- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Stereotaxic Surgery for Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Lesions in Mice
立体定向外科手术治疗小鼠视交叉上核病变
发布: 2017年06月20日第7卷第12期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2346 浏览次数: 19376
评审: Xi FengXiaoyu LiuHélène M. Léger

相关实验方案
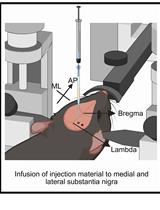
基于 rAAV-α-Syn 与 α-Syn 预成纤维共同构建的帕金森病一体化小鼠模型
Santhosh Kumar Subramanya [...] Poonam Thakur
2025年12月05日 1637 阅读
Abstract
Site-specific lesions are invaluable methods for investigating the function of brain regions within the central nervous system and can be used to study neural mechanisms of behaviors. Precise stereotaxic surgery is required to lesion small regions of the brain such as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which harbors the master circadian clock. In this protocol, we describe stereotaxic surgery optimized for bilateral lesion of the mouse SCN by loading electric current. Success of the SCN lesion is verified histologically and behaviorally by monitoring arrhythmic locomotor activity. The SCN-lesioned mouse allows for the evaluation of behavioral, biochemical, and physiological consequences of ablation of the master circadian clock.
Keywords: Suprachiasmatic nucleus (视交叉上核)Background
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a small region within the hypothalamus of the mammalian brain. It is positioned bilaterally above the optic chiasm and contains approximately 20,000 neurons. The SCN is known as the location of the master circadian oscillator (clock) and is required for synchronization with the light-dark cycle. Ablation of the SCN is a useful strategy for assessing the physiological influence of the master circadian clock.
