- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Isolating and Measuring the Growth and Morphology of Pro-embryogenic Masses in Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze (Araucariaceae)
灯台南洋杉(南洋杉科)中原胚团的分离及生长和形态测定
发布: 2016年12月05日第6卷第23期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2031 浏览次数: 9592
评审: Scott A M McAdamAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
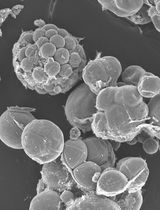
Embryogenic suspension cultures of Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze (Araucariaceae) can be used as a model to test the effects of compounds added to the culture medium on the cellular growth and morphology of Pro-Embryogenic Masses (PEMs). PEMs are formed by embryogenic and suspensor-type cells. To measure changes in the cellular growth of embryogenic cultures, we performed sedimented cell volume (SCV) quantification, which is a non-destructive method. Morphological analysis by microscopy allowed for the observation of growth and development of PEMs and the alterations in embryogenic and suspensor-type cells. The methods used here provide an efficient means for monitoring the cellular growth of PEMs and identifying morphological changes during the development of embryogenic cultures. These studies can also be combined with biochemical and molecular analyses, such as proteomics, to further investigate embryo growth and morphology.
Keywords: Somatic embryogenesis (体细胞胚胎发生)Background
Silveira et al. (2006) used SCV measurements to analyze the effects of exogenous polyamines on the morphological changes of A. angustifolia PEMs and Osti et al. (2010) tested the effect of different nitric oxide donors on cellular growth and PEM morphology. Recently, Douétts-Peres et al. (2016) studied the effect of a cellular growth inhibitor on cellular growth and PEM morphology using SCV, fresh and dry weight, PEM area, and individual diameters of embryogenic-type cells, including the length and width of the suspensor-type cells. In addition, alterations to cellular growth and morphology in response to endogenous compounds, such as polyamines, nitric oxide and specific proteins have been evaluated using this method (Silveira et al., 2006; Osti et al., 2010; Douétts-Peres et al., 2016).
Materials and Reagents
- Falcon tube rack (Kasvi, catalog number: K30-1552 )
- 12-well cell culture plates - disposable (TPP, catalog number: 92012 )
- Manual pipette 200 µl tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: T-200-Y )
- Manual pipette 1,000 µl tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: T-1000-B )
- Aluminum foil
- Glass slides (Kasvi, catalog number: K5-7101 )
- Cover slips (Kasvi, catalog number: K5-2450 )
- Falcon tubes, 50 ml (Kasvi, catalog number: K19-0050 )
- Embryogenic suspension cultures of A. angustifolia, induced according to the methodology established by Steiner et al. (2005)
- Cellulase (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 22178 )
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000944 )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000199 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V001861 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000104 )
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 104873 )
- MnSO4·H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S2036 )
