- EN - English
- CN - 中文
A Surface Plasmon Resonance Method to Study HCV NS5B Inhibitors
采用表面等离子体共振研究HCV NS5B抑制因子
发布: 2014年02月20日第4卷第4期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1044 浏览次数: 9491
评审: Anonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
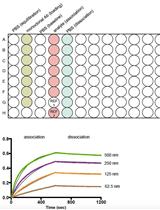
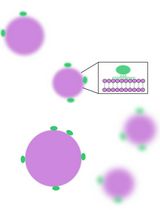
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) technology is a well-established platform used to evaluate the kinetic parameters of protein-small molecule interactions. Below, we describe the use of the ProteOn XPR36 biosensor from Bio-Rad (Hercules, CA) to evaluate the binding of small molecule inhibitors to recombinant NS5B protein. The high pI (> 9) of this construct allows for chemical immobilization using HEPES-buffered saline at pH 7.5. This is in contrast to traditional biosensor protocols that use both low pH and ionic strength. The use of a more physiological buffer to immobilize this enzyme leads to improved surface activity.
Keywords: Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) (表面等离子体共振(SPR))Materials and Reagents
- HCV NS5B inhibitors
- Purified recombinant HCV NS5B ΔC21 soluble protein [cloned and purified according to Boyce et al. (2014) and Hung et al. (2011)]
- ProteOn GLH Sensor Chip (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 176-5013 )
- HEPES solution (1 M) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3537-1L )
- MgCl2 (1 M) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M1028-100ML )
- EDTA (0.5 M) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E7889-100ML )
- NaCl (5 M) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6546-1L )
- KCl (2 M) (Life Technologies, Ambion®, catalog number: AM9640G )
- Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C4706-10G )
- Surfactant P20 (10% v/v) (General Electric Company, catalog number: BR-1000-54 )
- DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 472301-100ML )
- ProteOn Amine Coupling Kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 176-2410 ) containing 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDAC or EDC), sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimide (Sulfo-NHS) and ethanolamine-HCl
- Preconditioning Reagents (see Recipes)
- Immobilization Buffer (see Recipes)
- Running Buffer (see Recipes)
- Running Buffer with 5% DMSO (see Recipes)
Equipment
- ProteOn Standard & Deep-Well Microplates (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog numbers: 176-6020 and 176-6023 )
- ProteOn Microplate Sealing Film (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 176-6040 )
- Nalgene Rapid-Flow Filter Units and Bottle Top Filters, PES Membrane, Sterile (VWR International, catalog number: 16211-056 ) (for the 1 L size)
- ProteOn XPR36 instrument (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- BenchTop Centrifuge for microfuge tubes
- BenchTop Centrifuge to spin ProteOn 96-well assay plate
Software
- ProteOn Manager Software Version 3.1.0.6
- Scrubber software designed for ProteOn data analysis (BioLogic Software)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Wong, M. and Papalia, G. A. (2014). A Surface Plasmon Resonance Method to Study HCV NS5B Inhibitors . Bio-protocol 4(4): e1044. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1044.
分类
生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 相互作用 > 蛋白质-配体相互作用
微生物学 > 微生物生物化学 > 蛋白质 > 相互作用
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link