- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Determination of Keto-deoxy-d-manno-8-octanoic acid (KDO) from Lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli
大肠杆菌脂多糖中酮基-脱氧-d-甘露-8辛酸(KDO)的测定
发布: 2015年12月20日第5卷第24期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1688 浏览次数: 17695
评审: Valentine V TrotterAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
2-Keto-3-deoxy-octonate (KDO) is an essential constituent of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that forms the outermost leaflet of Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane. LPS is mainly composed of lipid A, O-antigen and a core oligosaccharide. Two molecules of KDO are present per one molecule of LPS. A proper level of LPS is required to maintain the outer membrane integrity and either high or low levels of LPS are toxic to the cell. Various methods are available for quantification of LPS; of these, determination of KDO is a simple and accurate method and it can be estimated either directly from crude bacterial cell lysates or from purified LPS by a simple colorimetric assay. Although this procedure can be theoretically used for any Gram-negative bacterium, we used it routinely to measure KDO from cell lysates of Escherichia coli (E. coli) K12 strains.
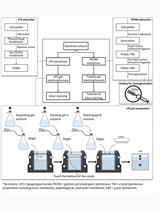
Method: The protocol is taken from Karkhanis et al. (1978). It is a simple, sensitive and reliable method to measure KDO. The assay is performed after complete acid hydrolysis of cell lysates or LPS to release the various components of LPS. Further, reaction with periodate, arsenite and thiobarbituric acid gives a pink to red color chromophore, which is measured at 548 nm after stabilizing with DMSO.
Materials and Reagents
- Bacterial strain(s) MG1655 (wild-type) (Escherichia coli K12 strain)
- Periodate (H5IO6) (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 10450-60-9 )
- Sodium Arsenite (NaAsO2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7400 )
- 2-Thiobarbituric acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T5500 )
- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 7664-93-9 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 802912 )
- HEPES (Merck Millipore Corporation, CalBiochem, catalog number: 7365-45-T )
- Quick Start-Bradford Reagent (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 5000205 )
- 2-Keto-3-deoxyoctonate ammonium salt (KDO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K2755 )
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9647 )
- Tryptone (Difco Laboratories, catalog number: 211705 )
Note: Currently, it is “BD, Bacto, catalog number: 211705”. - Yeast extract (Difco Laboratories, catalog number: 212750 )
Note: Currently, it is “BD, Bacto, catalog number: 212750”. - Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sisco Research Laboratories, catalog number: 7647-14-5 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 7647-01-0 )
- Ultra Pure water (Milli Q water) Millipore Progard TL1Cl2, MilliQ system (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: PROGTLCS1 )
- LB broth (see Recipes)
- 0.1 M periodate reagent (see Recipes)
- 4% sodium arsenite reagent (see Recipes)
- 0.6% thiobarbituric acid reagent (see Recipes)
- 0.5 N sulphuric acid (see Recipes)
- 10 mM HEPES buffer (see Recipes)
- 0.5 N HCl (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Sonicator (Probe size, 3 mm) (Sonics Vibra, model: VLB 3X )
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Eppendorf, model: 5417R )
- UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, model: LAMBDA-35 )
- Thermo heating bath (Labnet International, Accu BlockTM Digital Dry bath)
- Pipettes (Gilson)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Sunayana, M. R. and Reddy, M. (2015). Determination of Keto-deoxy-d-manno-8-octanoic acid (KDO) from Lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Bio-protocol 5(24): e1688. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1688.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 糖类
生物化学 > 糖类 > 多糖
生物化学 > 脂质 > 脂质测定
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link