- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Campylobacter jejuni γ-glutamyltranspeptidase Activity Assay
空肠弯曲杆菌γ-谷氨酰胺转肽酶活性鉴定
发布: 2016年03月05日第6卷第5期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1747 浏览次数: 8148
评审: Valentine V TrotterAnna A. ZorinaAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
The enzyme γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT, EC 2.3.2.2) is highly conserved among eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms (Heisterkamp et al., 2008) and has a key function in glutathione metabolism. Although the enzyme is highly conserved and found throughout organisms ranging from bacteria to plants and animals several major difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic GGT can be noticed. They mainly concern the enzyme localization and posttranslational modification. Eukaryotic GGT is cell membrane anchored and highly glycosylated whereas prokaryotic GGT does not undergo this posttranslational modification and is a soluble periplasmic protein. GGT amino acids sequences of diverse origin exhibit high amino acid similarity (Ong et al., 2008). The prokaryotic GGT enzymes are produced as proenzyme, equipped with a typical prokaryotic signal sequence and transported through the inner membrane into the periplasm where the enzyme undergoes autocatalytic cleavage. This proteolysis yields a mature dimer which transfers the γ-glutamyl moieties from extracellular glutathione and related compounds to amino acids or peptides (Hanigan et al., 1998). The GGT enzyme activity can be easily measured as it catalyzes the transfer of a γ-glutamyl group from a colorless substrate, L-γ-glutamyl-3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide, to the acceptor, glycylglycine with leads to the production of yellow colored product, p-nitroaniline (Figure 1) which can be measured by a spectrophotometer (Figure 2). Here we describe a protocol to measure the GGT activity in the Gram-negative bacterium Campylobacter jejuni, with some minor modifications; this protocol also works for other Gram-negative bacterial species.
Figure 1. Yellow colored product, p-nitroaniline formed during the GGT enzyme assay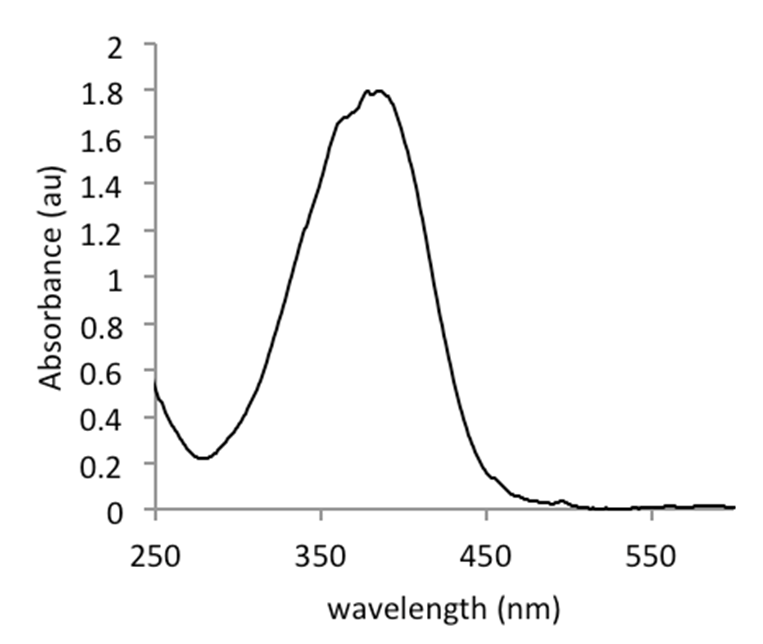
Figure 2. Spectral curve of pNA in Tris/HCl buffer, recorded on a Biodrop µLite (Isogen)
Materials and Reagents
- 25 mm culture flasks with vent cap (Corning, catalog number: 430639 )
- 96 well plate flat bottom (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 3599 )
- Campylobacter culture
- UltraPure™ Tris Buffer (powder format) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 15504-020 )
- Lysozyme from chicken egg white (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L-6876 )
- L-Glutamic acid γ-(3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide) ammonium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 49525 )
- Glycylglycine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G3915 )
- Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo Scientific™, catalog number: 23227 )
- 4-nitroaniline (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 185310 )
- Hearth Infusion medium (Thomas Scientific, Oxoid, catalog number: CM1032B )
- Tris/HCl (pH 7.6 and pH 8.2)
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Reaction buffer (see Recipes)
- pNA stock solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Absorbance microplate reader (such as BMG Labtech GmbH, Fluorstar Omega or equivalent)
- Vibra-Cell™ Sonicater (Sonics & Materials, model: VC40 )
- Refrigerated table top centrifuge
- The anoxomat system (MART Microbiology)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
van der Stel, A. and Wösten, M. M. S. M. (2016). Campylobacter jejuni γ-glutamyltranspeptidase Activity Assay. Bio-protocol 6(5): e1747. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1747.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link