalog numbers: 1111-1806 , 1111-3800 )
- CELLSTAR Filter Cap Cell Culture Flasks T75 (Greiner Bio One International, catalog number: 658175 )
- 15 ml tube
- Glass slides (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 4951PLUS4 )
- Coverslips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 25X25-1 )
- Silicone rubber compound (PDMS) (Momentive, catalog number: RTV615 )
- PVP-treated PCTE Membranes, 13 mm diameter, 400 nm pore (Sterlitech, catalog number: PCT0413100 )
- B16-F10 melanoma cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-6475 )
- Mouse CD4 (L3T4) MicroBeads (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-049-201 )
- Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P1585-1MG )
- Ionomycin calcium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I0634-1MG )
- Ficoll-paque plus (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17144003 )
- Recombinant mouse IL-2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, eBioscienceTM, catalog number: 14-8021-64 )
- Recombinant human IL-2 (gift from Dr. Kendall A. Smith, Cornell University)
- Trypsin/EDTA solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: R001100 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4417 )
- Glycine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 50046 )
- Ovalbumin peptide SIINFEKL (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7951-1MG )
- Cell Trace Far-Red (DDAO-SE) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: C34564 )
- Poly-L-lysine solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8920-100ML )
- Paraformaldehyde solution, 4% in PBS (Alfa Aesar, Affymetrix, catalog number: J19943 )
- Methanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: MX0490-4 )
- Fluoromount Aqueous Mounting Medium (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F4680-25ML )
- Triton 100-X (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 0230022101-1l )
- α-CD4, Alexa700, Pacific Blue (BD Bioscience clone RM4-5, BD, catalog numbers: 557956 , 558107 )
- α-IL-2Rα, PE (Miltenyi Biotec clone 7D4, Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-102-593 )
- Primary antibody rabbit α-phospho-STAT5 (pY694) (Cell Signaling clone C71E5, Cell Signaling Technology, catalog number: 9314S )
- Primary antibody rabbit α-phospho-STAT1 (pY701) (Cell Signaling clone 58D6, Cell Signaling Technology, catalog numbers: 9167L )
- Secondary polyclonal antibody α-rabbit IgG, Alexa 488 (Jackson ImmunoResearch, catalog number: 711-176-152 )
- RPMI 1640 media with L-glutamine (Biological Industries, catalog number: 01-100-1A )
- Heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (Biological Industries, catalog number: 04-127-1A )
- HEPES buffer (Biological Industries, catalog number: 03-025-1B )
- Non-essential amino acids (Biological Industries, catalog number: 01-340-1B )
- Sodium pyruvate (Biological Industries, catalog number: 03-042-1B )
- Penicillin-streptomycin solution (Biological Industries, catalog number: 03-031-5B )
- β-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3148-25ML )
- Complete RPMI (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes
- Heraeus centrifuge with microplate swinging rotor (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: HeraeusTM BiofugeTM StratosTM )
- Zeiss Axiovert 200M microscope (ZEISS, model: Axiovert 200M )
Software
- MATLAB, Mathworks Inc.
- LabVIEW, National Instruments
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Oyler-Yaniv, A. and Krichevsky, O. (2018). Imaging Cytokine Concentration Fields Using PlaneView Imaging Devices. Bio-protocol 8(7): e2788. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2788.
分类
免疫学 > 免疫细胞功能 > 细胞因子
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 共聚焦显微镜
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link