- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Identification of Factors in Regulating a Protein Ubiquitination by Immunoprecipitation: a Case Study of TRF2 on Human REST4 Ubiquitination
免疫沉淀法识别调节蛋白质泛素化的因子:TRF2在人REST4泛素化中的案例研究
发布: 2015年07月05日第5卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1525 浏览次数: 12259
评审: Vivien Jane Coulson-ThomasAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
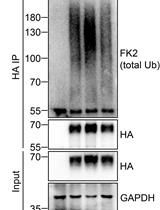
Ubiquitination is the first step of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway that regulates cells for their homeostatic functions and is an enzymatic, protein post-translational modification process in which ubiquitin is transferred to a target protein substrate by a set of three ubiquitin enzymes (Weissman et al., 2011; Bhattacharyya et al., 2014; Ristic et al., 2014). Given the importance of this process, it is plausible that ubiquitination is under strict control by many factors and that the regulatory machineries are protein-specific. An assay for the detection of a specific protein ubiquitination will enable us to examine whether a factor has a function to regulate the ubiquitination of this protein. Here we describe a protocol that detects the ubiquitination status of the human REST4 protein in cultured cells, a neural alternative splicing isoform of REST (RE-1 silencing transcription factor), that antagonizes the repressive function of REST on neural differentiation and neuron formation. Using this protocol, we show that the telomere binding protein TRF2 stabilizes the expression of the human REST4 by inhibiting its ubiquitination. This indicates that TRF2 plays a positive role in neural differentiation (Ovando-Roche et al., 2014). This protocol is also useful for the detection of ubiquitination of other proteins of interest.
Keywords: TRF2 (TRF2)Materials and Reagents
- Cells and plasmid
- TRF2-HEK293T cells: 293T cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3216 ) that have been stably transfected with TRF2 expressing vector
- Control-HEK-293T cells: 293T cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3216) that have been stably transfected with empty control vector
- Myc-REST4 expressing vector: generated by modifying the Myc-REST plasmid (Huang et al., 2011) as detailed in Ovando-Roche et al. (2014)
- HA-ubiquitin expressing vector: (Addgene, catalog number: 17608 )
- TRF2-HEK293T cells: 293T cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3216 ) that have been stably transfected with TRF2 expressing vector
- Antibodies
- Anti-TRF2 antibody (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 05-521 )
- Anti-HA antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H6908 )
- Anti β-Actin antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A5441 )
- C-Myc antibody (Santa Cruz, catalog number: SC-40 )
- Goat anti-mouse light chain specific (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, catalog number: 115-035-174 )
- Mouse anti-rabbit light chain specific (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, catalog number: 211-032-171 )
- Normal mouse IgG (Santa Cruz, catalog number: SC-2025 )
- Anti-TRF2 antibody (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 05-521 )
- Reagents
- Dulbeccos modified eagles medium (DMEM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5671 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F7524 )
- Calcium phosphate transfection kit (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CAPHOS )
- 2-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M6250 )
- Bromophenol blue (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 161-0404 )
- CaCl2 (VWR International, catalog number: 22317.297 )
- Dynabeads protein G (Life Technologies, catalog number: 10003D )
- EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: ED-1KG )
- EGTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E4378 )
- Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516 )
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- KCl (VWR International, catalog number: JT3040-1 )
- MG132 (Calbiochem, catalog number: 474791 )
- MgCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 63063 )
- NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: s-3014 )
- NaOH (VWR International, catalog number: 28244.263 )
- Nonidet P40 (VWR International, catalog number: E109-100ML )
- Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93482 )
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8340 )
- SDS (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71725 )
- Tris-HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T3253 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787 )
- Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416 )
- Ubiquitin aldehyde (Boston Biochem, catalog number: U-201 )
- Dulbeccos modified eagles medium (DMEM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5671 )
- Buffers
- Antibody binding buffer (see Recipes)
- HEPES lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- 2x electrophoresis sample buffer (see Recipes)
- Antibody binding buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 100 mm cell culture dish (Corning, catalog number: 430167 )
- Cell scraper (Corning, catalog number: 3010 )
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (StarLab, catalog number: S1615-5500 )
- BD Microlance 3 21G needle (BD, catalog number: 301156 )
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 forced-air incubator (Binder, model: C150 )
- Microcentrifuge (Hettich, model: 200R )
- Thermomixer compact (Eppendorf, model: 5350 )
- Rotator (Stuart, model: SB3 )
- Dynamag 2 magnet (Life Technologies, catalog number: 12321D )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Cui, W. and Ovando-Roche, P. (2015). Identification of Factors in Regulating a Protein Ubiquitination by Immunoprecipitation: a Case Study of TRF2 on Human REST4 Ubiquitination. Bio-protocol 5(13): e1525. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1525.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 修饰
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link