- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Primary Culture of Mouse Neurons from the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn
小鼠脊髓背角神经元的原代培养
发布: 2017年01月05日第7卷第1期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2098 浏览次数: 17321
评审: Jia LiGeoff LauFabiana Scornik
Abstract
Primary afferents of sensory neurons mainly terminate in the spinal cord dorsal horn, which has an important role in the integration and modulation of sensory-related signals. Primary culture of mouse spinal dorsal horn neuron (SDHN) is useful for studying signal transmission from peripheral nervous system to the brain, as well as for developing cellular disease models, such as pain and itch. Because of the specific features of SDHN, it is necessary to establish a reliable culture method that is suitable for testing neural response to various external stimuli in vitro.
Keywords: Neuron (神经元)Background
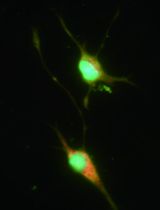
Unlike existing protocols for culturing isolated mice primary neurons from hippocampus or cerebral cortex, few methods of culturing SDHN in vitro have been reported. This protocol was mainly based on previously described methods (Hu et al., 2003; Hugel and Schlichter, 2000). Here we made a few modifications including reagents, recipes, dissection and described step-by-step procedures of the dissection and culture of primary SDHN from newborn mice. In this protocol, neurons were gained using the enzymatic (papain) digestion method from fresh spinal dorsal horn tissues directly. The culture of SDHN in vitro can be used for further experiments, such as electrophysiological recordings, immunocytochemistry, and Ca2+ imaging, which better support cell behaviors in the spinal cord.
Materials and Reagents
- Coverslips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 174950 )
- 24-well cell culture plate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 142475 )
- Cell culture dishes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 153066 )
- Sterile centrifuge tubes (5 ml and 50 ml)
- Cotton ball
- Pipette tip
- Cell strainer (40 μm) (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352340 )
- Ice
- 3 days-old mice
- Diethyl ether (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 346136 )
- 75% ethanol
- Cytosine arabinoside (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C6645 )
- 4% formaldehyde
- 5% goat serum
- MAP2 antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M1406 )
- Anti-mouse FITC-conjugated secondary antibody
- DAPI (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9542 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Collagen (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C7661 )
- Poly-D-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7405 )
- HEPES (1 M) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15630080 )
- HBSS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14025092 )
- Papain (Worthington Biochemical, catalog number: LS003119 )
- Neuro basal (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10888022 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 1099141 )
- Heat-inactivated horse serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 26050070 )
- B27 (50x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 17504044 )
- Glutamax (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 35050061 )
- Penicillin/Streptomycin (100x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140122 )
- Collagen stock solution (see Recipes)
- Poly-D-lysine (PDL) stock solution (see Recipes)
- Coating solution (see Recipes)
- HBSS + HEPES solution (see Recipes)
- Papain solution (see Recipes)
- Culture media (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Surgical scissors (decapitation/dissecting spinal column from body) (RWD Life Science, catalog number: S14014-14 )
- Blunt-tipped forceps (dissecting/holding spinal column) (RWD Life Science, catalog number: F13017-12 )
- Long and narrow-tipped spring scissors (dissecting spinal cord/cutting nerve roots) (66 Vision, catalog number: 54053B )
- Small-tipped spring scissors (cutting dura) (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 15000-02 )
- Microforceps (holding spinal cord/trimming off dura) (World Precision Instruments, catalog number: 14098 )
- Scalpel #15 sterilized surgical blade (cutting spinal cord to isolate dorsal horn) (Shanghai Jinhuan Medical, catalog number: YY0174-2005 )
- Tissue culture hood (Suzhou Antai Airtech, model: SW-CJ-1F(D) )
- Stereomicroscope (OLYMPUS, model: SZ61 )
- Benchtop centrifuge (4 °C, 50 ml tube) (Eppendorf, model: 5430R )
- Pipette (Eppendorf, model: ES-1000 )
- Haemocytometer (Shanghai anxin optical instrument manufacture, model: XB-K-25 )
- Stackable CO2 incubator (Eppendorf, model: Galaxy®170R )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Cao, D., Jing, P., Jiang, B. and Gao, Y. (2017). Primary Culture of Mouse Neurons from the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn. Bio-protocol 7(1): e2098. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2098.
分类
神经科学 > 细胞机理 > 细胞分离和培养
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分离
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link