An electrolytic lesion of the SCN has advantages that enable fast and localized ablation of the master circadian clock in comparison to gene modification by virus injection or SCN-specific promoters. Location of the lesion by electrical impulse can be verified right after surgery by Nissl staining, and monitoring activity rhythm can be started one day after the surgery. In addition, lesion by administration of chemicals often results in non-specific damage and thus it is not as precise as lesion by electrical impulse, especially for small targets such as SCN. Therefore, this protocol provides a useful strategy to evaluate effects (outputs) of master circadian clock.
Materials and Reagents
- Adult mouse (C57BL/6J, usually 8-14 weeks old)
- Ketamine (Daiichi Sankyo Propharma, Ketalar for intramuscular injection 500 mg)
- Xylazine (Bayer, Serakutaru 2% injection)
- Bacteriostatic saline (Otsuka pharmaceutical, 20 ml ampoule)
- 70% ethanol
- For confirmation of SCN-lesioning
- Glacial acetic acid
- 0.2% cresyl violet acetate solution (see Recipes)
- Filter paper
- Glacial acetic acid
Equipment
Note: Refer to Figures 1, 2, 3 for the Equipment used in this protocol.
- Stereotaxic frame (NARISHIGE, model: SR-6M-HT )
- Stereotaxic micromanipulator (NARISHIGE, model: SM-15R/L )
- Wide-field dissecting microscope (ZEISS, model: Stemi 2000 ) with boom stand
- Cold light source (ZEISS, model: CL 1500 ECO )
