往期刊物2024
卷册: 14, 期号: 20
生物化学
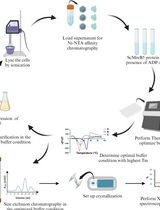
Improving Stability of Spiroplasma citri MreB5 Through Purification Optimization and Structural Insights
通过纯化优化和结构解析提高柑桔螺原体MreB5的稳定性
Chromogranin B Purification for Condensate Formation and Client Partitioning Assays In Vitro
嗜铬蛋白B的纯化用于体外凝聚体形成及客户蛋白分配实验
生物信息学与计算生物学
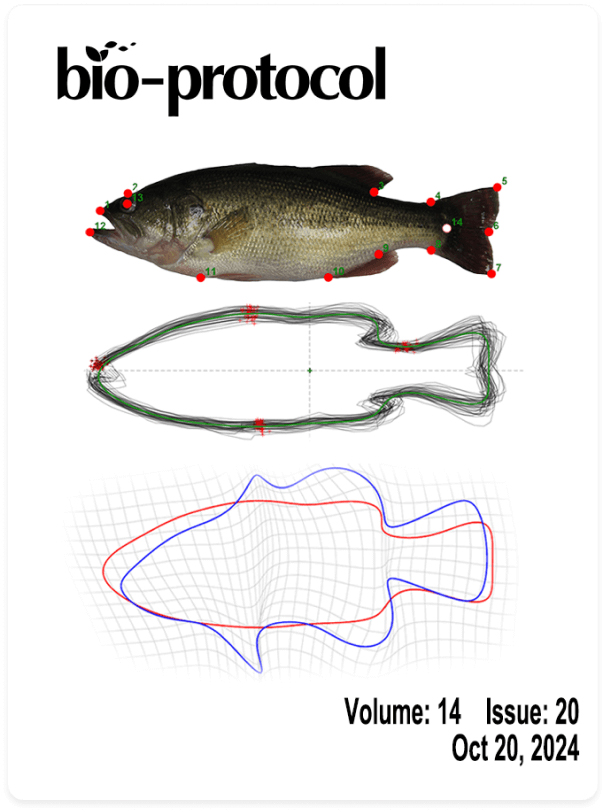
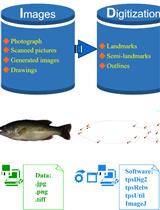
Quantitative Analysis of Fish Morphology Through Landmark and Outline-based Geometric Morphometrics with Free Software
利用标记点和轮廓几何形态测量结合免费软件对鱼类形态进行定量分析
癌症生物学
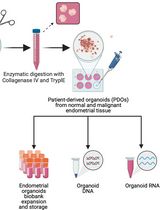
Generation and Maintenance of Patient-Derived Endometrial Cancer Organoids
患者来源的子宫内膜癌类器官的构建与维持
细胞生物学
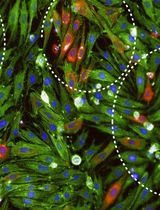
Single Cell Isolation from Human Diabetic Fibrovascular Membranes for Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
从人类糖尿病纤维血管膜中分离单细胞用于单细胞RNA测序
发育生物学
Detecting Native Protein–Protein Interactions by APEX2 Proximity Labeling in Drosophila Tissues
利用APEX2邻位标记技术检测果蝇组织中的天然蛋白质相互作用
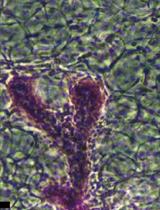
Development of the Mammary Gland in Mouse: A Whole-Mount Microscopic Analysis
小鼠乳腺的发育:整体显微分析
免疫学
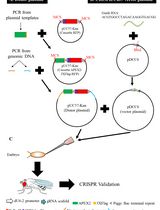
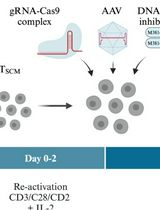
Expansion and Precise CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Repair of Autologous T-Memory Stem Cells from Patients with T-Cell Immunodeficiencies
扩增及精确CRISPR-Cas9基因修复来自T细胞免疫缺陷患者的自体记忆性T干细胞
微生物学
An Improved Focus-Forming Assay for Determination of the Dengue Virus Titer
登革病毒滴度测定改良聚焦形成法
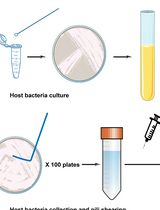
Host Receptor Pili for Cryo-EM Single-Particle Reconstruction
宿主受体菌毛用于冷冻电镜单颗粒重构
分子生物学
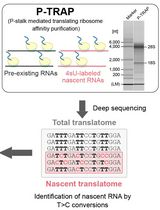
Metabolic RNA Labeling and Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification for Measurement of Nascent RNA Translation
过代谢RNA标记和翻译核糖体亲和纯化测量新生RNA的翻译
神经科学
Chemogenetic Silencing of Neonatal Spontaneous Activity of Projection Neurons in the Dorsal Striatum of Mice
通过化学遗传学沉默小鼠背侧纹状体投射神经元的新生期自发活动