- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Catalase Activity Assay in Candida glabrata
光滑念珠菌中过氧化氢酶活性分析
发布: 2014年03月20日第4卷第6期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1072 浏览次数: 19900
评审: Fanglian HeAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
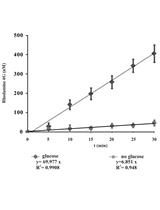
Commensal and pathogenic fungi are exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by macrophages of the host. Pathogenic fungi counteract the harmful effects of H2O2 with the enzyme catalase (EC 1.11.1.6), which decomposes two molecules of H2O2 to two molecules of H2O and O2. Contribution of antioxidant systems on fungal virulence is actively studied. Measurement of catalase activity can contribute to the elucidation of the factors that influence the regulation of this pivotal enzyme. Here we describe a simple spectrophotometric method in which the activity of catalase is measured in total yeast extracts. Decomposition of H2O2 by the yeast extract is followed by the decrease in absorbance at 240 nm. The difference in absorbance through time (ΔA240) is inferred as the measure of catalase activity.
Keywords: Catalase (过氧化氢酶)Materials and Reagents
- Yeast strains
Note: BG14 was used as the C. glabrata parental strain. The hst1Δ and the cta1Δ null mutants were used as a positive and the negative controls, respectively. - Catalase from bovine liver (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C9322 )
- Bradford reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6916 )
- Bovine serum albumin - fraction V (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 85040C )
- Zirconia/silica beads (0.5 mm diameter) (Bio Spec Products, catalog number: 11079105z )
- Sterile water
- Ice
- One tablet of protease inhibitors cOmplete ULTRA Mini EASYpack is used in 10 ml of phosphate buffer (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 05 892 970 001 )
- H2O2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 349887 )
- Catalase lyophilized powder (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C9322)
- YPD broth (see Recipes)
- 50 mM Phosphate buffer (PB) (pH 7.0) (see Recipes)
- 30 mM H2O2 (see Recipes)
- Catalase solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Orbital incubator shaker
- Microfuge tubes
- 50 ml conical tubes
- Corning 96 well clear flat bottom (Corning, catalog number: 3595 )
- Standard 10 mm light path quartz cuvette with PTFE cover
- UV/Vis Spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, model: UV-1700 , catalog number: 206-55401-92)
- Microplate spectrophotometer system (Benchmark Plus Microplate reader) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 170-6931 )
- Centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Allegra® 25R, catalog number: 369464 )
- Microfuge
- Stopwatch
- Parafilm
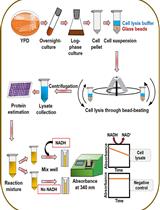
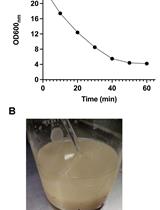
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Orta-Zavalza, E., Briones-Martin-del-Campo, M., Castano, I. and Penas, A. D. L. (2014). Catalase Activity Assay in Candida glabrata. Bio-protocol 4(6): e1072. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1072.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 活性
生物化学 > 其它化合物 > 活性氧
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link