- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Delayed-matching-to-place Task in a Dry Maze to Measure Spatial Working Memory in Mice
采用日间迷宫中延迟位置匹配任务来衡量小鼠的空间工作记忆
发布: 2017年07月05日第7卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2389 浏览次数: 8926
评审: Soyun KimEdel HennessyAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The delayed-matching-to-place (DMP) dry maze test is a variant of DMP water maze (Steele and Morris, 1999; Faizi et al., 2012) which measures spatial working/episodic-like learning and memory that depends on both hippocampal and cortical functions (Wang and Morris, 2010; Euston et al., 2012). Using this test we can detect normal aging related spatial working memory decline, as well as trauma induced working memory deficits. Furthermore, we recently reported that fractionated whole brain irradiation does not affect working memory in mice (Feng et al., 2016). Here we describe the experimental setup and procedures of this behavioral test.
Keywords: DMP dry maze (DMP干迷宫)Background
The reference-memory water maze (RMW) was originally used to measure spatial reference memory in rats. In this task animals are trained to find a hidden platform in a fixed location under opaque water by using distal clues outside of the water maze (Morris, 1981). Over the years it has evolved into various tasks, that allow probe trials, over training, reverse learning and an on-demand platform (Morris et al., 1982; Morris et al., 1990; Spooner et al., 1994; Lipp and Wolfer, 1998). Later the Morris lab developed a delayed matching-to-place (DMP) water maze that requires frequently updated, ‘delayed’ memory of escape locations in an unchanging environment (Steele and Morris, 1999). These variations of Morris water maze (MWM) are widely used in the neuroscience field to study spatial cognitive functions that involve different brain regions in both rats and mice (Vorhees and Williams, 2006). The main concern for these tests is that forced swimming might induce stress for animals (Vorhees and Williams, 2014). To exclude this limitation, Faizi et al. (2012) designed a dry maze based on the principles of the DMP water maze. The DMP dry maze is believed to measure the same working/episodic-like memory as the DMP water maze with a less intense test paradigm for both the experimenter and test subjects.
Materials and Reagents
- Paper towels (Renown, catalog number: REN06116-WB )
- Red paper towels (KCWW, Kimberly-Clark, catalog number: 05930 )
- C57BL/6J male adult mice (3-18 months of age)
Note: C57BL/6J male adult mice (3-18 months of age) housed in a room with reversed light cycle for at least two weeks prior to test. Behavior experiment is conducted during the dark cycle (7 AM-7 PM, see Note 1). - 70% ethanol (v/v in ddH2O) in a spray bottle
