- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Using CRISPR/Cas9 for Large Fragment Deletions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
利用CRISPR/Cas9对酿酒酵母基因组进行大片段敲除
发布: 2017年07月20日第7卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2415 浏览次数: 14168
评审: Daan C. SwartsKabin XieAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9) systems have emerged as a powerful tool for genome editing in many organisms. The wide use of CRISPR/Cas9 systems may be due to the fact that these systems contain a simple guide RNA (sgRNA) that is relatively easy to design and they are very versatile with the ability to simultaneously target multiple genes within a cell (Varshney et al., 2015). We have developed a CRISPR/Cas9 system to delete large genomic fragments (exceeding 30 kb) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. One application of this technology is to study the effects of large-scale deletions of non-essential genes which may give insight into the function of gene clusters within chromosomes at the molecular level. In this protocol, we describe the general procedures for large fragment deletion in S. cerevisiae using CRISPR/Cas9 including: how to design CRISPR arrays and how to construct Cas9-crRNA expression plasmids as well as how to detect mutations introduced by the system within S. cerevisiae cells.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9 system (CRISPR/Cas9系统)Background
The CRISPR/Cas9 system is a rapid, efficient, low-cost, and versatile method for genome editing that can be applied in the fields of biology, agriculture, and medicine. To date, several protocols have been reported on how to make large-scale deletions within genomes. Each of these methods contains its own unique characteristics and advantages. The recently developed CRISPR/Cas9 system for excising large stretches of chromosomes has potential advantages over other methods such as the Latour system (Hirashima et al., 2006). The CRISPR/Cas9 system requires two components: (1) the Cas9 endonuclease for DNA cleavage and (2) a variable guide RNA (gRNA) that directs the Cas9 enzyme in a DNA sequence-specific manner (Cong et al., 2013). When Cas9 is targeted to a genomic locus by a gRNA, Cas9 initiates a DSB. The cell will respond to the DSB by repairing the damage via one of two major pathways: high-fidelity homology-dependent repair or error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ).
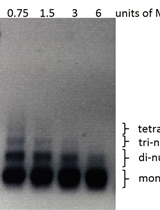
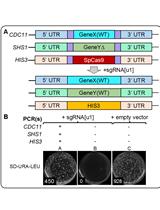
The CRISPR/Cas9 system described here requires four components: Cas9 endonuclease, CRISPR array, trans-activating crRNA (tracrRNA), and RNase III (this activity is present in the host cell). The CRISPR array is a genomic locus from which pre-crRNAs are transcribed. In this system, the CRISPR array, engineered on the pCRCT plasmid, expresses multiple spacers flanked by direct repeats driven by a single promoter. Cas9 cannot be targeted by crRNA alone, it requires a crRNA-tracrRNA duplex to target it to a specific site within the genome. Two DNA oligonucleotides that encode for spacer sequences interspaced by a direct repeat (DR) were directly synthesized. The formed dsDNA encoding the crRNA was cloned into a Cas9 expression vector. Once the desired plasmid is constructed, transform S. cerevisiae with it and screen the transformants to obtain mutants with large genomic fragment deletions. In this protocol, the deletion efficiency (10%) is lower than described for deletion of genomic fragments using CRISPR/Cas9 in rice (Zhou et al., 2014). There are two possible reasons. The first one is that the genome may be repaired more rapidly in S. cerevisiae in comparison with that in rice. Another one is a stronger selection pressure used for screening rice transformants. In rice, the selection marker for transformants is hygromycin B, while in yeast Uracil as a selection marker is employed. The stronger selection pressure possibly increase the plasmid copy numbers in rice cells.
Materials and Reagents
- Escherichia coli: DH5ɑ (sanyou Biopharmaceuticals)
- S. cerevisiae strain: W303 (MATa ura3-52)
- pCRCT plasmid (Addgene, catalog number: 60621 )
- Salmon DNA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D1626 )
- Restriction enzyme: 10 U/μl Bsal (Takara Bio)
- 10x buffer G (Takara Bio)
- Taq DNA polymerase (Takara Bio)
- Antibiotic: 100 µg/ml ampicillin (Siyao)
- Pure plasmid mini kit (CWBIO)
- Yeast Gen DNA Kit (CWBIO)
- DNA oligonucleotide primers (GENEWIZ)
- PEG: Poly (ethylene glycol), BioXtra avg. molecular weight 3,350 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3640 )
Note: This product has been discontinued.
- Yeast extract (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0021 )
- Tryptone (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0042 )
- Dextrose
- Agar (Solarbio, catalog number: A8190 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent)
- Peptone
- Primers
CasYZF: 5’---ACGCTGTAGAAGTGAAAGTTGG---3’
CasYZR: 5’---TAGTATGCTGTGCTTGGGTGTT---3’
- Glucose (Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent)
- Adenine (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Lithium acetate dihydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L6883-1KG )
- Agarose gel recovery kit (Biomiga)
- YPD liquid media (see Recipes)
- LB plates (with appropriate antibiotics included) (see Recipes)
- YPDA liquid medium (see Recipes)
- SC medium without uracil (see Recipes)
Equipment
- PCR machine (or similar) (Biometra, model: TPfofessional )
- 42 °C water bath (or similar) (XINBAO, catalog number: HH-501BS )
- DNA electrophoresis apparatus (or similar) (SIM International, model: BIO-PRO 200E , catalog number: 0401RHSI049)
- Microcentrifuge (SCILOGEX, model: D2012 )
- Incubator (or similar, capable of incubation of agar plates at 37 °C or 28 °C) (CIMO, model: DNP-III )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Hao, H., Huang, J., Liu, T., Tang, H. and zhang, L. (2017). Using CRISPR/Cas9 for Large Fragment Deletions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bio-protocol 7(14): e2415. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2415.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物遗传学 > 诱/突变
微生物学 > 微生物遗传学 > DNA > 染色体
细胞生物学 > 细胞工程 > CRISPR-cas9
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link