THRIFTY—A High-throughput Single Muscle Fiber Typing Method Based on Immunofluorescence Detection
THRIFTY-一种基于免疫荧光检测的高通量单肌纤维分型方法
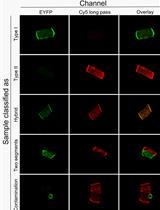
Skeletal muscle consists of a mixture of fiber types with different functional and metabolic characteristics. The relative composition of these muscle fiber types has implications for muscle performance, whole-body metabolism, and health. However, analyses of muscle samples in a fiber type–dependent manner are very time consuming. Therefore, these are often neglected in favor of more time-efficient analyses on mixed muscle samples. Methods such as western blot and myosin heavy chain separation by SDS-PAGE have previously been utilized to fiber type–isolated muscle fibers. More recently, the introduction of the dot blot method significantly increased the speed of fiber typing. However, despite recent advancements, none of the current methodologies are feasible for large-scale investigations because of their time requirements. Here, we present the protocol for a new method, which we have named THRIFTY (high-THRoughput Immunofluorescence Fiber TYping), that enables rapid fiber type identification using antibodies towards the different myosin heavy chain (MyHC) isoforms of fast and slow twitch muscle fibers. First, a short segment (<1 mm) is cut off from isolated muscle fibers and mounted on a customized gridded microscope slide holding up to 200 fiber segments. Second, the fiber segments attached to the microscope slide are stained with MyHC-specific antibodies and then visualized using a fluorescence microscope. Lastly, the remaining pieces of the fibers can either be collected individually or pooled together with fibers of the same type for subsequent analyses. The THRIFTY protocol is approximately three times as fast as the dot blot method, which enables not only time-sensitive assays to be performed but also increases the feasibility to conduct large-scale investigations into fiber type specific physiology.Graphical OverviewGraphical overview of the THRIFTY workflow. Cut off a small segment (0.5 mm) of an individually dissected muscle fiber and mount it onto the customized microscope slide containing a printed grid system. Using a Hamilton syringe, fixate the fiber segment by applying a small droplet of distilled water on the segment and let it fully dry (1A). The remaining large segment of the fiber should be placed in the corresponding square on a black A4 paper (1B). Once the microscope slide has been fully mounted with fiber segments, submerge the slide in a polypropylene slide mailer (illustrated as a Coplin jar in the figure) containing acetone to permeabilize the fiber segments. Thereafter, incubate the slide with primary antibodies targeting MyHC-I and MyHC-II. Following washes in PBS solution, incubate the slides with fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies, wash again, and mount with a cover glass and antifade reagent (2). Identification of fiber type can be performed using a digital fluorescence microscope (3), whereafter the remaining pieces of the fiber segments (large) are pooled together according to their fiber type or individually collected for experiments on single fibers (4). Image modified from Horwath et al. (2022).