- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Fluorescently Labelled Aerolysin (FLAER) Labelling of Candida albicans Cells
使用荧光标记的嗜水气单胞菌溶素变异体(FLAER)标记白色念珠菌细胞
发布: 2017年06月05日第7卷第11期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2303 浏览次数: 10747
评审: Yanjie LiEmmanuel ZavalzaMichael Tscherner

相关实验方案
一种基于流式细胞术的利用基因编码荧光报告测定酵母活细胞内pH值的方法
Catherine G. Triandafillou and D. Allan Drummond
2020年06月20日 4770 阅读
Abstract
In this protocol we describe a nonradiolabelled labelling of GPI anchor in Candida albicans. The method uses a fluorescent probe to bind specifically to GPI anchors so that the level of GPI-anchored proteins at the cell surface can be measured. The labelling does not need permeabilization of cells and can be carried out in vivo.
Keywords: FLAER (FLAER)Background
The GPI (glycosylphosphatidylinositol) anchor is a post translational modification occurring in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The preformed GPI anchor is attached in the lumen of the ER to the C-terminus of specific proteins that carry a GPI anchor attachment signal sequence. These proteins are subsequently transported (and extensively further modified) by the secretory pathway to the cell surface where the proteins are present anchored to the extracellular leaflet of the plasma membrane or covalently linked to the cell wall in organisms that have a wall. A variety of proteins get GPI anchored proteins in eukaryotes, for example, hydrolytic enzymes, cell surface adhesion molecules or receptor proteins (Orlean and Menon, 2007). In fungal pathogens, such as Candida albicans, many of the adhesins involved in host recognition and adherence, as well as several pathogenesis and virulence factors are GPI anchored proteins; besides, several GPI-anchored proteins in Candida albicans have proteolytic activity (Richard and Plaine, 2007; Nobile et al., 2008). The pathway is essential in Candida albicans and downregulating it or targeting it could be a useful strategy to combat Candida infections. The protocol used for assessing GPI anchor levels in Candida albicans is elaborated here.
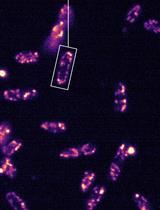
Fluorescently Labelled Aerolysin (FLAER) is a fluorescein labelled inactive derivative of aerolysin, a Gram-negative bacterial toxin, which binds to GPI-anchored proteins in the cell membrane of the eukaryotic host and forms pores (Howard et al., 1987; Parker et al., 1994). In FLAER, proaerolysin is tagged with Alexa Fluor 488 dye which can bind to GPI anchors of eukaryotic cells without any harm to the cell (Sutherland et al., 2007). FLAER is also clinically used to detect GPI anchor levels in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) cells, a disease caused by somatic mutations in PIGA (a subunit of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-N-acetylglucosamine transferase enzyme complex) in mammals (Brodsky et al., 2000). Once stained with FLAER, the fluorescence of cells can be monitored/quantified under a confocal fluorescence microscope in the GFP channel and the data used as a measure of GPI anchored proteins on the cell surface. In a previous study, we monitored the levels of GPI-anchored proteins on the cell surface of a GPI biosynthetic mutant, Cagpi14, in Candida albicans by using FLAER (Singh et al., 2016). CaGPI14 encodes for the catalytic subunit of the first mannosyltransferase of the GPI-anchor biosynthesis pathway. Deficiency in CaGpi14 severely affects cell growth and wall integrity in the organism although low levels of expression appear to be sufficient to make the cells viable. Its homolog in S. cerevisiae is essential (Kim et al., 2007). The protocol for FLAER labelling used to assess GPI anchor levels in this mutant of Candida albicans is described here.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips
- Sterile plastic toothpick
- Culture tubes (50 ml)
- 1.5 ml micro-centrifuge tubes
- Glass slides
- Cover slips
- Candida albicans strains CAF2-1 (URA3/ura3::imm434 IRO1/iro1::imm434) and conditional null mutant of CaGPI14 (CAF2-1::Cagpi14/pMET3-CaGPI14), encoding the catalytic subunit of the first mannosyltransferase in the GPI biosynthetic pathway, for this study
- Synthetic defined (SD) medium with Uridine+Cys-Met- dropout mix was made in the lab for this study since the strains were uridine auxotrophs. Cys/Met was used to repress CaGPI14 expression (all L-amino acids were obtained from Sisco Research Laboratory). This was possible because the conditional mutant strain had the only surviving allele of CaGPI14 placed under the control of the MET3 promoter, which permits gene expression in the absence of Cys/Met and represses its expression in the presence of Cys/Met
- Liquid FLAER (25 µg/0.5 ml) from Pinewood Scientific Services Inc. (FL1S-C)
- 50% glycerol (Merck, catalog number: 1.07051.0521 )
- D-glucose (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: D16-500 )
- Yeast nitrogen base (HiMedia Laboratories, catalog number: M878 )
- Cysteine (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 034890 )
- Methionine (Sisco Research Laboratory, catalog number: 134869 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15915 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Merck, catalog number: 1049360500 )
- Sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S374-3 )
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Merck, catalog number: 1.93205.0521 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- SD Uri+Cys-Met-/SD Uri+Cys+Met+ broth (100 ml) (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.5) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes
100-1,000 µl (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 4642090 )
20-200 µl (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 4642080 )
2-20 µl (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 4642060 ) - Vortex mixer (REMI GROUP, model: CM-101 )
- Shaker incubator (Set at either 30 °C or 20 °C according to requirement) (Labtech, model: LSI-5002M )
- Centrifuge (Plasto Craft Industries, model: Micro-spin R-V/FM )
- Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: MultiskanTM GO Microplate Spectrophotometer , catalog number: 51119300)
- Andor spinning Disk confocal microscope
- Autoclave
Software
- Andor iQ2.7 (for image capturing)
- GIMP 2.8.18 software (for quantification)
- Origin 0.5 software
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Singh, S. L. and Komath, S. S. (2017). Fluorescently Labelled Aerolysin (FLAER) Labelling of Candida albicans Cells. Bio-protocol 7(11): e2303. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2303.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物细胞生物学 > 细胞成像
细胞生物学 > 细胞成像 > 荧光
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link