- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Physicochemical Quantification of Abscisic Acid Levels in Plant Tissues with an Added Internal Standard by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography
通过添加内标的超高效液相色谱法对植物组织中的脱落酸水平进行组织化学定量测定
发布: 2015年09月20日第5卷第18期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1599 浏览次数: 13649
评审: Marisa RosaSara Posé Sriema L. Walawage
Abstract
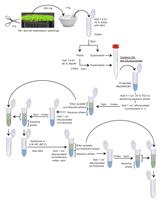
The phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) is critical for a range of plant responses to the environment, most importantly in closing the stomata of seed plants during drought (Mittelheuser and Van Steveninck 1969; Brodribb et al. 2014). The high precision quantification of this hormone by physicochemical methods is a relatively simple process, essential for studies that aim to investigate the role or action of this hormone in plants. Outlined here is a method for the extraction, purification and quantification of ABA levels in plant tissues. This method involves methanolic extraction of ABA from homogenised tissue. Purification of ABA is then undertaken by a simple etheric partitioning method. A focus is placed on determining ABA levels in leaves; however this method is suitable for all tissue types, including plant solutes such as xylem sap, seeds (both dry and green) and large samples of tissue such as root systems.
Keywords: Plant hormones (植物激素)Materials and Reagents
- Methanol (Merck Schuchardt OHG, catalog number: 603-001-00-X )
- 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol (BHT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B1378 )
- Liquid nitrogen (optional for manual homogenization method only)
- Labelled or deuterated ABA (such as 13C labelled, [2H6] ABA or other form with any number of deuterium atoms) (e.g. OlChemIm Ltd, catalog numbers: 03 2721-03 2723 ; catalog numbers: 35671-08-0 )
- Acetic acid (Analytical grade, any supplier)
- Diethyl ether (Analytical grade, any supplier)
- Acetonitrile (for UPLC-MS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 271004 )
- Aluminium foil
- 50 ml conical centrifuge tube (Greiner Bio-One GmbH, catalog number: 210261 )
- 0.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (any brand will suffice)
- 2 ml screw-cap tubes (Scientific Specialities, catalog number: 2330-00 ) with tethered screw tube caps (Scientific Specialities, catalog number: 2002-59 ) (optional for very small samples or samples that require long-distance freight)
- Whatman no. 1 filter paper (optional for large samples only)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (any brand will suffice)
- Centrifuge for 2 ml Eppendorf tubes
- Filtered glass 150 mm Pasteur pipettes (Poulten & Graf GmbH, model: D810 )
- Rubber nipple for Pasteur pipette
- 10-100 µl pipette (any brand will suffice)
- 100-1,000 µl pipette (any brand will suffice)
- 5 ml pipette and tips (any brand will suffice)
- 80% methanol in water (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 2% acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 80% methanol in water (v/v) with added butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) (see Recipes)
- 80% methanol in water (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 2% acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 5% methanol, 94% water and 1 % acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
- 1% acetic acid (v/v) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Balance (±0.001 g)
- Scholander pressure chamber (e.g. PMS Instrument Company, model: 600 ) (optional for specialised experiments or quantification of ABA from xylem sap)
- Stainless steel beads 7 mm (QIAGEN, catalog number: 69989 / 69990 ) (optional for very small samples only)
- Modelling clay or Blu-tak (Bostik) (optional for very small samples only)
- Glass beaker (variable size) (optional for large samples)
- General purpose 21 cm scissors
- Tissue homogeniser [either modified Ba-mix® or Physcotron (Microtec Co., model: NS-7 )]
- Cell lysis machine (e.g. QIAGEN, model: TissueLyser II ) (optional for very small samples only)
- Conventional Ba-mix® or similar hand-held blender (optional for large samples only)
- Ceramic mortar and pestle (optional for manual homogenization method only)
- Büchner funnel (optional for large samples only)
- Vacuum flask (optional for large samples only)
- Vacuum sample concentrator (or rotary evaporator with 100 ml round bottom flask, optional for large samples)
- Fume hood
- Heating block that can contain 0.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (gentle stream of nitrogen gas, passing through a low flow regulator, tubing and funnelled through a standard 100 µl pipette tip, if desired) (e.g. Ratek Instruments, model: DBH10DP )
- A LCGC Certified Clear Glass 12 x 32 mm Screw Neck Vial, with Cap and PTFE/silicone Septum , 2 ml Volume, 100 /pkg [(Waters, catalog number: 186000272C ), Insert 150 µl with preinstalled plastic spring (Waters, catalog number: WAT094171 )]
- Aerosol barrier pipette tips for both µl pipettes (these are important to prevent sample contamination of the pipette which can compromise future samples. They can be made by inserting a small amount of cotton wool into the barrel end of the pipette tip.) (any brand will suffice)
- Ultra-performance liquid chromatograph and multiple reaction-monitoring tandem mass spectrometer [Water Acquity H-series UPLC coupled to a Waters Xervo triple quadrupole mass spectrometer, containing a Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 mm x 100 mm x 1.7 µm particles)]
Software
- Waters MassLynx and TargetLynx software
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- McAdam, S. A. M. (2015). Physicochemical Quantification of Abscisic Acid Levels in Plant Tissues with an Added Internal Standard by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Bio-protocol 5(18): e1599. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1599.
- McAdam, S. A. and Brodribb, T. J. (2014). Separating active and passive influences on stomatal control of transpiration. Plant Physiol 164(4): 1578-1586.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 植物激素
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link