Equipment
- A well-lit (1,200 lux) behavior room isolated from noises and a close-by holding room (Figure 1A)
- White shower curtains (Figures 1B and 1C)
- Two large visual clues (Figures 1B and 1C)
- A Polystyrene circular DMP dry maze platform (Diameter = 122 cm, thickness = 1.2 cm) with 40 escape holes (D = 5 cm)
Note: 16 holes on the outer ring, 16 on the middle ring and 8 holes on the inner ring with distance of 50, 35 and 20 cm to the center of platform, respectively (Figure 1B). ABS tubes (Inner diameter = 52 mm, outer diameter = 60 mm) are attached to each escape hole which allows easy attach and detach of the escape tube (Figure 1D). It is important to use black or dark colored escape tube so mice would prefer to enter. In addition, dark color minimizes the chance of leaving visual clues around escape holes over time. - A 3” ABS plug (NIBCO, catalog number: 5818 )
- Escape tube assembled using black ABS pipes (2”, NIBCO, catalog numbers: C5806-2 and C5807-V Figure 1E) with a removable plug (to be attached to escape holes) at the other end (NIBCO, catalog number: 5818 , Figure 1F). When connected to the escape hole, the resulting depth from the top pf maze to the floor of escape tube is about 8 cm
- A metal stand to support the platform to 90 cm above the floor (Figure 1 D)
- A small non-transparent transfer box
Note: We use a pipette tip box without the lid (Figure 1I). - Fish net with extended handle or a similar item (Figure 1I)
- Timer
- Speakers capable of playing at 85 dB or louder (Figure 1B)
- Noise-cancelling headphones or similar items (Figure 1I)
- Overhead camera (GigE, catalog number: XCFS-BC6o# )
- A computer (with Windows 7 64bit Professional) connected to the camera
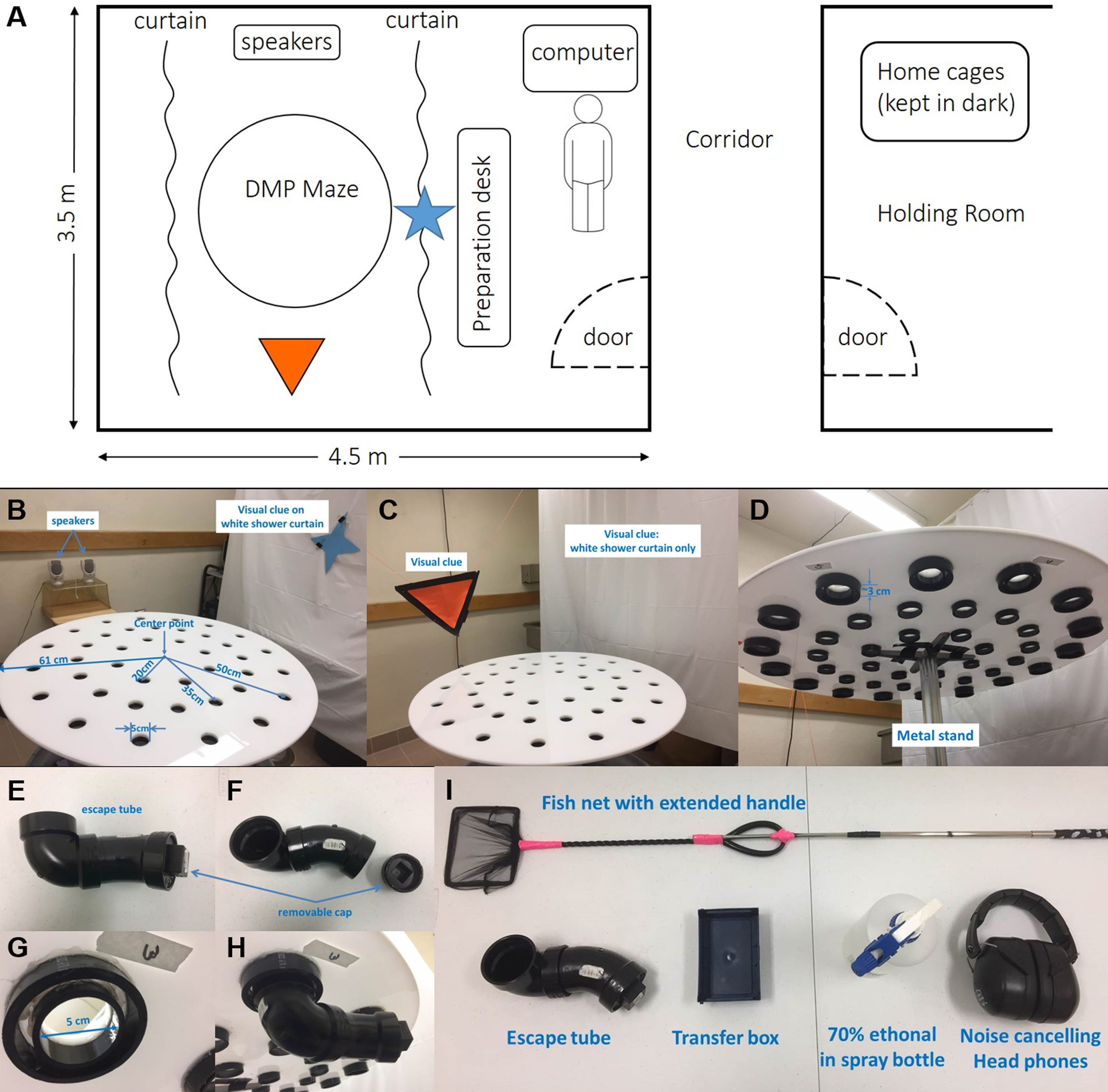
Figure 1. Platform and room setup. A. Sketch of the behavior room and holding room layout; B. A picture showing the details of platform layout and visual clues on two sides of the platform; C. A picture of visual clues on other two sides; D. A picture showing the bottom of platform; E-H. Pictures to show the escape tube, an escape hole and how they are connected; I. Other items needed for the task.
Software
- Recording and tracking software (Noldus, Ethovision XT v 11.5.1026)
- Audio file of a recorded tone at 960 Hz with > 90 sec length (audio file 1)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Feng, X., Krukowski, K., Jopson, T. and Rosi, S. (2017). Delayed-matching-to-place Task in a Dry Maze to Measure Spatial Working Memory in Mice. Bio-protocol 7(13): e2389. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2389.
分类
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 学习和记忆
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