- ZnSO4·7H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S1072 )
- Boric acid (H3BO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 31146 )
- Potassium iodide (Kl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000130 )
- Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000213 )
- CuSO4·5H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S1054 )
- Sodium molybdate dihydrate (Na2MoO4·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M1651 )
- FeSO4·7H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S1057 )
- Na2EDTA (Labsynth, catalog number: E2005 )
- Myo-inositol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I17508 )
- Nicotinic acid (Labsynth, catalog number: A1043 )
- Pyridoxine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9755 )
- Thiamine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4625 )
- L-glutamine (Labsynth, catalog number: G1011 )
- Sucrose (Labsynth, catalog number: 2731 )
- MSG culture medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Cell dissociation sieve-screens, 150 mesh (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CD1-1KT ) sterilized by autoclave (121 °C, 30 min)
- Chamber flow (or its equivalent) (Pachame, model: PA 220 )
- Adapted glass Erlenmeyer flasks (custom-made) (Figure 1), sterilized by autoclave (121 °C, 30 min). This adjustment to the flask can be performed by a company that produces laboratory glassware, fusing a glass tube to an Erlenmeyer flask
- Ruler
- Orbital shaker (or its equivalent) (Cientec Equipamentos para Laboratório, model: CT-165 )
- Analytical balance (or its equivalent) (Shimadzu, model: BL3200H )
- Spatula sterilized by autoclave (121 °C, 30 min) (VWR, catalog number: 231-2233 )
- AxioPlan light microscope (Carl Zeiss, model: AxioPlan )
- Manual pipettes (or their equivalent) (Eppendorf, catalog numbers: 3120000062 and 3120000054 )
- Forced air circulation drying oven (or its equivalent) (Ethik Technology, model: 420-6D )
- AxioCam MRC5 digital camera (Carl Zeiss, model: AxioCam )
- Desktop computer
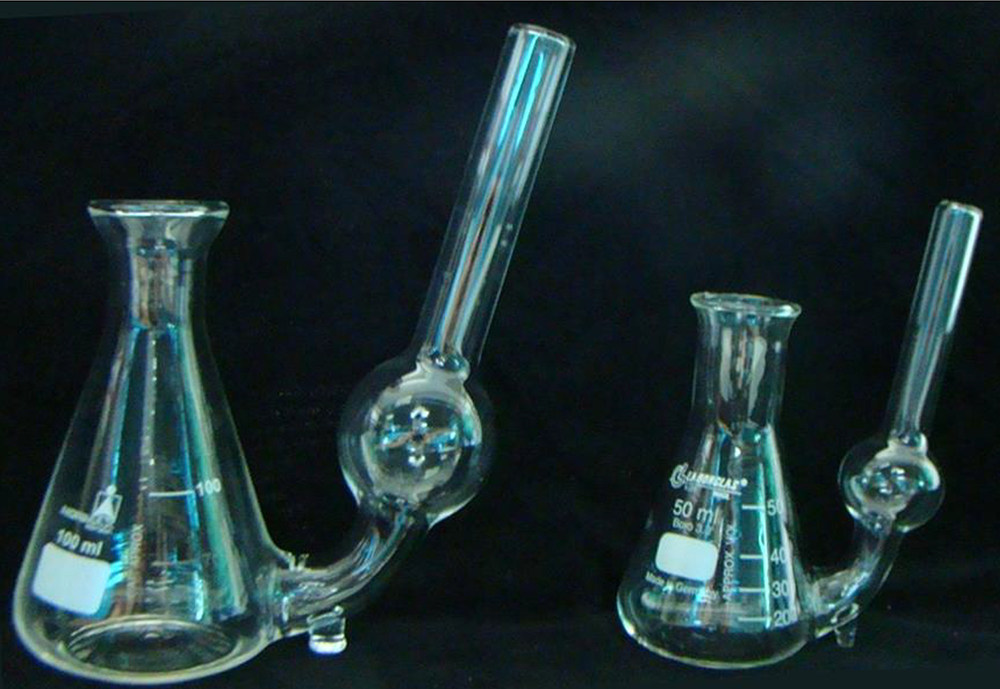

Figure 1. Adapted Erlenmeyer flasks (100 and 50 ml) used in SCV analyses. For an adapted Erlenmeyer flask of 100 ml capacity, we used 25 ml of culture medium and 500 mg of fresh cells. For an adapted Erlenmeyer flask with 50 ml capacity, we used 10 ml of culture medium and 200 mg of fresh cells, with a ratio of 20 mg fresh cells to 1 ml of culture medium.
Software
- AxioVision Rel. 4.8 software (Carl Zeiss, AxioVision)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Douétts-Peres, J. C., Silveira, V., Cruz, M. A. L. and Santa-Catarina, C. (2016). Isolating and Measuring the Growth and Morphology of Pro-embryogenic Masses in Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze (Araucariaceae). Bio-protocol 6(23): e2031. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2031.
- Douétts-Peres, J. C., Cruz, M. A., Reis, R. S., Heringer, A. S., de Oliveira, E. A., Elbl, P. M., Floh, E. I., Silveira, V. and Santa-Catarina, C. (2016). Mps1 (Monopolar Spindle 1) protein inhibition affects cellular growth and pro-embryogenic masses morphology in embryogenic cultures of Araucaria angustifolia (Araucariaceae). PLoS One 11(4): e0153528.
分类
植物科学 > 植物发育生物学 > 形态建成
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞生长
细胞生物学 > 组织分析 > 组织分离
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link