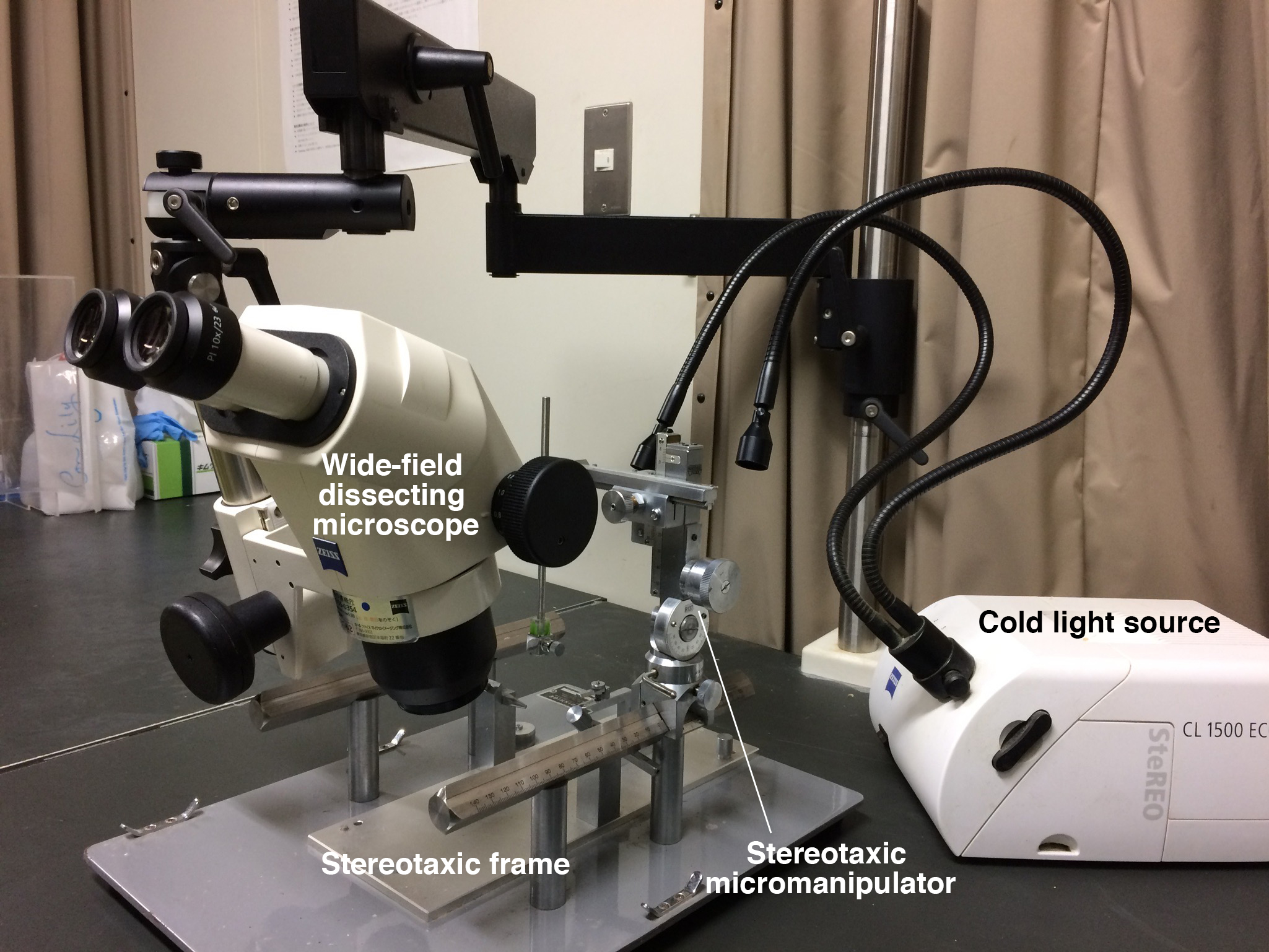
Figure 1. Equipment list 1-4 - Auxiliary ear bar (NARISHIGE, model: EB-5N )
- Scissors (e.g., Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 14068-12 )
- Scalpel (FEATHER Safety Razor, catalog number: No.11 )
- Surgical needle with suture (e.g., NATSUME SEISAKUSHO, catalog number: C21-40 )
- Hemostats (e.g., Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 13008-12 )
- Forceps (e.g., Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11009-13 or 11008-13 )
- Tuberculin syringe with needle (e.g., Terumo Medical, catalog numbers: SS-01T and NN-2719S )
- Razor (e.g., FEATHER Safety Razor, catalog number: FAS-10 )
- Cotton swabs (e.g., Q-tip)
- Heating pad (e.g., electric heating pad for pets)
- Hand drill with engraving cutter (DREMEL, model: 106 )
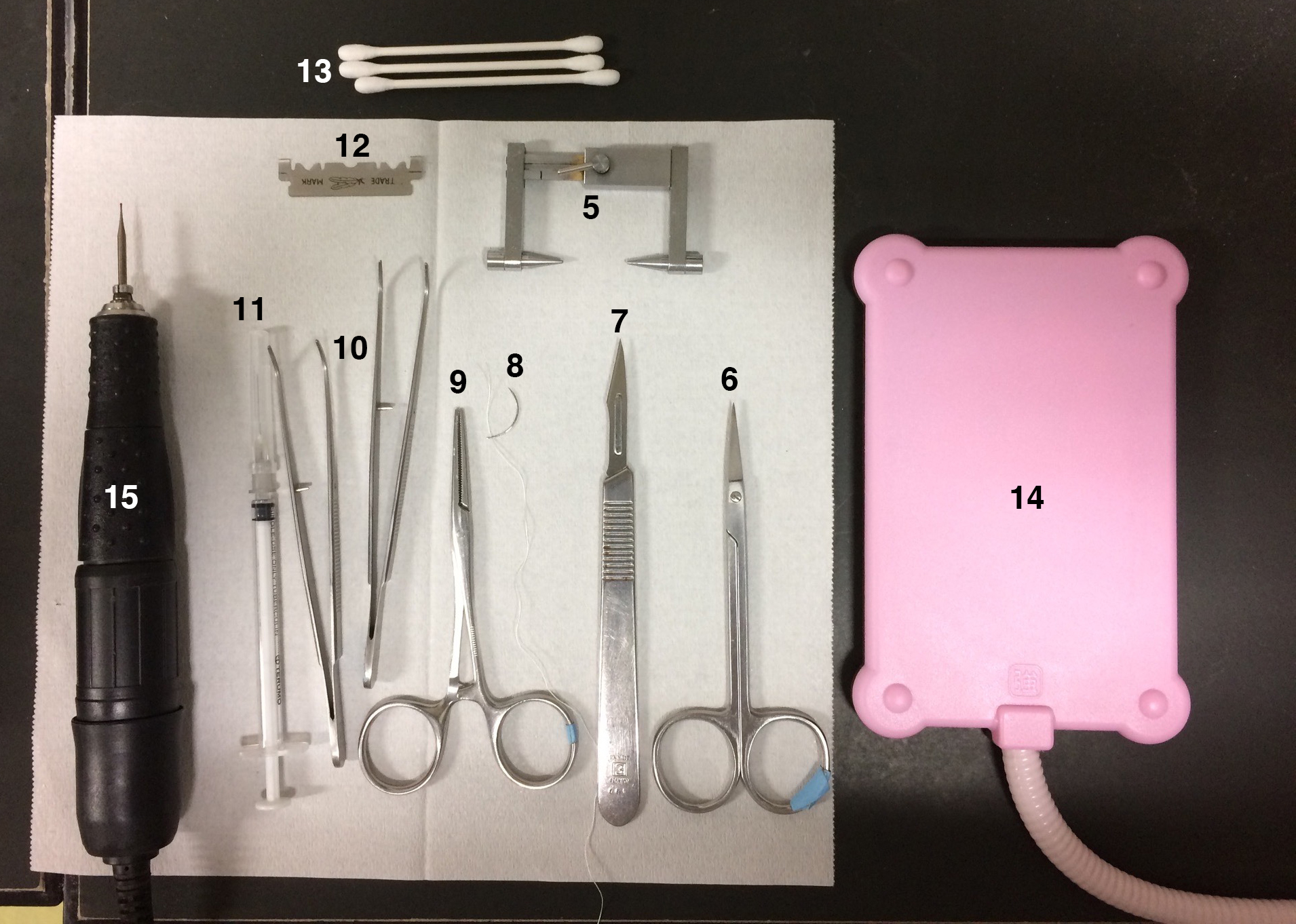
Figure 2. Equipment list 5-15 - Lesion-making device (Ugo Basile, catalog number: 53500 )
- Electrode (100 μm, coated with epoxy except for 200 μm at the tip, Neuroscience)
- Plug connecter cables with crocodile clip
- Area sensor with an infrared detector for confirmation of SCN-lesioning (EK, catalog number: PS-3241 )

Figure 3. Equipment list 16-18
Software
- ClockLab software
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Shimizu, K. and Fukada, Y. (2017). Stereotaxic Surgery for Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Lesions in Mice. Bio-protocol 7(12): e2346. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2346.
分类
神经科学 > 神经解剖学和神经环路 > 动物模型
神经科学 > 神经系统疾病 > 动物模型
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link