- EN - English
- CN - 中文
An Assay to Test Manganese Tolerance in Arabidopsis
拟南芥的耐锰实验分析
发布: 2015年05月05日第5卷第9期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1460 浏览次数: 9137
评审: Arsalan DaudiSamik BhattacharyaRenate Weizbauer
Abstract
Manganese (Mn) is an essential nutrient required for the catalytic or regulatory function of several cellular enzymes. However, excessive Mn concentrations in plant tissues are toxic to plant cells as they negatively affect enzymatic activities, lead to oxidative stress and disturb the uptake and distribution of other essential mineral elements (Ca, P, Mg or Fe). Plants have developed multiple mechanisms to avoid heavy metals (including Mn) toxicity, including transport across the plasma membrane or tonoplast. The genes encoding transporters involved in Mn detoxification are now being identified in different plant species, and functional characterization of genes isolated from species can be easily carried out in Arabidopsis.
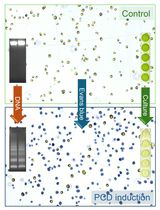
Here we provide a method to evaluate the tolerance to excess Mn of Arabidopsis lines transformed with empty vector pMDC43 or the same vector carrying cucumber gene CsMTP8 encoding putative manganese transporter localized in the vacuolar membrane. We analyzed the growth and developmental phenotypes of plants grown in controlled conditions (phytotrone) on sterile plates containing different concentrations of MnSO4 during a 16 days period. Mn accumulation was measured in the same plants grown in liquid medium supplemented or not (control) with toxic Mn concentration.
Materials and Reagents
- The seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Columbia (Col-0) transformed with empty vector (pMDC43) or with vector pMDC43 carrying the coding sequence of CsMTP8 gene under 35S CaM promoter (35S::CsMTP8)
- 96% ethanol
- 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) (commercial detergent ACE produced by Procter and Gamble)
- Sterile water
- 1 M KOH (for pH establishment)
- Murashige & Skoog Basal Medium (MS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5519 )
- Phytagel (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8169 )
- Salts for media preparation:
Ca(NO3)2 (POCH, catalog number: 874582797 )
MgSO4.7H2O (POCH, catalog number: 613780111 )
KH2PO4 (POCH, catalog number: 742020112 )
K2HPO4 (POCH, catalog number: 742100117 )
HNO3 (POCH, catalog number: 5296041 )
KNO3 (POCH, catalog number: 738910115 )
FeSO4.7H2O (POCH, catalog number: 902840115 )
MnSO4.H2O (POCH, Poland, catalog number: 616940119 )
H3BO3 (POCH, catalog number: 531360115 )
CuSO4.5H2O (POCH, catalog number: ACRS42361 )
ZnSO4.7H2O (POCH, catalog number: Ph. Eur. 6-265762730 )
(NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O (POCH, catalog number: 139000115 )
Na2EDTA.2H2O (BioShop, catalog number: OM19432 )
- Medium composition for growing plants on plates (see Recipes)
- Medium composition for growing plants in liquid solution (see Recipes)
- 10 mM Na2EDTA (see Recipes)
- 65% HNO3 (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Square (120 x 120 mm) petri dishes polystyrene sterile
- Growth chamber or phytotrone (16/8 h photoperiod at 250 μmol·m−2·s−1 and 23 °C during the day and 22 °C during the night)
- Fume hood
- Laminar flow cabinet
- Autoclave
- Shaker
- Forceps
- Tubes 1.5 ml (Axygen)
- Heating digester with closed vessels (mineralizator) (Kiejdal Digestion Unit DK-20, VELP Scientifica, catalog number: F30100350 )
- Atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer, model: AAS 3300 )
- Image capturing device (regular digital SLR-single less reflex camera, e.g. Nikon D40 camera)
- Precision balance (± 0.0001)
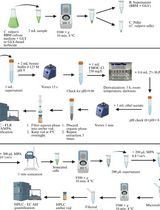
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Migocka, M. and Biskup, R. (2015). An Assay to Test Manganese Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Bio-protocol 5(9): e1460. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1460.
分类
植物科学 > 植物生理学 > 非生物胁迫
植物科学 > 植物生理学 > 植物生长
植物科学 > 植物生物化学 > 其它化合物
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link