- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Detection of Alternative Oxidase Expression in Arabidopsis thaliana Protoplasts Treated with Aluminium
检测铝处理的拟南芥原生质体中交替氧化酶的表达
发布: 2015年07月05日第5卷第13期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1515 浏览次数: 9752
评审: Arsalan DaudiAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
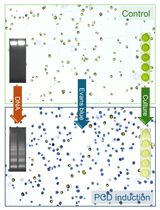
Aluminium (Al), a non-essential metal widespread in the environment that is known to be toxic to humans as well as to plants, can cause damage not only to the roots but also to the aerial parts of plants. Its toxicity has been recognized as one of the major factors that limit crop production on acid soil. Alternative oxidase, the respiratory terminal oxidase in plants, which contributes to maintain the electron flux and reduce mitochondrial ROS levels, is often dramatically induced to make plants to adapt better to stress conditions like Al stress. In this protocol, the expression of alternative oxidase induced by Al treatment was detected in Arabidopsis protoplasts using an adaptation of previous methods (Yamamoto et al., 2002; Li et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2014), which contribute to research on the mechanism of alternative oxidase in Al treatment.
Materials and Reagents
- Rosette leaves of Arabidopsis (Columbia, 3 weeks)
- AlCl3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 237051 )
- CaCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C7902 )
- HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 258148 )
- FDA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 596-09-8 )
- TRI reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93289 )
- Cellulase R10 (Yakult Honsha, catalog number: C6260 )
- Macerozyme R10 (Yakult Honsha, catalog number: 8032-75-1 )
- Mannitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4125 )
- MES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8250 )
- KCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3911 )
- Bovine serum albumin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A-6793 )
- NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6150 )
- Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7528 )
- Trition X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T-8787 )
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626 )
- Tris (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1378 )
- SDS (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L6026 )
- (NH4)2S2O8 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A3426 )
- TEMED (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9281 )
- Tween-20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416 )
- SuperScript II first-strand synthesis system (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11904-018 )
- SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, catalog number: RR420A )
- Bio-Rad protein assay kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 500-0001 )
- Anti-AOX antibody (Agrisera, catalog number: AS10699 )
- Anti-Rubisco antibody (Agrisera, catalog number: AS03037 )
- Anti-rabbit IgG (DylightTM 800 4x PEG Conjugate) secondary antibody (CST, catalog number: 5151 )
- Anti-mouse IgG (DylightTM 800 Conjugate) secondary antibody (CST, catalog number: 5257 )
- Enzyme solution (see Recipes)
- W5 solution (see Recipes)
- 5 mM AlCl3 solution in Ca medium
- Real time PCR reaction solution (see Recipes)
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- 10 ml separating gel (see Recipes)
- 6 ml stacking gels (see Recipes)
- TBST (see Recipes)
Equipment
- pH meter
- Thermal Cycler (Roche, model: Light cycler 2.0 )
- Confocal laser-scanning microscope (Carl-Zeiss, model: LSM510/ConfoCor2 )
- Auto microplate reader (Tecan Trading AG, model: infinite M200 )
- Two-color infrared imaging system (Odyssey, model: 9120 )
- Centrifuge
- Orbital shaker
- PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 162-0177 )
- Nylon mesh
- 96-well plates
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube
- Generic razor blade
- Vacuum pump (Vacuubrand, model: MZ 2C )
- BioPhotometer (Eppendorf, model: AG 22331 )
Software
- Image J 1.43 software
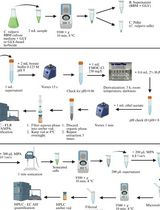
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Liu, J., Li, Z. and Xing, D. (2015). Detection of Alternative Oxidase Expression in Arabidopsis thaliana Protoplasts Treated with Aluminium. Bio-protocol 5(13): e1515. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1515.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 其它化合物
植物科学 > 植物生理学 > 非生物胁迫
生物化学 > 其它化合物 > 活性氧
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link