- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Implantation of Human Peripheral Corneal Spheres into Cadaveric Human Corneal Tissue
将人外周角膜球体植入尸体人角膜组织
发布: 2017年07月20日第7卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2412 浏览次数: 7702
评审: Federica PisanoAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
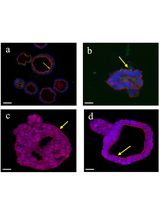
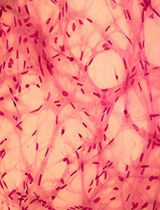
Stem and progenitor cells isolated from human limbal tissue can be cultured in vitro as spheres. These spheres have potential for use as transplantable elements for the repopulation of corneal tissue (Mathan et al., 2016). Herein we describe the detailed protocol for the implantation of human corneal spheres into cadaveric human corneal tissue. This protocol describes the procedure for sphere formation and culture, preparation of tissue for sphere implantation, corneal limbus microsurgery and sphere implantation.
Keywords: Cell Culture (细胞培养)Background
Previous research has focused on isolation of limbal cells which were exclusively epithelial (limbal stem cell) or stromal (keratocyte progenitor cell) in order to decipher their individual roles in corneal homeostasis and wound repair. This protocol aims to isolate limbal cells by their functional ability to form spheres in culture and which by their very nature will include a diversity of cells both epithelial and stromal which contribute to the formation of the limbal niche. Subsequent to isolation of these spheres we are investigating their potential use in corneal restoration after implantation. Here we describe an in-vitro surgical protocol for the implantation of these spheres into human corneal tissue and the downstream analysis.
Materials and Reagents
- Scalpel blade (ProSciTech, profile 11) (Swann Morton, catalog number: LSB11 )
- 20 x 100 mm cell culture dish (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 353003 )
- Cotton buds (Cotton Tips double ended, Protec Solutions, catalog number: 941001690389 )
- Transfer pipette (3 ml) (Interlab, catalog number: KJ622-1A )
- 5 ml tubes (Techno Plas, catalog number: P5016UL )
- 40 µm strainer (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352340 )
- Glass coverslips (covergalss #1 30 mm diam.) (PST, catalog number: G430 )
- 6-well tissue culture plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 140675 )
- 35 x 10 mm cell culture dish (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 353001 )
- Fresh and frozen human cadaveric donor corneoscleral tissue obtained post-surgery from the New Zealand National Eye Bank
- 70% ethanol (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 1009832500 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) sterile (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4417-100TAB )
- Phosphate buffered saline and 10% glycerol (AnalaR NORMAPUR) (VWR, catalog number: 24388.320 )
- Dispase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 17105041 )
- Collagenase (Blend Type L) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C8176 )
- Hyaluronidase (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3506 )
- Neurobasal-A Medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10888022 )
- Human Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) (PeproTech, catalog number: AF-100-15 )
- Human Fibroblastic Growth Factor (FGF) Basic (PeproTech, catalog number: 100-18B )
- B-27 Supplement, 50x (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12587010 )
- N-2 Supplement, 100x (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 17502048 )
- GlutaMAX, 100x (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 35050061 )
- MEM with GlutaMAX (Minimum Essential Medium) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 41090036 )
- Foetal bovine serum (New Zealand origin) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10091148 )
- Antibiotic/Antimycotic 100x (Anti/Anti) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15240062 )
- Supplemented Neurobasal-A medium (see Recipes)
- Standard culture medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Tissue culture hood (Heal Force, model: HFsafe 1800 )
- Straight scissors (World Precision Instruments, catalog number: 500216 )
- Fine forceps (World Precision Instruments, catalog number: 14142 )
- Orbital shaker (Ratek Instruments, model: MM1 )
- Centrifuge (Sigma Laborzentrifugen, model: 3-15 )
- Tissue culture incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: HereausTM HeraCell 150 )
- Laminar flow cabinet (Gelman, model: HLF 120 )
- Binocular Stereo microscope (Carl Zeiss, catalog number: 474110-9904 )
- Biological safety cabinet (Email Air Handling, catalog number: 1687-2340-618-3 )
- 2-20 µl Eppendorf® Pipette (Eppendorf, catalog number: 3120000038 )
- Feather MicroScalpel (pfm medical, catalog number: 200300715 )
- Crescent Bevel Up Ophthalmic Knife 2.3 mm (MANI, catalog number: MCU26 )
- NIKON Digital sight DS-UI camera (Nikon Instruments, model: DS-UI )
- Leica DMIL inverted contrasting microscope (Leica Microsystems, model: Leica DMIL )
- Leica DM-RA upright fluorescence microscope (Leica Microsystems, model: Leica DM-RA )
Software
- NIS-Elements Br Microscope Imaging Software version 3.0
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Mathan, J. J., Ismail, S., McGhee, J. J. and Sherwin, T. (2017). Implantation of Human Peripheral Corneal Spheres into Cadaveric Human Corneal Tissue. Bio-protocol 7(14): e2412. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2412.
分类
干细胞 > 成体干细胞 > 细胞移植
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 3D细胞培养
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link