往期刊物2022
卷册: 12, 期号: 3
癌症生物学
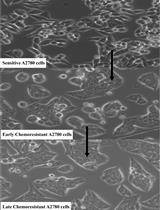
Developing Clinically Relevant Acquired Chemoresistance Models in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines
上皮性卵巢癌细胞临床相关获得性化疗耐药模型的建立
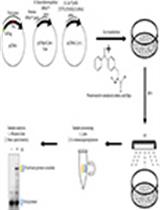
Enrichment of Tyrosine Phosphorylated Peptides for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Analysis of RTK Signaling Dynamics
丰富酪氨酸磷酸化肽用于RTK信号动力学的定量质谱分析
Studying Chemotactic Migration in Dunn Chamber: An Example Applied to Adherent Cancer Cells
在Dunn Chamber中研究趋化迁移:应用于粘附癌细胞的案例
细胞生物学
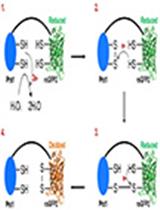
A Hypersensitive Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Indicator (roGFP2-Prx1) Enables Continuous Measurement of Intracellular H2O2 during Cell Micro-cultivation
超灵敏基因编码荧光指示剂 (roGFP2-Prx1) 在细胞微培养期间连续测量细胞内 H2O2
药物发现
Amber Suppression Technology for Mapping Site-specific Viral-host Protein Interactions in Mammalian Cells
哺乳动物细胞中定位特异性病毒-宿主蛋白相互作用的琥珀抑制技术
免疫学
Investigation of Microvesicle Uptake by Mouse Lung-marginated Monocytes in vitro
小鼠肺边缘单核细胞体外微囊泡摄取
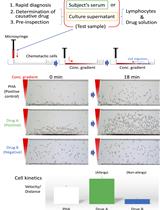
HiSAT: A Novel Method for the Rapid Diagnosis of Allergy
HiSAT:一种快速诊断过敏的新方法
微生物学
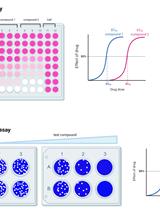
Cytopathic Effect Assay and Plaque Assay to Evaluate in vitro Activity of Antiviral Compounds Against Human Coronaviruses 229E, OC43, and NL63
细胞病变效应试验和空斑试验评估抗病毒化合物对人冠状病毒229E、OC43和NL63的体外活性
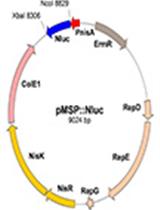
Listeria innocua Biofilm Assay Using NanoLuc Luciferase
用NanoLuc荧光素酶检测李斯特菌生物膜
神经科学
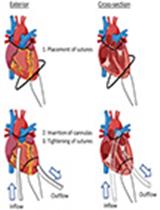
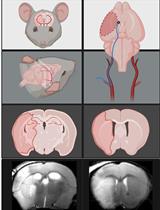
Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with an Intraluminal Suture Enables Reproducible Induction of Ischemic Stroke in Mice
经腔内缝合的短暂性大脑中动脉闭塞可重复诱导小鼠缺血性脑卒中
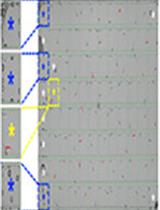
Large-scale Analysis of Sleep in Zebrafish
对斑马鱼睡眠的大规模分析
Induction of Repeated Social Defeat Stress in Rats
大鼠持续性社交失败压力诱导
干细胞
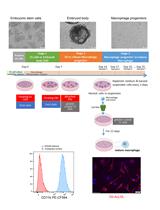
Efficient Method to Differentiate Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells into Macrophages in vitro
将小鼠胚胎干细胞体外分化为巨噬细胞的有效方法