- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Cytosolic and Nuclear Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9-ribonucleoprotein for Gene Editing Using Arginine Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles
使用精氨酸功能化金纳米粒子进行CRISPR/Cas9-核糖核蛋白的细胞溶质和细胞核递送以用于基因编辑
发布: 2017年10月20日第7卷第20期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2586 浏览次数: 13195
评审: David CisnerosAndrea PuharAnonymous reviewer(s)

相关实验方案
利用EpiCRISPR系统通过靶向DNA甲基化诱导Alpha TC1-6细胞产生胰岛素
Marija B. Đorđević [...] Melita S. Vidaković
2025年10月20日 1231 阅读
Abstract
In this protocol, engineered Cas9-ribonucleoprotein (Cas9 protein and sgRNA, together called Cas9-RNP) and gold nanoparticles are used to make nanoassemblies that are employed to deliver Cas9-RNP into cell cytoplasm and nucleus. Cas9 protein is engineered with an N-terminus glutamic acid tag (E-tag or En, where n = the number of glutamic acid in an E-tag and usually n = 15 or 20), C-terminus nuclear localizing signal (NLS), and a C-terminus 6xHis-tag. [Cas9En hereafter]
To use this protocol, the first step is to generate the required materials (gold nanoparticles, recombinant Cas9En, and sgRNA). Laboratory-synthesis of gold nanoparticles can take up to a few weeks, but can be synthesized in large batches that can be used for many years without compromising the quality. Cas9En can be cloned from a regular SpCas9 gene (Addgene plasmid id = 47327), and expressed and purified using standard laboratory procedures which are not a part of this protocol. Similarly, sgRNA can be laboratory-synthesized using in vitro transcription from a template gene (Addgene plasmid id = 51765) or can be purchased from various sources.
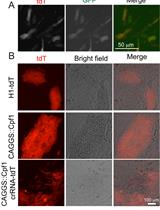
Once these materials are ready, it takes about ~30 min to make the Cas9En-RNP complex and 10 min to make the Cas9En-RNP/nanoparticles nanoassemblies, which are immediately used for delivery (Figure 1). Complete delivery (90-95% cytoplasmic and nuclear delivery) is achieved in less than 3 h. Follow-up editing experiments require additional time based on users’ need.
Synthesis of arginine functionalized gold nanoparticles (ArgNPs) (Yang et al., 2011), expression of recombinant Cas9En, and in vitro synthesis of sgRNA is reported elsewhere (Mout et al., 2017). We report here only the generation of the delivery vehicle i.e., the fabrication of Cas9En-RNP/ArgNPs nanoassembly.
Background
Delivery of Cas9-ribonucleoprotein provides an alternative strategy for CRISPR gene delivery, offering a transient way of editing genes. Although a few strategies for Cas9-RNP delivery have been reported, these strategies suffer from endosomal entrapment of both Cas9 protein and sgRNA (Liu et al., 2015). Mechanical methods including membrane deformation (Han et al., 2015), electroporation (Schumann et al., 2015), and the use of hypertonic agents (D’Astolfo et al., 2015) provide direct delivery, however, they require specialized instrumentations and are generally not practical for in vivo therapeutic applications. Our protocol provides an approach for direct cytoplasmic and nuclear delivery of Cas9-RNP that can find applications in both gene editing and genome imaging.
Materials and Reagents
- Round bottom 35 mm confocal dish (MATTEK, catalog number: P35G-0-14-C )
- 24-well plates (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 3524 )
- Sterile 1.5 ml tubes (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 05-408-129 )
- Sterile pipette tips
- Cell lines (i.e., HeLa)
- Stock solution of ArgNP gold nanoparticles (~50 μM in water), freshly purified Cas9En protein (~10-20 μM), and sgRNA (~150 μM)
- 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (GE Healthcare, HyCloneTM, catalog number: SH30028.02 )
- Plain DMEM media (No serum and antibiotics, appropriate media for cell culture, i.e., HeLa cells) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10567014 )
- Alexa Fluor 488 NHS Ester (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: A20000 )
- AmpliScribe T7-Flash- Transcription Kit (Epicentre, catalog numbers: ASF3257 and ASF3507 )
Equipment
- Pipettes
- Cell culture incubator at 5% CO2 and 37 °C
- Fluorescence microscope (any confocal microscope)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Mout, R. and Rotello, V. M. (2017). Cytosolic and Nuclear Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9-ribonucleoprotein for Gene Editing Using Arginine Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Bio-protocol 7(20): e2586. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2586.
分类
细胞生物学 > 细胞工程 > CRISPR-cas9
分子生物学 > DNA > DNA 修饰
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link