往期刊物2019
卷册: 9, 期号: 22
生物物理学
Super-resolution Microscopy at Cryogenic Temperatures Using Solid Immersion Lenses
固体浸没透镜应用于低温条件下的超分辨率显微镜
Opto-magnetic Selection and Isolation of Single Cells
单细胞的光磁筛选及分离
癌症生物学
Isolation and Quantification of Metabolite Levels in Murine Tumor Interstitial Fluid by LC/MS
LC/MS法对小鼠肿瘤间质液中代谢产物的分离和定量
Labeling and Isolation of Fluorouracil Tagged RNA by Cytosine Deaminase Expression
利用胞嘧啶脱氨酶表达进行氟尿嘧啶标记RNA标记和分离
发育生物学
Measurement of Mitotic Spindle Angle and Mitotic Cell Distance in Fixed Tissue of Drosophila Larval Brains
果蝇幼虫固定脑组织中有丝分裂纺锤体角度和有丝分裂细胞距离测定
免疫学
Bacterial Synchronized Transfer Assays in Bone Marrow Derived Macrophages
骨髓衍生巨噬细胞中的细菌同步转移测定实验
微生物学
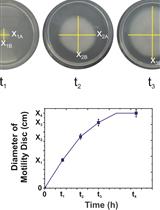
Assessing Different Ways of Bacillus subtilis Spreading over Abiotic Surfaces
枯草芽孢杆菌在非生物表面传播途径的不同检测方法
Leishmania Parasite Quantification by Bioluminescence in Murine Models
在小鼠模型中利用生物发光进行利什曼原虫的定量分析
Imaging Cryptococcus spp. Capsule by Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy Using Percoll®
利用 Percoll®在微分干涉显微镜下对隐球菌荚膜成像
分子生物学
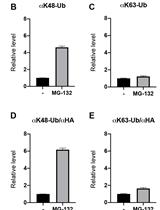
ELISA Based Protein Ubiquitylation Measurement
基于ELISA的蛋白质泛素化检测
Determination of Chromatin Accessibility in Drosophila Midgut Enterocytes by in situ 5mC Labeling
利用原位5mC标记进行果蝇中肠细胞染色质开放性的鉴定
神经科学
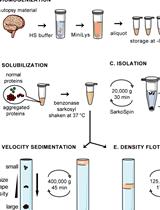
SarkoSpin: A Technique for Biochemical Isolation and Characterization of Pathological TDP-43 Aggregates
SarkoSpin:一种用于生化分离和鉴定病理性TDP-43聚集体的方法
Gallyas Silver Impregnation of Myelinated Nerve Fibers
有髓神经纤维的Gallyas银浸染法
植物科学
Method for Assessing Virulence of Colletotrichum higginsianum on Arabidopsis thaliana Leaves Using Automated Lesion Area Detection and Measurement
应用损伤面积的自动化检测和测量评价炭疽菌对拟南芥叶片致病性的方法