- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Virus Binding and Internalization Assay for Adeno-associated Virus
腺相关病毒的病毒结合和内化测定实验
发布: 2017年01月20日第7卷第2期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2110 浏览次数: 12931
评审: Yanjie LiAngela CoronaKristin Shingler
Abstract
The binding and internalization of adeno-associated virus (AAV) is an important determinant of viral infectivity and tropism. The ability to dissect these two tightly connected cellular processes would allow better understanding and provide insight on virus entry and trafficking. In the following protocol, we describe a quantitative PCR (qPCR) based method to determine the amount of vector bound to the cell surface and the amount of subsequent virus internalization based on viral genome quantification. This protocol is optimized for studying AAV. Nevertheless, it can serve as a backbone for studying other viruses with careful modification.
Keywords: Adeno-associated virus (腺相关病毒)Background
Studies that assess AAV biology generally use transgene expression as the experimental endpoint. However, there are a number of critical steps AAV must successfully navigate before it reaches the nucleus and transduces the cell. Therefore, there are multiple distinct steps in the AAV infectious pathway that could be disrupted individually or collectively, leading to altered transduction. Assessment of AAV binding and internalization are important first steps in determining the cause of transduction differences observed upon cellular modification by small molecules, CRISPR-based gene knockout, siRNA-based gene knockdown, or other experimental procedures.
Materials and Reagents
- 12-well tissue culture (TC) treated plates (Corning, catalog number: 3513 )
- GeneMate 1.7 ml microcentrifuge tubes (BioExpress, catalog number: C-3262-1 )
- Tips
- Lightcycler 96-well qPCR plates (Roche Molecular Systems, catalog number: 04729692001 )
- Cell lifter (Corning, catalog number: 3008 )
- HeLa cells (ATCC, catalog number: CCL-2 )
- Purified single-stranded AAV (any serotype) (Grieger et al., 2012)
- 1x PBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14190144 )
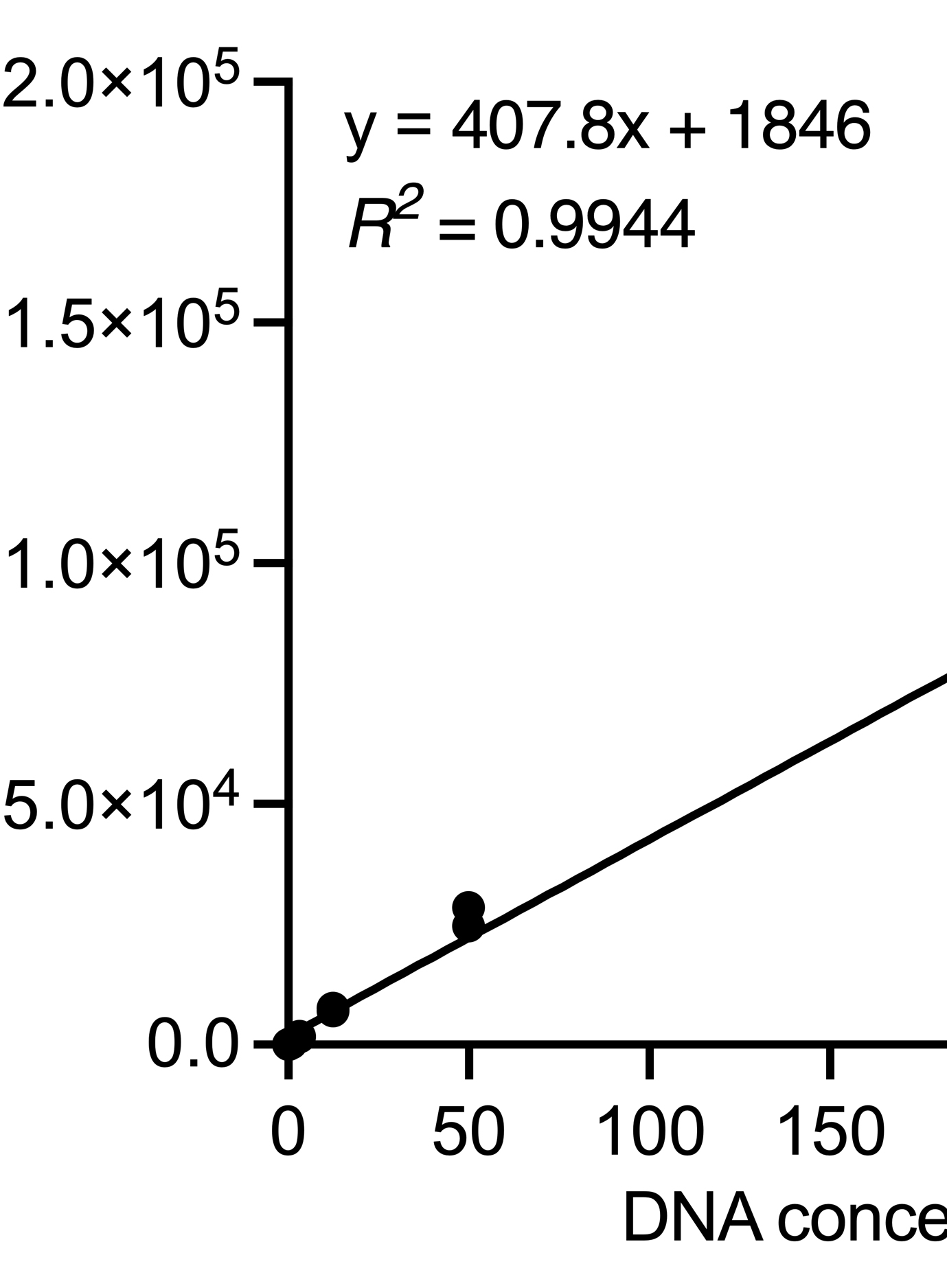
- DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 69504 )
- Molecular grade water (Mediatech, catalog number: 46-000-C )
- DMEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11995065 )
- Trypsin-EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 25300054 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F2442 )
- 100x penicillin/streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140122 )
- FastStart Essential DNA Green Master Mix (Roche Molecular Systems, catalog number: 06402712001 )
- Virus-specific qPCR primers (at a working concentration of 20 µM each)
- fLuc-F – AAAAGCACTCTGATTGACAAATAC
- fLuc-R – CCTTCGCTTCAAAAAATGGAAC
- Human genomic qPCR primers (at a working concentration of 20 µM each)
- hLB2C1-F – GTTAACAGTCAGGCGCATGGGCC
- hLB2C1-R – CCATCAGGGTCACCTCTGGTTCC
- 10 ng/μl CBA-fLuc plasmid stock solution (see Recipes)
- 100 ng/μl HeLa genomic DNA stock solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipette
- Biosafety cabinet
- CO2 tissue culture incubator (NuAire, model number: NU-5500 )
- Tabletop centrifuge (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022620401 )
- Lightcycler 96 qPCR instrument (Roche Molecular Systems, catalog number: 05815916001 )
- PCR plate microcentrifuge (VWR, catalog number: 89184-608 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Berry, G. E. and Tse, L. V. (2017). Virus Binding and Internalization Assay for Adeno-associated Virus. Bio-protocol 7(2): e2110. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2110.
- Berry, G. E. and Asokan, A. (2016). Chemical modulation of endocytic sorting augments adeno-associated viral transduction. J Biol Chem 291(2): 939-947.
分类
免疫学 > 补体分析 > 病毒
分子生物学 > DNA > DNA 定量
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link