- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Assessment of Wheat Resistance to Fusarium graminearum by Automated Image Analysis of Detached Leaves Assay
通过离体叶片的自动图像分析评估小麦对禾谷镰刀菌的抗性
发布: 2016年12月20日第6卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2065 浏览次数: 12542
评审: Arsalan DaudiMalou FraitureBaohua Li
Abstract
Fusarium head blight (FHB) caused by Fusarium pathogens is a globally important cereal disease. To study Fusarium pathogenicity and host disease resistance, robust methods for disease assessment and quantification are needed. Here we describe the procedure of a detached leaves assay emphasizing the image analysis. The protocol provides the different steps of a rapid, automatic and quantitative image analysis to evaluate leaf area infected by Fusarium graminearum.
Keywords: Detached leaf assay (离体叶片测定)Background
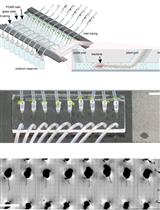
Evaluation of wheat FHB resistance at the whole plant level is estimated by visual scoring at flowering stage which is laborious, time consuming and requires space. Therefore in vitro methods that expedites disease assessment for FHB resistance at early plant stage have been developed, such as seed germination assay (Browne, 2009), coleoptiles assay (Shin et al., 2014), detached leaf assay (Browne and Cooke, 2004) and seedling assay (Li et al., 2010). Detached leaves assay is commonly used to assess host responses to Fusarium and was successful in identifying components of FHB resistance (Browne and Cooke, 2004). In such assays pathogen establishment is visually assessed which is time-consuming and limits accurate measurement. The method described recently by Perochon et al. (2015) and detailed here resolved these two limitations by using an automatic method that quantifies leaf area infected by image analysis based on particle size.
Materials and Reagents
- Petri dish, triple vent 94 x 15mm (Greiner Bio One, catalog number: 633 185 )
- Filter paper (Whatman, catalog number: 1001-090 )
- Parafilm (Parafilm, catalog number: PM992 )
- Plant container pots, 3 L (National Agrochemical Distributors, catalog number: POTS34 )
- John Innes compost No. 2 (Westland Horticulture)
- Square Petri dish 100 x 100 x 20 mm (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 82.9923.422 )
- Glass Pasteur pipette (VWR, catalog number: 14673-010 )
- Fusarium graminearum strain GZ3639 (Proctor et al., 1995)
- Plant agar (Duchefa, catalog number: P1001.1000 )
- Benzimidazole (Stock solution at 500 mM in ethanol stored in aliquots at -20 °C) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 194123 )
- Ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E7023 )
- Tween-20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P2287 )
Equipment
- Incubator (20 °C)
- Glasshouse (Cambridge HOK production glasshouse) (20-22 °C with a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod at 300 μmol m-2 s-1 and 70% relative humidity)
- Plant growth room (20 °C with a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod at 200 μmol m-2 s-1 and 70% relative humidity)
- Digital camera (Nikon, model: COOLPIX P500 with a NIKKOR 36X wide optical ZOOM ED VR, 4.0 - 144 mm, 1:3.4 - 5.7)
- Copy stand (RPS Studio RS-CS920 copy stand)
- Lights (cold-light fluorescent lighting system)
Software
- Fiji (http://fiji.sc/)
Note: Fiji is an open source software using the same functionality as ImageJ with many bundled plugins. For that reason the image analysis presented here could be executed with ImageJ.
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Perochon, A. and Doohan, F. M. (2016). Assessment of Wheat Resistance to Fusarium graminearum by Automated Image Analysis of Detached Leaves Assay. Bio-protocol 6(24): e2065. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2065.
- Perochon, A., Jianguang, J., Kahla, A., Arunachalam, C., Scofield, S. R., Bowden, S., Wallington, E. and Doohan, F. M. (2015). TaFROG encodes a Pooideae orphan protein that interacts with SnRK1 and enhances resistance to the mycotoxigenic fungus Fusarium graminearum. Plant Physiol 169(4): 2895-2906.
分类
植物科学 > 植物免疫 > 病害生物测定
微生物学 > 微生物-宿主相互作用 > 体内实验模型 > 植物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
提问指南
+ 问题描述
写下详细的问题描述,包括所有有助于他人回答您问题的信息(例如实验过程、条件和相关图像等)。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link