往期刊物2020
卷册: 10, 期号: 15
生物物理学
Expression and Purification of Functionally Active Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor in Insect Cells Using Low-titer Viral Stock
低滴度病毒载体在昆虫细胞中表达和纯化功能性5-HT2A受体
癌症生物学
SMART (Single Molecule Analysis of Resection Tracks) Technique for Assessing DNA end-Resection in Response to DNA Damage
SMART(切除轨迹单分子分析)技术用于评估DNA末端切除对DNA损伤的反应
细胞生物学
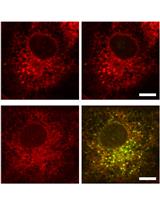
Measuring Intracellular Vesicle Density and Dispersion Using Fluorescence Microscopy and ImageJ/FIJI
使用荧光显微镜和ImageJ / FIJI测量细胞内囊泡的密度和分散度
Buoyant Density Fractionation of Small Extracellular Vesicle Sub-populations Derived from Mammalian Cells
哺乳动物细胞来源的胞外小囊泡亚群浮力密度分级
A Quantitative Single-cell Flow Cytometry Assay for Retrograde Membrane Trafficking Using Engineered Cholera Toxin
使用基因工程霍乱毒素进行逆行膜转运的定量单细胞流式细胞术分析
发育生物学
Mechanical Tissue Compression and Whole-mount Imaging at Single Cell Resolution for Developing Murine Epididymal Tubules
小鼠附睾小管发育过程中的组织机械压缩和单细胞分辨率全胚胎成像
免疫学
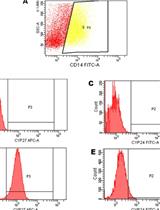
Flow Cytometry of CD14, VDR, Cyp27 and Cyp24 and TLR4 in U937 Cells
流式细胞术检测U937细胞CD14、VDR、Cyp27、Cyp24和TLR4
微生物学
High-level Production of Recombinant Membrane Proteins Using the Engineered Escherichia coli Strains SuptoxD and SuptoxR
利用工程大肠杆菌SuptoxD和SuptoxR高效生产重组膜蛋白
RETRACTED: Paper Lateral Flow Biosensor for Nodavirus Reverse Transcribed RNA Detection
用于诺达病毒逆转录RNA检测的纸侧向流生物传感器
分子生物学
A Method for User-defined Mutagenesis by Integrating Oligo Pool Synthesis Technology with Nicking Mutagenesis
一种集成引物池合成技术和切口诱变的用户自定义突变方法
神经科学
Generation of Functional Mouse Hippocampal Neurons
功能性小鼠海马神经元的产生
In vivo Blood-brain Barrier Permeability Assays Using Clostridium perfringens Epsilon Toxin
应用产气荚膜梭菌ε毒素测定体内血脑屏障通透性
Development of the Deoxycorticosterone Acetate (DOCA)-salt Hypertensive Rat Model
醋酸脱氧皮质酮盐型高血压大鼠模型的建立
Multiple Simultaneous Acute Stresses in Mice: Single or Repeated Induction
小鼠多重同时急性应激:单次或重复诱导
植物科学
The ATPase Activity of Escherichia coli Expressed AAA+-ATPase Protein
大肠杆菌表达的AAA + -ATPase蛋白的ATPase活性